1c enterprise installation of hasp driver. Tmplts folder structure reminder
This article will discuss in detail the algorithm for installing the client part of the 1C:Enterprise system. 8.3 (for versions 8.2 , 8.1 And 8.0 The installation algorithm is similar to the one about installing the 1C:Enterprise system 7.7 I wrote) in operating systems of the . Typical options for the operation of 1C:Enterprise are considered, and a brief description of all components of the system will be provided.
0. Basic information about the 1C:Enterprise system
The 1C:Enterprise system is a set of software modules designed for the development and use of application solutions ( configurations) - on accounting and automation of economic activities of enterprises. The software modules of the 1C:Enterprise system are universal and can work with any configuration. R Working with information bases is possible as in file, and in client-server option.
In the case of working with a file information base, the database files are located either directly on the computer of the user working in the program “1C:Enterprise”, or on a network resource to which “1C:Enterprise” is connected to work with the information base. The figures below show the most common scenarios for the 1C:Enterprise system working with file databases.

This mode of operation is only suitable for information bases with which a small number of users work simultaneously.
If it is expected that a large number of users will work with the information base simultaneously, or a significant load on the information base is expected, you should use server cluster "1C:Enterprise". In this case, the database files will be located in a separately installed DBMS (database management system), and the server cluster will interact with this DBMS for the end user. In general, the operation scheme of the 1C:Enterprise system will then be as follows:

I wrote in detail about installing a 1C:Enterprise server cluster in the article. Next we will talk only about installation client application the 1C:Enterprise system, i.e., system modules necessary to work with file information databases or to connect to an existing 1C:Enterprise server cluster. For this we need:
- A computer capable of installing a client application of the 1C:Enterprise system running Windows OS.
- Local administrator rights on this computer.
- Distribution kit for installing modules of the 1C:Enterprise system. This example uses the version 8.3.4.389 . Installation of modules of the 1C:Enterprise system of earlier versions is similar.
- or , suitable for the required 1C:Enterprise operating mode.
1. Installation of 1C:Enterprise system components
Open the directory with the 1C:Enterprise installation files and run the filesetup.exe.

The 1C:Enterprise 8 installation assistant will start, click “ Further" on the first page.

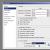
On the next page you can change the folder for installing 1C:Enterprise modules by clicking the button Change"and specifying a new path for installation, and you also need to select the components that will be installed. The list of components depends on what needs to be installed. Depending on the distribution type, not all components may be available for installation. If you need to install a component (or cancel the installation), you need to mark it by clicking the icon to the left of the component name (or the Space), in the menu that appears, select one of the options:
- This component will be installed on your local hard drive.
- This component will not be available.
Here is a brief description of the installed components:
- 1C:Enterprise— the main components of 1C:Enterprise, including components for administration, configuration, thick and thin clients.
- 1C:Enterprise - thin client— thin client components only for working in client-server mode.
- 1C:Enterprise - thin client, file version— thin client components, including components for working with the file version of the infobase.
- Server 1C:Enterprise— components of the 1C:Enterprise server (read more about installing the 1C:Enterprise server).
- Web server extension modules— web server extension modules required for the operation of the web client and Web services (read more about setting up web access to 1C:Enterprise databases).
- Administration of the 1C:Enterprise server— additional components for administering a cluster of 1C:Enterprise servers.
- Interfaces in different languages— user interfaces in various languages.
- 1C:Enterprise configuration storage server— components of the 1C:Enterprise configuration storage server.
- Converter IB 1C:Enterprise 7.7— information base converter.
Having selected the necessary components for installation, click “ Further».

At the next step, you need to select the interface language to be used in the future (the operating system language is the default). Having specified the interface language, click “ Further».

Click " Install" to start the installation of the 1C:Enterprise system.

Upon completion of the installation process, the assistant will offer to install the protection driver - HASP Device Driver. It is necessary to install the protection driver only if the USB port given a HASP4 NET hardware protection key will be installed on the computer (the driver installation can be performed later using the menu item " Start» — « Programs» — « 1C Enterprise 8» — « Installing HASP Device Driver"). Leave or remove the flag "Install protection driver" and click " Further».

If the installation is successful, the final page of the installation assistant appears. If you leave the flag " Open Readme file", then a file will be opened with information that seems to be recommended to be read before using this version of the system. Click " Ready» to complete the wizard.

2. Adding an infobase to the list of infobases
During installation, a shortcut to launch 1C:Enterprise will be created on the desktop. If you launch it, the 1C:Enterprise launcher will open with an empty list of infobases and a proposal to add a new infobase to the list.

The next steps depend on the specific situation:
- If you need to create a new database to start accounting, click " No"And first of all, we install a standard configuration template, and only then, based on the template, we create a new information base. Read more about this in the article
- If you need to connect to an existing information base, click “ Yes"and add this database to the list of information bases. Read the article on how to do this.
3. Installing a 1C:Enterprise license
Software products "1C:Enterprise" version 8can be protected from copying by hardware LPT or USB keys such as HASP4 Net from the company Aladdin , or using a software licensing system. It is also possible to use both types of protection simultaneously. After installing the system "1C:Enterprise" and creating information databases, all that remains is to install a license to operate "1C:Enterprise".
- I wrote about installing and configuring HASP protection keys in the article “”
- I wrote about the software licensing system in the article “”, as well as about the case of obtaining a license for the first time in the article “”.
Did this article help you?
Protection of the 1C:Enterprise system can be built on the use of the HASP4 Net network protection system. In this case, user counting can be carried out either by the 1C:Enterprise server part or by a special program - HASP License Manager. This article is devoted to installing the HASP License Manager and configuring the 1C:Enterprise system to work with it.
Security keys and their markings
HASP4 Net hardware protection keys are connected to the USB ports of the computer. The total number of users who can work with the 1C:Enterprise system is equal to the sum of available licenses from all computers on the network to which the hardware keys are connected and the HASP License Manager is configured.
Hardware keys are similar to a USB flash drive and look something like this:
They may vary in color and markings. By the marking you can determine what kind of key it is: what software products it is suitable for and how many licenses it provides.
- ORGL8- Local client key;
- NET5 ORGL8- Multi-user client key for 5 users;
- NET10 ORGL8- Multi-user client key for 10 users;
- NET20 ORGL8- Multi-user client key for 20 users;
- NET50 ORGL8- Multi-user client key for 50 users;
- NET100 ORGL8- Multi-user client key for 100 users;
- NET250+ ORG8A- Multi-user client key for 300 users;
- NET250+ ORG8B- Multi-user client key for 500 users;
- ENSR8- Local key of the 32-bit server;
- EN8SA- Local key of the 64-bit server.
So, the photo above shows a multi-user client key for 5 users. It should be noted that only one key of each series (ORGL8, ORG8A and ORG8B) can work on one computer. If you connect several keys of the same series to one computer, only one of them, chosen at random, will be used.
Installing the security driver
HASP Device Driver must be installed on those computers to which hardware protection keys are directly connected. This driver is included in the 1C:Enterprise package and can be installed from the Start menu:
 Installing the security driver from the Start menu
Installing the security driver from the Start menu Or from the command line:
C:\>"Program Files\1cv8\common\haspdinst.exe" -i
For Linux OS you need to download the driver from the SafeNet website. The downloaded archive contains a DEB package for Ubuntu/Debian, an RPM package for RedHat/SuSE and a script for automatic installation. Let's try the option with a script; to do this, download and unpack the required archive. Next, make the dinst file executable and run it:
sudo chmod +x ./dinst
The result will look something like this:

It is recommended to install the driver on any operating system with the USB key disconnected.
The HASP License Manager distribution can be found on the SafeNet website. When installing on Windows OS, you will need to select the installation option - application or service; usually select the service:

On Linux OS, installing HASP LM is a little more complicated. The archive from the SafeNet site contains two RPM packages for RedHat and SuSE (probably for these systems, installing HASP LM is quite simple) and a packaged hasplm file for everything else. Following the instructions from the ITS website, I was unable to run the hasplm file on Ubuntu 16.04.
Therefore, I had to use a solution from Etersoft. We go to the FTP company and find the desired version. For my 64-bit Ubuntu 16.04 I chose this version: http://ftp.etersoft.ru/pub/Etersoft/HASP/stable/x86_64/Ubuntu/16.04/. Download the files and first install the necessary packages; in my case, I needed to install the make package:
sudo apt-get install make
and the libc6-i386 package (even though I downloaded the 64-bit version of HASP LM, it is essentially still a 32-bit application and requires 32-bit libraries):
sudo apt-get install libc6-i386
after that we install the HASP LM packages:
sudo dpkg -i haspd_7.60-eter1ubuntu_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i haspd-modules_7.60-eter1ubuntu_amd64.deb
Restarting the service:
sudo service haspd restart

As you can see from the screenshot, the settings file is located here: /etc/haspd/hasplm.conf.
Settings
nhsrv.ini
On Windows OS, the nhsrv.ini file can be located in different places:
- directory with HASP LM installed (for example, C:\Program Files (x86)\Aladdin\HASP LM);
- Windows directory (C:\Windows);
- Windows system directory (C:\Windows\system32 or C:\Windows\system).
For Linux OS, the settings file is specified using the “-c” parameter and its name and location are not defined by default.
The HASP LM settings are specified by the parameter values of the section of the nhsrv.ini file:
- NHS_IP_LIMIT- defines the range of IP addresses served by HASP LM. For example: 192.168.*.*, 192.168.1.1/24.
- NHS_ADAPTER- defines the IP address of one or more network cards that will serve HASP LM. Applicable when using HASP LM with Win32. For example: 10.1.1.111, 255.255.0.0.
- NHS_USERLIST- defines the maximum number of users simultaneously connected to HASP LM Default value: 250 (important for keys for 300 and 500 users).
nethasp.ini
To configure the interaction of the 1C:Enterprise system with HASP LM, use the nethasp.ini configuration file. Although in most cases no additional configuration is required, it is useful to have an idea of the capabilities offered by this file.
The nethasp.ini file, in Windows OS, is usually located in the 1C directory (for example, C:\Program Files\1cv8\conf), and in Linux OS it can be located in the user’s home directory or in the /etc directory.
The example below specifies that the security server is located at 192.168.0.12 and disables the TCP/IP broadcast mechanism.
NH_TCPIP=Enabled
NH_SERVER_ADDR=192.168.0.12
NH_USE_BROADCAST=Disabled
Section
- NH_IPX- use or not use the IPX protocol for communication with HASP LM, options: Enabled, Disabled (Enabled by default);
- NH_NETBIOS- use or not use the NetBIOS protocol for communication with HASP LM, options: Enabled, Disabled (Enabled by default);
- NH_TCPIP- use or not use the TCP/IP protocol for communication with HASP LM, options: Enabled, Disabled (Enabled by default);
- NH_SESSION- sets the interval in seconds during which the program tries to establish a connection with HASP LM (default 2 seconds);
- NH_SEND_RCV- sets the maximum time for HASP LM to receive or send a packet (default 1 second).
The last two parameters can be used in all sections.
Section
- NH_USE_SAP- use or not use the SAP service to search the HASP LM network, options: Enabled, Disabled (Enabled by default);
- NH_USE_BROADCAST- use only the Broadcast mechanism to search the HASP LM network, options: Enabled, Disabled (Enabled by default);
- NH_BC_SOCKET_NUM- defines the socket number (number in hexadecimal) for the broadcast mechanism (default: 7483Н);
- NH_SERVER_NAME- determines whether the application will exchange data only with a HASP LM located on the local network, or with any other HASP LM, options: localnet, Internet (Internet by default);
- NH_DATFILE_PATH- the path along which the haspaddr.dat and newhaddr.dat files containing the HASP LM network address will be searched.
Section
- NH_NBNAME- sets the HASP LM name (no more than 8 characters);
- NH_USELANANUM- sets the number of the communication channel.
Section
- NH_SERVER_ADDR- sets the IP addresses of HASP LM servers (the number of addresses is not limited);
- NH_SERVER_NAME- exchanges data with HASP LM with a specific name (maximum 6 names, each no more than 7 characters);
- NH_PORT_NUMBER- sets the network port number (default 475);
- NH_TCPIP_METHOD- sends a TCP or UDP packet; access to HASP LM is always performed via UDP, regardless of the value of this parameter;
- NH_USE_BROADCAST- use the UDP broadcast mechanism, options: Enabled, Disabled (Enabled by default).
That's all, I hope that this article was useful to you.
How to install 1C Enterprise 8.3? This question plagues many beginners, but in fact it is much easier than you might think! You don't have to be at all to do this. In this step-by-step instructions, I will tell you the process of installing the 1C 8.3 program and how to install the 1C configuration using the example of “1C Enterprise Accounting 8” with the Windows operating system. The procedure is absolutely similar for other applications, such as 1C Trade Management.
By the way, if you have not yet purchased 1C, you can order any 1C program and configuration services from. Delivery and installation of 1C PROF in Moscow and the regions for free!
The installation can be roughly divided into 2 small steps:
- First of all, install the 1C 8 platform itself and
- Installing the configuration: there are a lot of 1C configurations, and it is not possible to consider installing all of them. For example, I take the most popular configuration - 1C Enterprise Accounting.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
As a rule, configuration files are packaged in an archive containing installation files. It looks something like this:

In the archive you need to find and run the “setup.exe” file.
The following window will appear:

Here you need to set the option “This component will be installed on the hard drive” for the first three points, as in the picture. You can also specify the one you need in the interface language menu (the default is Russian/English).
In addition, 1C:Enterprise software products version 8 can be protected from copying by hardware LPT or USB keys such as HASP4 Net from Aladdin. This article provides information about the type, marking and purpose of various HASP4 Net keys from 1C:Enterprise. As well as an overview of software products from Aladdin, which are used for installing, configuring and administering these keys (for Windows operating systems).
1. Marking and assignment of keys
All HASP4 Net keys can be divided into 2 types: “Client” and “Server”:
The purpose of a specific key can be determined by its blossom And labeling. In the pictures below, the key marking is highlighted with a frame. The remaining characters on the key have no special meaning for program users. 
 The type and purpose of the key by marking can be determined from the table below:
The type and purpose of the key by marking can be determined from the table below:
| Type/color | Marking/series | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SINGLE USER VERSIONS OF BASIC DELIVERY AND CLIENT KEYS | ||
| H4 M1 ORGL8 |
|
|
| NETWORK VERSIONS OF MAIN DELIVERY AND MULTI USER KEYS | ||
| H4 NET5 ORGL8 |
|
|
| H4 NET5 ORGL8 |
|
|
| H4 NET10 ORGL8 |
|
|
| H4 NET20 ORGL8 |
|
|
| H4 NET50 ORGL8 |
|
|
| H4 NET100 ORGL8 |
|
|
| NET250+ ORG8A |
|
|
| NET250+ ORG8B |
|
|
| KEYS TO SERVER 1C:ENTERPRISE 8.* | ||
| H4 M1 ENSR8 |
|
|
| Max EN8SA |
|
|
| KITS | ||
|
||
|
||
|
||
The size of USB keys may differ from the size of the keys shown in the pictures. Software products of the 1C:Enterprise system produced before 2009 were equipped with USB keys in a longer form factor - 52 mm. The color scheme and markings of the keys remain unchanged.
2. What you need to know when installing keys
There are a few things to consider before installing HASP keys, namely:
- The total number of users who can work with the 1C:Enterprise system is equal to the sum of licenses available in each of the client keys.
- Two or more keys of the same cannot work on one physical computer Series, because these keys are indistinguishable and only one of them (chosen at random) will actually be used. The key series can be determined by the last 5 characters in the marking (ORGL8, ORGL8A, ENSR8, etc.). Keys of different series can be installed on one computer without any problems.
- Client keys can be installed on any computer on the network (if the HASP License Manager is running).
- If there are several keys, licenses are issued in the following order:
- in ORGL8 series key
- in ORGL8A series key
- in ORGL8B series key
- Also valid “remembering the key”, i.e. when accessing again, an attempt will first be made to obtain a license from the key whose license was received by the user during the last connection.
- The server key must be installed directly on the same computer that is used as the cluster server "1C:Enterprise". It will not work over the network.
- Server 64-bit keys can also be used on 32-bit systems.
- There are certain problems with forwarding a server key from a physical environment to a virtual one on some hypervisors. For example, I was never able to forward the server key to a virtual machine in .
- A COM connection also requires a license.
- Web services do not require client licenses to operate.
- Full algorithm for searching for a license when starting “1C:Enterprise” for the version 8.3 described, for version 8.2 — .
3. Features of accounting for client licenses
When launched, the 1C:Enterprise client can use to obtain licenses:
- Local key— a key installed on the physical computer from which 1C:Enterprise is launched. Gives the right to launch on a computer with a key from one Windows session an arbitrary number of system instances in 1C:Enterprise or Configurator mode. When working in terminal mode, allows only one user to work, who has connected to the terminal session with ID 0.
- Multi-user key accessible over the network via HASP License Manager— Ensures simultaneous operation of as many computers as there are users with a key. Similar to a local key, on one computer in one Windows session, it is possible to launch an arbitrary number of system instances in any mode within the framework of one license. When working in terminal mode, installation of the HASP License Manager is also required.
- 1C:Enterprise server or web server extension module— In addition to the HASP License Manager program, licenses can also be issued by the 1C:Enterprise server or a web server extension module (only when working with a file database via a Web client). In this case, the calculation of licenses is carried out directly by the 1C:Enterprise server or the web server extension module. In this case, unlike the two previous options, licenses are consumed on the basis of “one session - one license”. Thus, if two instances of 1C:Enterprise are running on one computer, then two licenses will be consumed.

Besides it is very important to know and take into account the following feature: if several multi-user client keys of the ORGL8 series are detected on the network, then the server will select one arbitrary key. After the licenses for this key have been exhausted, you can use one multi-user key ORG8A, and then it is possible to use one multi-user key ORG8B.
4. Programs for administering HASP keys
4.1 HASP Device Driver
At the time of writing, version 6.62.1 was current. You can download from the official website or from.
This is nothing more than a regular device driver. It is needed so that the HASP4 Net key is identified in the system. Install following the installer's instructions.

4.2 HASP HL License Manager
from the official website or from .
A license manager is a utility that serves as a link between the network key and 1C running on a remote machine. When installed, HASP License Manager automatically creates a . However, for a protected application to work on a remote workstation, it is necessary to verify that UDP and TCP packets can pass unimpeded on port 475 in both directions. It is advisable to install the manager as a service by selecting “ Service (nhsrvice.exe)" during installation.

Well, after installation the corresponding service should appear.

When installing two or more license managers on a network, they must be configured for correct operation. Otherwise, a collision between license managers by name may occur on the network - at startup they take the same name by default, and as a result, there are several resources with the same names on the network. It is worth noting that managers often work normally without settings. However, be aware that a problem may occur. In addition, configuration may be necessary, for example, to separate clients into different license managers. Read more about this.
4.3 Aladdin HASP Monitor
At the time of writing, version 8.32.5 was current. You can download from the official website or from.
This utility is used to monitor key access and occupied licenses. After installation and launch, the program scans the network in search of a license manager and shows active connections of client applications to these services. The monitor allows you to see the names of the hosts on which the service and HASP keys are installed, the maximum number of licenses in the key, the number of occupied licenses and the names of clients who received the license.

It should be understood that the monitor itself can only show the presence of a license manager at a particular address. He will be able to see the key only after the protected application has successfully opened at least one session with the key. In addition, it should be taken into account that Aladdin Monitor only works over the UDP protocol, port 475, so for the program to work you need. Thus, the absence of key data in the monitor does not mean that the key is not available to the application.
5. View the received license in 1C
The list of all visible keys, as well as the location where the current license was obtained, can be viewed directly from 1C:Enterprise. It is enough to launch 1C in 1C:Enterprise mode, select “ Reference» — « About the program…» or click the icon with an exclamation mark on the panel.

In the window that opens, information about licenses can be viewed in the “ License». 
Here we will see the key that issued the license to this user, as well as all visible network keys. Information about issued licenses is also present in the 1C:Enterprise Server Administration Console in the list of infobase sessions (starting from platform version 8.2.15).

Did this article help you?
It is well known that a license is required to work in 1C. 1C supplies various protection keys: local and network. A local key can be used only on one computer, having the appearance of a familiar flash drive.
Network keys can provide licenses for multiple users depending on their series. At large enterprises, keys for 300 and 500 connections are most often used, but if necessary, you can purchase fewer. Please note that one computer cannot have more than one key of the same series.
In this article, we will look step by step at how to configure the 1C 8.3 license manager so that the network protection key is on one computer. Users from other computers will receive licenses from him. Simply put, there is one key, but there are many user sessions.
Setting up a HASP license manager
Let's start by installing a license manager on the computer that will distribute licenses. In what follows we will call this computer a license server. All required software is included in the 1C:Enterprise package.
You can download Alladin HASP License Manager for Windows x64 and x32 from the link.
For the manager to work properly, you need to make some preliminary settings. The file where you will produce them is called nhsrv.ini. Most often it can be found at "C:\Program Files\Aladdin\HASP LM" if the license manager is installed as an application. Otherwise (installed as a service) it will be in the operating system's system directory.
Open the file you found in any text editor, for example, Notepad and add the line there:
NHS_IP_LIMIT = 192.168.*.*
Instead of asterisks, you can enter any number from 0 to 254. Also, if you leave the “*” signs, this will mean that the licenses will be “seen” by all computers on the network whose address begins with 192.168.
For example, if you have the NHS_IP_LIMIT = 192.168.1.* add-on specified in the nhsrv.ini file, then licenses will only be available to computers with an IP in the range from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.254.
Settings on client PCs
After you have made all the necessary settings on the 1C license server, you need to configure the client computers themselves.
When running 1C on a user's PC, the program makes a request for a license to the address specified in the nethasp.ini file. You can find it in the “conf” folder of the directory where the 1C platform is installed. In our case, the address is as follows: “d:\Program Files (x86)\1cv8\conf\”.
Without any additional settings, the 1C program will search for licenses throughout the local network. To speed up this process, we can independently specify the IP address of the license server in this file by adding the text highlighted in the figure below.