Analysis of wifi channels. Monitoring and Displaying a Wi-Fi Signal with NetSpot
As a result, we obtain the formula for communication range:
Using all the above data, you can calculate the range of the wi-fi signal. Practical part Important digression: At first it was planned to get a number in decibels that corresponds to attenuation when a signal passes through obstacles. But this idea failed, because It was not possible to establish the reason why the transmitter with a fixed bitrate, for example 54mbit, when going beyond the boundary of the zone at which this speed can be reached, switches to a bitrate below (48mbit). Therefore, it was decided to get the result in meters. The following equipment was used for practical experiments: wi-fi router ASUS WL500G Premium version 1 Transmitter power - 18dbm Antenna power - 5dbm netbook hp compaq mini 311 Antenna power - 5dbm UPS We calculate the signal range in the ideal case: 13 channel f = 2484 MHz, 54MBps speed at which the sensitivity is -66dbm. Find the total system gain: Y = 18dbm + 5dbm + 4dbm + 66dbm - 1dbm - 1dbm = 95dbm FSL = Y - SOM = 95 - 10 = 85 D = 10 ^ (85/20 -33/20 - lg2472) = 10 ^ - 2.05 = 0.165 kilometers In theory, it turned out that the approximate range of the wi-fi signal in our case will be equal to 165 meters. Let's check these calculations in practice. The following territory was chosen as a testing ground: 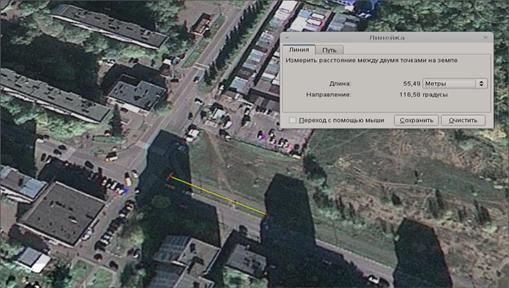
The router connected to the UPS and was fixed at the starting point. A man stopped along the road every 25 meters and took measurements using a laptop. Here is the result of measurements:
| Measurement number | Bitrate mbps | Signal, dB | Noise, db | Distance, m |
| 1 | 54 | 30 | 78 | 25 |
| 2 | 54 | 45 | 82 | 50 |
| 3 | 36 | 55 | 88 | 75 |
| 4 | 24 | 58 | 83 | 100 |
| 5 | 18 | 63 | 73 | 125 |
| 6 | 18 | 72 | 81 | 150 |
| 7 | 1 | 81 | 57 | 200 |
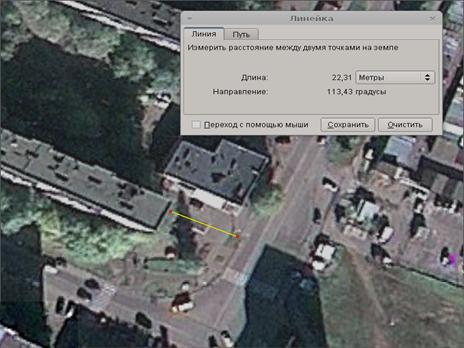
Our router was installed on the first floor of the building. Thus, it turns out that we measure the signal from the “iron-concrete box”. Here are the measurement results:
| Measurement number | Bitrate mbps | Signal, dbm | Noise dbm | Distance, m |
| 1 | 54 | 56 | 87 | 4 |
| 2 | 36 | 53 | 84 | 25 |
| 3 | 2 | 53 | 84 | 50 |
| 4 | 1 | 82 | 58 | 100 |
Wi-Fi signal booster tips:
In today's world, man is surrounded by wireless devices ... from laptops and netbooks to smartphones, tablet PCs and e-book readers. Even printers and hard drives can be connected to a WiFi network. Therefore, it is important to get the most powerful signal from the wireless router. The WiFi signal is a type of radio signal, therefore, with weak reception, it is enough to simply raise its power to such a level that the receiver still receives the same power as before. There are a variety of ways to extend the range of a WiFi signal, most of them do not require additional costs. Here are ten ways to increase the level of the WiFi signal.
Choosing the location of the router - of course, the choice of its installation location is important. If the laptop or tablet PC with a wireless connection is in another room, the signal to get to such a device, you need to pass through walls and other obstacles. Try to rearrange the router so that the signal flow conditions to different devices are approximately the same. For example, in the case of an open office space, do not place the router in a corner, but try to install it in the center, from where the signal will spread more evenly, better covering the entire served area.
1.
If optimal wireless coverage is required for different parts of the house, it is recommendedplace the router in the center of the house. The overall signal level is likely to increase if the router instead of the floor is placed on a shelf or bookshelf. If there is only one computer and it is always located in the same place (for example, in the office, in the kitchen or near the hammock), it is advisable to place the router near the computer, and not in the center of the house. However, the best way to find the best option is to experiment. There are cases where a very weak signal was because the router was placed TOO CLOSE to the computer.
2. Avoid unwanted neighborhoods.. Remember that the wifi signal is a radio signal, so the radiation from microwave ovens, cordless phones and even fluorescent lamps can interfere with and cause poor reception. Other objects that could disrupt wireless networks are bluetooth devices, wireless game console controls, neighbor wireless routers, and powerful WiMAX signal sources operating in this area. Even poor electrical connections in the home can interfere with wireless signals due to the generation of broadband radio emissions. Eliminating as many of these problems as possible will improve the quality of wifi signal reception.
3. Lengthen the antenna. Sold good amplifiers for wireless antennas, which can be installed as a prefix to the wifi router, which will further increase the range of the signal. Simply connect the amplifier to a router (often called a wireless access point) - and the required signal gain will be provided. Several types of antenna amplifiers for wireless communications company produces Hawking. One of the most powerful indoor models is the Hawking Technologies HAI15SC, which can boost the power of a wireless signal from typical 2 dBi to 15 dBi! The HAI15SC high-gain antenna replaces the external wireless access point antenna, significantly increasing signal strength, as well as effective distance and wireless performance. This device is priced at about $ 45. It can be found in Amazon and in many other online stores.
4. Repeaters and range extenders. Small devices of this kind receive a radio signal, amplify in a certain way and emit it. Position the repeater within range of the router, close to the computer that needs the wireless signal. Linksys and D-Link offer customers repeaters, also called range extenders. For Apple computers, an Airport Express repeater is offered.
5. Try to make your own auxiliary devices and devices.. - Offered interesting ways for self-repetition, allowing you to expand the area of coverage or increase the signal strength of Wi-Fi. One example is the use of an antenna in the form of a tin can without a bottom. This may sound like quackery, but this is exactly the method described in the Building Wireless Community Networks book by O Reilly, November 2001. Another proven method is to connect a home-made parabolic set-top box to the router's antenna. The use of a satellite dish and cell phone is a carefully crafted hoax.
6. Buy a new router. If your router has been around for several years, it may be advisable to buy a new device with significantly better performance. Some of the newest models provide a much higher power radio signal. New “N-class” routers, as a rule, emit a more powerful radio signal and are able to work with old 02.11B or G adapters connected to the computer.
7. Experiment with the settings. The router has additional features. Some of them can be quite useful, others - not. Read the instructions for the router and configure it to suit your needs. Most modern devices are sold ready for use, you just need to connect the necessary wires, but they may have the means to increase the signal power and adjust it to the parameters of the computer adapter. For example, most routers are configured to operate on channel 6, but there may be less interference and noise on another channel. Try switching to another channel, from 1 to 11, and see if there is a difference.
8. Is your wireless router secure?Check if your neighbor uses traffic from your router and downloads materials that may cause problems for you. Protect your network so that no one else can use this signal. Enable the security features of the router and use secure passwords. Find online wireless security security materials and follow the recommendations there. If you have not yet seen the need to secure your wifi network, read the article on user errors from a security point of view that you should NOT allow.
9. Update the router software.. Another necessary thing that can be done at no additional cost is the router software update. To do this, visit the router manufacturer's website: Linksys, D-Link, or another. Using the model number, make all the necessary updates.
10. Find alternative firmware. The original firmware of the routers would have to meet all your needs, but in some such devices the possibility of emitting the output signal with the maximum possible power is limited. You can search for alternative firmware, such as OpenWRT's BackFire, manufacturers of which promise to increase the power of the radio signal. However, be careful with the flashing - if you load the wrong program into the router, it can fail without repair. This option can be recommended only to users with a sufficient level of knowledge and qualifications.
If your surfing is like a snail crawling, and your network suffers from the constant loss of signals, or you have dead zones in which you do not receive a signal at all. Our advice will help you.
Troubleshooting a wireless network performance may seem like an incomprehensible and complicated procedure to a newbie. While you think so, let's open a secret: there are, in fact, only two main factors that are responsible for the performance of a Wi-Fi network - this coating and speed. And you can have one, but not the other.
For example, it's great, of course, that you have fast wifi internet, but only the laptop is in close proximity to the router. Fast internet within a meter from the router is not the best option. It is necessary to increase the range of the signal. If you can barely open a photo of friends on Facebook when you are in the same room with a router, then there are problems with the speed of the Internet.
In general, all questions are combined as a performance problem. Probably any user wishes increase speed and coverage, as much as possible. There are several factors that can affect both aspects.
Distance can certainly reduce performance. You may have a room in your home or office that is too far from your wireless router. Signals can disappear due to the large number of angles and walls that can cause problems, although there are technologies in new routers called “beamforming” that can help direct the signal to the router’s wireless clients.
Interfering with another wifi signal can also greatly affect performance. If you live in a block of flats, your apartment may simply be inundated with signals from all other routers. Also, the availability of other equipment near the router will not help you: a microwave oven, a washing machine, and a dryer, etc.
Performance also affects the software you are using. Routers need periodically update firmwareas drivers on a computer or laptop.
These are just some of the possible causes of a low speed connection, and sometimes even its complete absence. Fortunately, there are many ways that increase the wireless signal, and most of them are associated only with a small setting of the router or laptop. Some of these methods involve the purchase of low-cost components, depending on the specific performance problem you are facing. We will go through the list of ten most useful improvements that will help save you from the slow Internet over Wi-Fi.
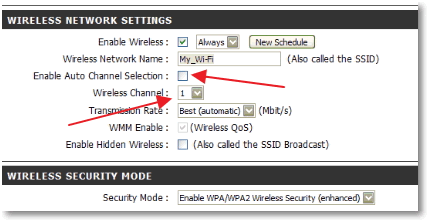
Change channel (Free)
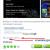
I think it’s no secret that Wi-Fi routers work on certain channels. When setting up a typical router, as a rule, the user selects a certain channel by default. Some routers are able to choose the least crowded channel, but not everyone can boast of this technology. Check for yourself which Wi-Fi channels are less crowded, by changing the channel you can improve the performance of the router and increase the range of the signal. For example, you can use the free tool. inSSIDer. Do not be afraid of graphs and redundant information. You need to focus your attention on the “Channel” column. See how many routers work on channel 6?
If your router is working on the same channel, you may already feel a drop in performance. can be in its administrative panel.
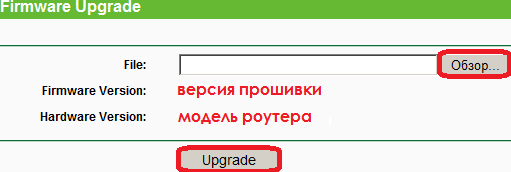
Firmware update firmware router (free)
Updating the firmware of the router is often ignored by users. Industrial network devices usually show some notifications when new device software is available for download. Home wireless routers, especially older models, do not always know how to display such messages. We recommend periodically checking for a new firmware version for the router. Each router has a special menu in the management interface for updating the firmware. However, you will have to open the router manufacturer’s website and look for the firmware, and then download it through the router's interface.
In addition, on the manufacturer's website, you can read the release notes, in which you will find out what this firmware version fixes. Often, such fixes help solve connection problems.
Network Card Driver Update (Free)
As well as the router, network cards on computers and laptops are subject to upgrade software. In this case, it will be about installing a new version of drivers. Remember that a good range of a wireless network and its performance depends not only on the router, but also on the network card on the client PC. Most laptops already have built-in network cards. Open the network settings in the Control Panel and find the name of your network card. Then open the website of the manufacturer of your motherboard or laptop to make sure that you have the latest drivers installed.
Changing the location of the router (free)
You have a wireless router located in the basement or in the attic, try to move it if you have a low signal level. Ideally, the Wi-Fi router should be in the center of the apartment or house.

Alternative DD-WRT Firmware (Free)
In a pinch, you can try open source. Not every router supports DDWRT, but the number of supported routers continues to grow rapidly.

Attention! Installation not official firmware may void the warranty on the router. Many manufacturers will not help you eliminate breakdowns with your router if you have dD-WRT installed. Thus, it is not very preferable for routers during the warranty period or in the corporate network. There is also no guarantee that the DD-WRT update will not adversely affect the router.
Nevertheless, many users use it as firmware to improve the performance of their router. If you have an old router, or if you decide on a crucial step in upgrading to an alternative firmware version, check if the model is supported on the DD-WRT website. Also note dD-WRT firmware not easy to remove from some routers, and rollback to the factory version may require quite a lot of work and time.
Configure a second router as an access point or repeater
Almost any router can be configured as a wireless access point. To do this, you need to connect the second router's LAN port to the primary LAN port. If your main router is 192.168.2.1 and its subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, you need to set the IP 192.168.2.2 of the second router and use the same mask. It is also important to assign a different ID and security on the second router and turn it on. New routers greatly simplify this process. If you have a second router and it is not too old, you can probably configure it to work in the “access point” or repeater mode.
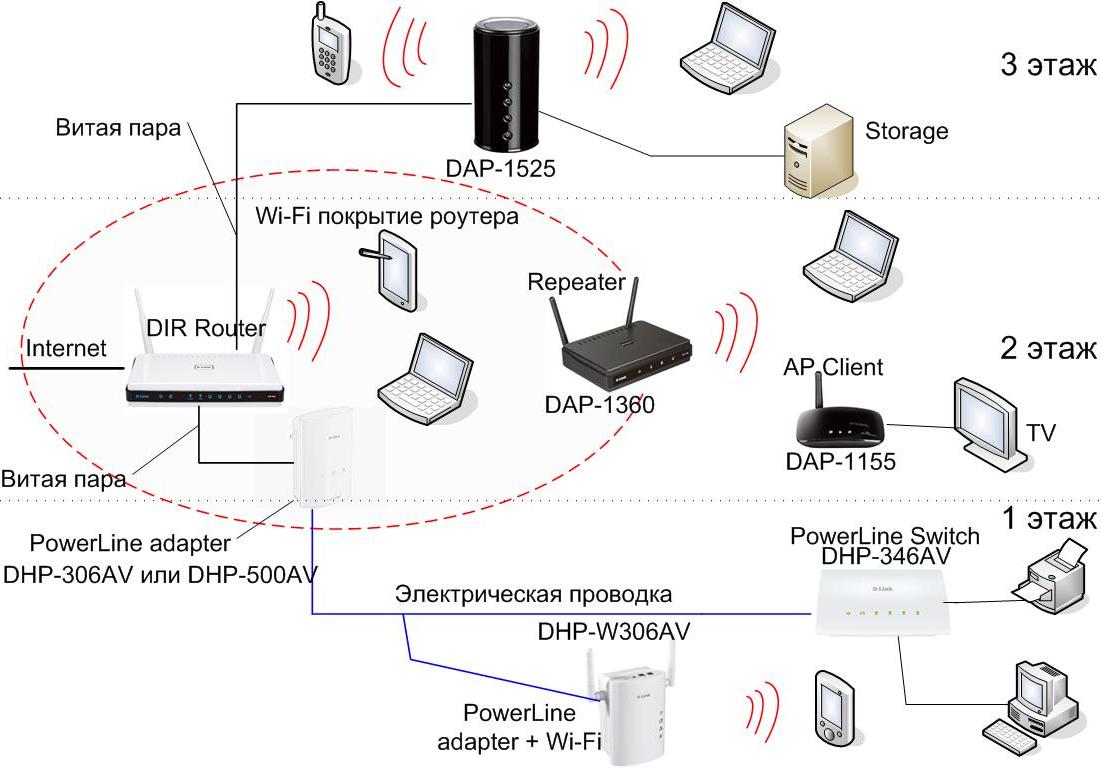
The setup is so simple that sometimes you just need to click on a couple of buttons in the administrative interface. You can also just buy a special access point. This is a more expensive option, but, most likely, it will relieve you completely of headaches due to the low signal level and small coverage area. If you choose this option, it will be better when you use an access point and a router from the same manufacturer. This will help avoid possible hardware conflicts.
Antennas
Newer 802.11n Wi-Fi routers are more often equipped with internal antennas.

But if your router supports connecting an external antenna, then with the help of its upgrade you can significantly improve the quality of communication.
Installing repeaters (repeaters) and extenders
Most major manufacturers of wireless networks offer devices that act as repeaters or wireless extenders for wireless coverage. Although they can increase the coverage of the WiFi signal, but sometimes they are difficult to install, they can also interfere with the signal, and good models are quite expensive. Let's immediately define the concepts in order not to confuse them, since they are different devices. Repeater repeats existing wireless network. This means that it duplicates encryption and SSID, and therefore you do not need to connect to another Wi-Fi network.
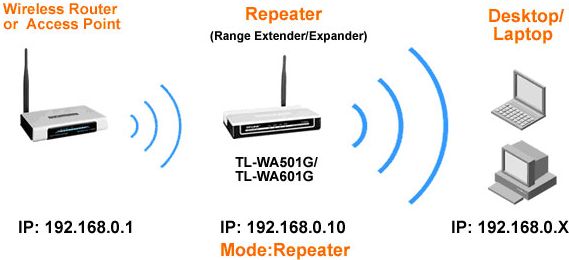
The extender increases the existing network using a different SSID that will require its own security settings. Nowadays, extenders are more common options for increasing coverage.
New router
How about buying a new router? Today's standard for 802.11n or dual-band routers is ideal because 5 GHz should give you a noticeable performance improvement. In fact, 2.4 has a wider range than 5 GHz, but it is more cramped and can reduce performance at 2.4 GHz. Increasingly, new routers are entering the market with the latest version of the 802.11.ac wireless network. These routers can increase throughput up to 1 Gbps. However, to use this speed, you need to have a network card that will also support the standard 802.11ac.

The latest generation of routers is usually one of the most expensive today. If you do not mind paying for the router more and can afford a new model, and you have devices with 802.11ac support, feel free to buy and you will not lose. Because 802.11ac routers are compatible with old Wi-Fi equipment, including 802.11n / b / g.
Go to the same manufacturer
Network equipment manufacturers have long been quick to say that their products will work with products from other manufacturers. However, this statement is not always true, the fact is that the manufacturer’s own products are most compatible with other equipment produced by the same manufacturer. If possible, try to buy network devices from one supplier: a router, a network card, antennas, repeaters, and access points.
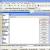
Step 1Download study range map
Download the map of the range you are going to scan, or use the NetSpot tools to draw a map, then click "Continue."
Step 2
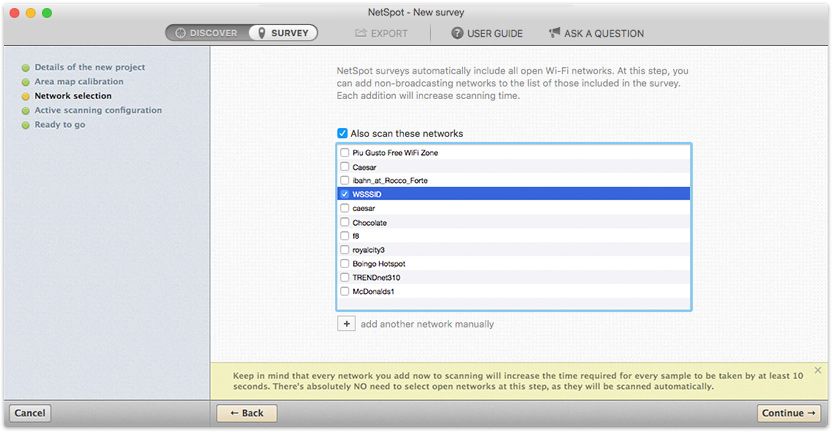
Non-broadcast SSID
Next, do not forget to include your network in the scanned list, if it has a hidden SSID (if it does not broadcast its name). You will need to do this, even if you are currently connected to your network, but it is still hidden. This feature is only available in NetSpot PRO and Enterprise versions. If you run the free version of NetSpot, you can temporarily make the Wi-Fi network you want to monitor visible to other users. In any case, the hidden SSID is not a very reliable method of protection. Then click "Continue."
Step 3
Active scan
To analyze the actual Internet connection speed of your network, you can optionally enable Active Scan on the screen. Do this or continue by clicking Continue.
Step 4You are now ready to monitor your wireless network. Walk through all the corners of the area that you want to monitor. Mark points on the map that correspond to where you are right now. Now NetSpot will record the first indicators (or data sample). Hold the dot until the end of the scan.
Step 5Ending Scan
Go to the next point and click on the map again to fix the following indicators. As soon as you scan at least three points, the ability to Stop scanning is activated, since you have collected the necessary minimum of data samples for building a report.
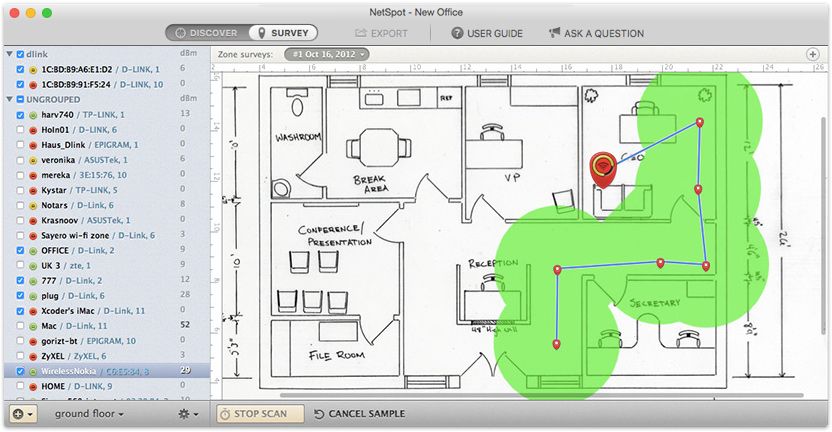
Step 6
Keep moving and scanning
Continue to move and scan until the entire area of the map is covered, then click the "Stop Scanning" button.
Step 7Find your WLAN in the list of networks
Find your WLAN in the list of networks on the left side of the window. Uncheck other wireless networks, leaving only your tested network.
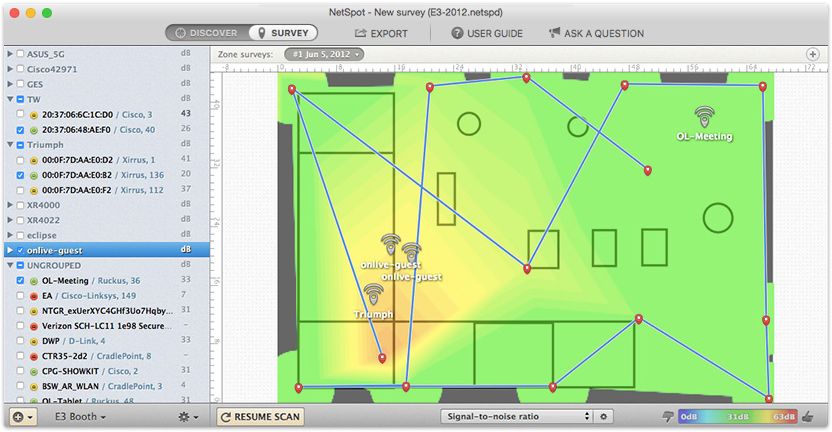
Step 8
Study of heatmaps
Examine the heat maps shown for your wireless network. Use the drop-down menu on the bottom toolbar to select the Wi-Fi monitoring visualization: Signal level, Signal-to-noise ratio, etc. You can export and save heat maps.