Formatting a hard drive using programs. How to format a hard drive before installing Windows in four different ways - step-by-step instructions. Cleaning the system local disk
Hard drives (hard drives, hard drives, HDDs) are unusually pampered devices. Just shake it a little, overheat it, look askance - and the disk is already covered with terrible “bad blocks” that threaten both it and all the information on it with inevitable death.
In the event of disk failures, the most important thing is to save valuable data. But what to do then with their carrier? Can it be used in the future? They say that one medicine helps with all such “sores”: low-level formatting of the hard drive. Let's figure out what this “pill” is and when it becomes necessary to prescribe it.
What is it really?
Low level formatting today is called something completely different from what it really is. In fact, this is one of the stages of manufacturing disk drives, and it is carried out at the factory.As you know, all . Each piece of data has a unique address where it can be found. Creating areas for recording data on a clean magnetic surface and assigning addresses to them is low-level formatting.
More precisely, this is the process of physically dividing the disk surface into tracks(circles or tracks along which the read/write heads move), their sectors(track sections are the smallest areas of information storage on a disk drive with their own address) and intersectoral intervals. And also - application servo tags– service records between sectors and within them, according to which the head control system ( servo system HDD) will be able to position the latter.

After marking, the disk surface is thoroughly scanned to identify defects in the magnetic layer (physically “broken” sectors), which must be excluded from addressing. Based on the test results, a list of defects and a translator are formed - a table correlating good physical sectors with logical (numbered) ones. This is also part of the factory formatting.
A long time ago, this entire procedure could be performed using the BIOS of a home PC. Today there are practically no such computers and storage devices left. Modern HDDs cannot be physically repartitioned without special equipment and software, and low-level formatting is the operation of “filling” the logical space with zeros (without access to the service areas in which the translator is stored).
As a result of this formatting:
- All information (except for service information) is deleted from the hard drive.
- A custom defect list is created with the addresses of bad sectors that will be hidden - excluded from subsequent read and write operations.
- Defective sectors are replaced with “healthy” ones from the reserve area (remap).
What problems does pseudo-low-level formatting help solve?
The operation is used:
- To prepare a computer for transfer into the wrong hands, so that the new owner cannot restore the files of the previous one.
- For corrections that cannot be removed using non-destructive methods.
- For the treatment of certain types of boot viruses.
It is effective:
- If the appearance of “broken” sectors is not associated with a malfunction of the mechanical and electrical components of the hard drive. For example, they formed after a short-term overheating of a disk or a sudden power outage of the computer, and their number is not growing.
- If there are relatively few defects.
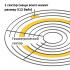
An example of detecting several unstable sectors when scanning a hard drive with the HD Tune utility:

It's useless:
- If the hard drive has suffered from a fall, drowning, or depressurization of the case (hermetic unit).
- If it makes grinding, knocking, grunting and other unnatural sounds when turned on or is poorly detected by the computer (disappears periodically).
The main area of this disk is occupied by unreadable sectors. Treatment with homemade “low-level” formatting will most likely not help him:

What and how to carry out “low-level” formatting at home
Any utility designed for this will be able to fill the surface of the hard drive with zeros and replace the “bad” sectors with normal ones. Even created by a manufacturer of hard drives of a different brand. Rewriting and remapping operations are launched by a standard algorithm that is understood by all disk controllers (the final decision on reassigning bad sectors is made by the controller). These utilities do not have the ability to use highly specific technological commands, so they are not able to cause any harm to the device.Which utility will do the job you need best? It’s not a fact that the native version of your hard drive will work more accurately than the universal one. One didn’t help, try another. There will be no harm from this, but there may be some benefit, since to correct one defective block sometimes you need to make several attempts.
Let's figure out how to perform “low-level” HDD formatting using three free utilities.
Universal HDD Low Level Format Tool (HDDLLFT) for Windows
- Let's connect the problem disk to a PC running Windows.
- Download and install the application HDDLLFT. After installation, select “ Continueforfree» (Continue for free).

- In the list of drives, mark the one that we are going to format and click the “ Continue>>>».

- In the next window, go to the section “ LowlevelFormat" and click " Formatthisdevice»

- Let's confirm the operation again and wait for it to finish.
SeaTools for DOS for HDD Seagate
SeaToolsforDOS released in iso image format for recording on bootable DVDs, flash drives and floppy disks. After starting the computer from such media, the main window of the utility immediately opens. For convenience, let’s switch it to Russian, mark the problematic drive in the list, go to the menu “ Additional functions"(Advanced Features) and click " Erase everything"(Erase all).

Windows Data Lifeguard Diagnostics for WD hard drives
W indows Data Lifeguard Diagnostics is one of Western Digital's proprietary applications with the function of “low-level” disk formatting. In addition to it, this function is supported by utilitiesWithout a doubt, today's computer users are much more technologically advanced than they were a decade ago. Much has already become familiar. People constantly install some programs, games and updates. With all this, a huge amount of both useful software and garbage gets into the system. Users greedily download music and movies, which take up all the space on local disks. Therefore, sooner or later, every user faces the question of how to format a computer and free up space.
Warning
For inexperienced users, this action can become a very serious problem. Therefore, below we will tell you what needs to be done. Users must be warned in advance that the formatting process will destroy all information on the media. That is why you need to perform the operation consciously and extremely carefully.
Formatting a disk in the Windows operating system

Perhaps it's worth starting with the tools that are built into the OS. Some people complain that the system does not allow one of the partitions to be cleared. How to format a computer if this happens? In fact, these people are trying to erase the system partition from under the system itself. Of course, this cannot be done. How can a system allow itself to be removed on its own? It follows that the OS can only help format additional partitions on hard drives, as well as external drives and flash cards. There are three ways in total.
First: from the operating system explorer
How to properly format a computer using this method? To do this, right-click and select “Format” in the context menu that opens. The system should display the corresponding window. Here you can select the file system. The best option is NTFS, since this system is more reliable and has no restrictions on file sizes. can be left unchanged. If you need to clean the disk quickly, you need to check this box. After clicking the “Start” button, the cleaning process will begin. In some cases, this takes quite a long time, since the disk may contain a lot of data.
Second: using the system console
This console is called “Disk Management”. In it you can also see all the media installed in the computer, their division into logical parts. On the desired disk, right-click and select “Format”. A window will open that differs from the previous one, but all the points here are the same. Therefore, there should not be any difficulties.
Third: Using the Command Line

How to format a computer using it? The command line is launched with administrator rights. Next, a command is written that enables formatting. It looks like this: format X. Instead of “X” the label of the logical drive is written. To indicate the required file system, an argument of the form /FS:(NTFS) is added to the command. Then simply press the Enter key and confirm the action using the Y key.
Cleaning the system disk
How to completely format a computer? To do this, you will need an installation disk with the operating system. If there is one, then you need to set the BIOS to boot from this media. Some people ask about how to format a computer using a flash drive. If there is no installation disk, then the flash card can be made bootable and perform exactly the same steps.

- Cleaning using the built-in tools of the installer. Everything is very simple here. You need to go through the steps of installing the OS and get to selecting the system drive. Next, select the disk with the system and click the settings icon. A panel with available actions will open. There is also formatting here. Once the cleaning is complete, OS installation will continue.
- Cleaning using third-party applications. Many assemblies contain additional software for operation. There are also utilities for working with hard drives. After downloading one of these programs, you need to select the system disk in the main menu and format it. Typically, such utilities perform the operation much faster than the OS itself. You can now restart your computer. All information will be deleted.
As you can see, all of the above operations should not cause any particular difficulties. How to format your computer? Very simple. First, all media except the system one are cleared from under the OS. Then the system partition is also cleaned during reinstallation of the OS or using third-party convenient utilities. Now the computer is completely empty.
You need to carefully monitor what is downloaded to disks. After all, most often these files are not used, but simply lie there as dead weight. It is better to manage free disk space wisely than to resort to formatting, which can destroy valuable user files. But it is not always possible to restore them.
Formatting your hard drive allows you to use it on your computer to install programs and store files. Drive compatibility will depend on its file system format. Formatting deletes all information available on the drive, so make a copy of your data before formatting it. You can format the second (third, fourth, etc.) drive of your computer, or even the boot drive, using the operating system installation disk. If you want to completely delete your data (without the possibility of recovery), then there are free tools for this, listed in the last section of this article.
Steps
Formatting a secondary drive (Windows)
- Look online for information on how to back up your data.
-
Install the hard drive. If you are formatting a new drive, then first you need to install it. Look online for information on how to install a hard drive. If the drive is external, then use the USB input of your computer.
Open My Computer. You can find the My Computer shortcut in the Start menu. However, you can click on Win+E, then this folder will open itself. In My Computer you will see a list of available hard drives.
Right-click on the selected drive. Select Format... The Format Disk Tool will open.
- Make sure you select the correct drive. After formatting, all data will be deleted.
-
The file system determines how files are stored and written on the hard drive, as well as its compatibility with the operating system. If the drive is internal and you only use it on a Windows computer, then select NTFS. If the drive is external, then select FAT32 or exFAT.
-
If you are using the disk for a specific purpose, then name it accordingly. For example, if you use a secondary drive for music, movies, and pictures, naming it “Media” will immediately help you identify what's on it.
Select whether to perform Quick Format or not. Quick Format is a quick format and will be sufficient for most users. Perform standard formatting only when the hard drive may have errors. Standard formatting can correct some errors, but will take longer than quick formatting.
- Quick Format does not affect secure deletion of data. If you want to completely delete data from the disk, then see the last section of this article.
-
Start formatting. Click on Start to start formatting. Click on OK to confirm the selected action, after which all data on the selected hard drive will be deleted. If you chose Quick Format, the process will only take a few seconds.
Formatting a secondary drive (OS X)
-
Make a copy of the data you want to keep. Formatting will erase all data on the drive, so be sure to back up important information. In the future, you can restore them to a new disk.
- You will not be able to make a copy of installed programs. You will have to reinstall the programs on the new drive. However, you can make a copy of the settings and parameters files.
-
Install the hard drive. If you are formatting a new drive, then first you need to install it. Look online for information on how to install a hard drive. If the drive is external, then use a USB input, FireWire or Thunderbolt.
Open Disk Utility. Click Go and select Utilities. If you don't see the option Utilities, then select Applications, and then double-click on the "Utilities" folder. Open Disk Utility.
Click on the "Erase" tab. Disk formatting options will open.
Select the file system type. The file system determines how files are stored and written on the hard drive, as well as its compatibility with the operating system. Use the Volume Format drop-down menu to select the file system type. If the drive is internal and you are using it only for OS X, then select "Mac OS Extended (Journaled)". If the drive is external, select "exFAT".
- FAT32 and exFAT can be read by any operating system. FAT32 is an older file system and does not support files larger than 4 GB, but is readable by any operating system. exFAT has no restrictions, but does not work on older operating systems such as Windows 95.
- Overall, exFAT will be the best choice for an external drive. It fits most operating systems and can store files of unlimited size.
-
Come up with a name for the disc. If you are using the disk for a specific purpose, then name it accordingly. For example, if you use a secondary drive for music, movies, and pictures, then naming it “Media” will immediately help you identify what's on it.
Start the formatting process. Click on the Erase button to start formatting the disk. The process should only take a few seconds.
- Formatting your drive does not permanently delete your data. To ensure that the data has been completely and permanently deleted from the disk, see the last section of this article.
Formatting the boot disk (Windows)
-
Make a copy of the data you want to keep.
-
Insert the Windows installation disc. You can use a boot disk or LiveCD. This way you can boot from a CD instead of a hard drive.
Set your computer's boot mode to CD. Change the computer's boot order in the BIOS to boot from disk. Look online or on wikiHow for information on how to change the boot order in the BIOS.
- To open the BIOS, restart your computer and click the appropriate button. Most often, these buttons are DEL, F10, F12, and so on.
-
Walk through the installation process. You need to get to the option to select a hard drive to install the new operating system.
Select the drive to format. You will see a list of available hard drives for formatting. Select or create a disk for installing the operating system and click on Format. Please note that the disk will be formatted in NTFS format, and all data on the hard disk will be deleted.
- Formatting the boot disk is only possible in the NTFS system.
-
Reinstall Windows. Once the drive is formatted, you can reinstall Windows or install Linux. In order to use your computer, you will need an operating system.
- Look online or on wikiHow for information on how to install different types of operating systems on your computer.
Formatting the boot disk (OS X)
-
Make a copy of the data you want to keep. Formatting will remove all operating system data from your drive, so prepare to reinstall the system. Having a backup copy of your important data will make the task of formatting your boot drive easier.
- You will not be able to make a copy of installed programs. You will have to reinstall the programs on the new drive. However, you will be able to make a copy of the settings and options files.
- Look online or on wikiHow for information on how to back up your data.
-
Make sure you are connected to the Internet. You will need an internet connection to reinstall the operating system at the end of the formatting process. Look online or on wikiHow for information on how to connect to the Internet on OS X.
Restart your computer. Click on the Apple icon and select Restart. Hold Command+R while rebooting. The boot menu will open.
From the boot menu, select "Disk Utility". A downloadable version of Disk Utility will open.
Select the drive in the left pane. All connected drives will be displayed in the left panel, in the Disk Utility program window. Select the desired drive.
Select the file system type. The file system determines how files are stored and written on the hard drive, as well as its compatibility with the operating system. Since the disk is bootable, select "Mac OS Extended (Journaled)".
Enter a name for the disc. For example, if you are installing an operating system, then name it "OS X".
Format the disk. Click on Erase to start formatting. Formatting should only take a few seconds.
Close Disk Utility. You will be returned to the boot menu.
Reinstall OS X. Select "Reinstall OS X" to begin the process of reinstalling the operating system.
Permanently deleting data from disk
-
Make a copy of the data you want to keep. During a secure format, all data on the hard drive will be permanently deleted. As a result, only government supercomputers will be able to recover some parts of the data from your drive.
- Look online or on wikiHow for information on how to back up your data.
-
It is usually recommended to format a hard drive before directly using any computer equipment. This procedure must be followed by every PC owner. Due to the special quality and capacity inherent in modern hard drives, they can be freely used throughout the entire period of use, without resorting to additional reformatting.
Why formatting is required
In some cases and over a certain period of time, it is necessary to format the hard drive (hard drive), as this allows you to easily update it. Due to the fact that the Windows operating system sometimes becomes clogged, that is, it contains irrelevant, old files on the disk that are not used by current programs, formatting will be very useful. It will help get rid of such files that occupy a certain amount of memory space and can have a negative effect on system productivity.
For their convenience, PC owners periodically install and remove the applications they need from their computer. As a consequence of this, a file dump arises and grows rapidly, causing serious problems: each application, having become part of the OS, affects the configuration of the entire environment. The solution to effectively solve this problem in the most optimal way is to format the HDD (hard drive) after certain periods of time and reinstall the operating system.
Despite the radical nature of this method, it is the most effective, because it destroys not only useless files, but also malware and viruses. For this reason, it is recommended that before formatting the hard drive, rewrite the main data to some other media so as not to lose it.
It is worth noting that when formatting, service marks are created on hard disk sectors, which are necessary for searching for data and working with it correctly (reading, writing, deleting). In addition to this procedure, formatting creates service information intended for the file system. Due to the fact that unpartitioned disks are useless for use, formatting acts as a priority operation to prepare a new “untested” disk for successful operation.
Thus, to reduce the risk of losing important data in the uncertain future, formatting will help achieve:
- guaranteed fast cleaning of the hard drive;
- effectively detecting the presence of badblocks (damaged disk sectors);
- high-quality monitoring of all kinds of defective areas.
Quick or regular formatting: process analysis
The user has two types of formatting according to the capabilities of the Windows OS - quick (Quick Format) or normal (Format). The uninitiated user will see the difference in them only in the time spent on performing each of these processes. But besides the visible factor, there is a more significant difference.
Quick formatting is a special disk cleaning method that allows you to create a table of files without overwriting it or deleting information on the hard drive. In terms of time, quick formatting occurs faster than regular formatting. As such, a quick format simply resets the file table: important information data can be restored - it is not destroyed. This method is appropriate when the user is confident that there are no damaged segments and the hard drive has not been previously formatted.
When resorting to conventional formatting, the PC owner always completely empties the disk of files and checks it for the possibility of incorrect, damaged segments. It is precisely the verification time that stretches, affecting the total duration of the entire process.
High-level formatting was discussed above, but practice shows that the understanding of the term low-level formatting is no less popular. When performing such an operation, special markings are applied to the disk plane, which are necessary for standard operation of the drive. This also allows you not only to save data and have open access to it, but also to ensure the correct operation of the internal circuits of the drive, in addition to hiding existing mechanical surface defects.
Can data be restored after formatting is complete?
Low-level formatting does not provide for the possibility of restoring previous information.
High-level formatting, in turn, gives significant chances to partially restore erased data. This is explained by the fact that at the time of formatting, new logical structures arise with selective overwriting of data.
Formatting Options: Practical Tour
It will be better to format a hard drive yourself if you move from theory to practice. Let's look at several methods, moving from the simple and most understandable to the more complex.
Formatting options:
- The simplest formatting method: open “My Computer”, right-click on the required type of formatting, select “Format” in the menu that appears and select the “Start” button.

- A special path in Windows: Open “Start” and go to the “Control Panel” to the “Administrative Tools” file, select “Computer Management”, and then “Disk Management”. We find the required disk and, to format it, perform the operations presented in the simple procedure.
Important: There may be slight differences in the path depending on the version of Windows.
- Command line: by pressing “WIN + R” and in the window that pops up, writing CMD followed by pressing ENTER, open the command line.

- There we write: format d: or format c: to start the process relative to the drive D:\ or C:\. After entering, by pressing ENTER you will see on the display: “ATTENTION, ALL DATA ON THE FIXED DISK WITH: WILL BE DESTROYED! Should I start formatting?
 When ready to delete data, select Y and press ENTER.
When ready to delete data, select Y and press ENTER. - When there is removable media with the operating system installation file. Those who have an installation disk and are familiar with installing Windows probably know when it's best to format drives. Perhaps this approach is used by few people only for formatting. However, it is very convenient if after the procedure the user plans to reinstall Windows.