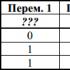
Write down the value of the resulting variable s. A fragment of the algorithm is depicted in the form of a block diagram. Determine what value of the variable S will be printed as a result of executing the algorithm. Basic function words of the algorithmic language
Data type
Description
8-bit (1 byte) unsigned numbers in the range from 0 to 255. The data type can be used when analyzing ASCII character codes or simple calculations, if it is known in advance that the result will not exceed the value 255. For example, using a Byte variable can store the number of days in a month, since the maximum value does not exceed 31.
16-bit integers in the range -32768 to 32767. The Integer numeric data type is often used to access the elements of an array or collection.
32-bit integers (4 bytes) in the range -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. Variables of this type allow you to store the results of arithmetic expressions that use fairly large integers. For example, the Long data type may be required when calculating large prime numbers, Fibonacci numbers, factorial of a number, etc.
96-bit (12 byte) unsigned numbers. In the fractional part, the power of the number is written. In this case, the number of decimal places can vary in the range from 0 to 28. In variables of type Decimal You can store super-large integers in the range from -79*10 28 to 79*10 28 .
64-bit (8 byte) double-precision floating-point numbers to work with numbers in the range -1.798E+308 to -4.941E-324 for negative values and 4.941E-324 to 1.798E+308 for positive values.
This data type is used in cases where increased calculation accuracy is required.
32-bit (4 byte) floating point numbers in the range -3.403E38 to -1.401E-45 for negative numbers and 1.401E-45 to 3.403E38 for positive numbers.
The data type is used to store string values of variable (up to 2 billion characters) or constant (64K characters) length.
A data type that allows you to work with calendar dates and times. In computer memory, the Date type is a 64-bit floating point number that can store dates in the range of January 1, 100 to December 32, 9999 and times in the range of 0:00:00 to 23:59:59.
16-bit numbers that accept two values: True (all bits of the number are set to one, which corresponds to -1) and False (all bits of the number are reset to zero, which corresponds to the number 0). Boolean variables are used when comparing expressions, in conditions, and in some types of loops.
Variable for storing references to objects in Visual Basic and other applications
Allows you to store data of any type - numbers, strings, dates and empty values.
An object type can be broken down into category types - forms, elements, printers, etc.
To declare a new variable, use the Dim statement, the syntax of which is as follows:
Dim<идентификатор> , <идентификатор1> ...
<идентификатор>- variable name.
<тип>- valid data type.
For example, the following construct declares the variable V1:
Dim V1 As Integer
The type of the variable and, accordingly, the construction As can be omitted. In this case, the variable is untyped. When declaring several variables at the same time, this construction Dim A, B, C As Integer is very often used. Moreover, it is assumed that all three variables are integers. Actually this is not true. Only variable C is integer, and variables B and C are untyped. A more correct way to write it is:
Dim A As Integer, B As Integer, C As Integer
Assigning a value to a variable
The initial value of the variable is 0 for numeric data types and the empty string "" for string values. In most cases, this value is quite suitable for the conditions of the problem. So, you can write a program for summing the rows of the array A without resetting the value of the variable S:
Dim S
For I = 1 To 5
S = S + A[I]
Next
Such a program will not produce an error when executed and will correctly sum the five elements of the array. But the rules of good form in programming still force you to assign an initial value to it before using a new variable. One more line should be added to the program for summing the array elements:
Dim S
S=0
For I = 1 To 5
S = S + A[I]
Next
You can assign a value to a variable in two ways: explicitly using appropriate language instructions Visual Basic for Application or in an implicit form, such as loop variables. The following examples show different ways to assign values to variables:
· numeric variable
Dim Year As Integer
Year = 2003
· boolean variable
Dim IsTrue As Boolean
IsTrue = True
date type variable
Dim BD As Date
BD = #10/4/03#
· calculation of the value of an expression
B = (3*(3+4))/4
· use of functions Visual Basic for Application
S = InputBox("Please introduce yourself")
· the initial value of the variable is 1, the final value is 5.
For I = 1 to 5
Debug.Print I
Next
· variable I can be used after the loop is completed
Algorithmization and programming
2. Absent in procedural programming languages 2) complex
Data type.
When developing a software product, comparing the results of the program with the results of observations or results obtained experimentally refers to the stage
1)debugging and testing the program
4. Designing programs by sequentially breaking a large task into smaller subtasks corresponds to... 3) top-down design
5. The language whose name is an abbreviation for “universal symbolic code for beginners” is 4)Basic
6. The identifier table during the translation process is used to store... 3). variable and function names
7. The concept of "Polymorphism" refers to 3)modular programming technologies
8. The modular structure of the program reflects one of the features 2) dynamic programming.

10. Loading module of the program - the result of work... 4) link editor (linker)
11. The object-oriented approach is based on the concept 3)class hierarchy
12. The first stage of solving a problem on a computer is 1) problem statement
13. Data markup languages are 1)HTML and XML


3)P=False;Q=False
16. The program is 2) an algorithm written in a programming language
Encapsulation in object-oriented programming means being able to
2) determination of the interface (specification) of methods for their implementation
18. Interpreters perform 1)operator-by-statement processing and program execution

The task: “enter two numbers and find their arithmetic mean and geometric mean and give the result” corresponds to an algorithm...
22. Does not apply to basic algorithmic constructions 1) substitution

The object-oriented approach to programming is based on the principle
4). bottom-up design

26. The Lisp language is a language 2)functional
Programming
27. When developing a software product, elimination of shortcomings noticed by the user is carried out at stage 4) maintenance of the software product
The basic principles of structured programming do not include
3) achieving an absolute minimum of characters and lines in the program text
29. Variable attributes in programming languages: a) name b) address c) visible/hidden d) value e) type f) functionality 2). a, b, d, d


1) number of zeros

A fragment of the algorithm is depicted in the form of a block diagram. Determine what value of the variable S will be printed as a result of executing the algorithm.

What value of the variable S will be printed after executing a fragment of the BASIC program?
For N = 1 To 3
Print S 4)6


4) finds the number of characters of the entered number

38. The definition of “suitability of an algorithm for solving a certain class of problems” refers to the property of algorithms, which is called 3) mass character
39. A translator that translates the source program into an equivalent resulting program in machine command language is called 4) Compiler
40. Procedural programming languages do not have 2) complex
Data type.
41. The concept of "Polymorphism" refers to 1)object-oriented programming technologies

Database

4) is key in both tables

1)parametric
3. Relational databases represent dependent data in the form 1) interconnected tables

5. The language for querying relational databases is 1)SQL
6. In a relational database, a field is 4) column in the table
7. Based on the method of accessing databases, DBMSs are divided into 2). client-server
How many records are there in the presented database? 4)4

9. What entries will be found after searching in the Computer text box with the condition “contains a Pentium”?
10. In a relational database, a table field 3)table column
11. In a relational database, all elements of one column in a table 1) have the same type and length
12. Fill in the missing words in the definition: Database management system is 1) a set of software and language tools necessary to create databases, keep them up to date and organize the search for the necessary information in them.
13. Fill in the missing words in the definition: A database is 2) named and structured a collection of data related to a specific subject area.
14. In a relational database table 3)each field has a unique name
15. In what order will the records be located in the database after sorting in ascending order in the Memory field? 
16. In a relational database 2) the data is presented in the form of one or more interrelated tables
17. Fill in the missing words in the definition: Field whose value 3)unambiguously identifies the corresponding entry , is called the key field.
18. When entering a condition for a date value in the Access DBMS, the correct entry is 1)>#01.01.55# And<#01.01.75#
19. A database field may contain 2) text, number and other types of data
20. The concept of a transaction corresponds to 1)Last. operations on data, which is considered in the DBMS as a single whole
2) many to many (M:M)
22. A form in Acess can be created based on 2) tables and queries
23. Relationships between tables in the MS Access DBMS are automatically established when using the Wizard 2) substitutions
Global and local networks
1. Network topology with sequential service of nodes is called 4)Ring
2) communication protocol with a remote computer
![]()
4. A computer that has 2 network cards and is designed to connect networks is called 1)router
6. The communication line with minimal delay is 2) fiber optic
7. An application for viewing hypertext pages is called 4) Browser
8. An IP address that is assigned automatically when a device connects to the network and is used until the connection session ends is called 4) Dynamic
9. FTP is 3) the name of the network protocol that serves the reception and transmission of files

4) twisted pair
11. The Open Network Interconnection (OSI) model includes 1) seven levels of interaction
![]()
1) common bus
13. Applies to browsers 1)Opera
14. The FTP protocol is designed for 1)file transfer

16. The browser is 2)web page viewer
17. Modem is 4) technical device
18. Electronic mail (e-mail) allows you to transfer 3)messages and attached files
19. A modem transmitting information at a speed of 28,800 bps can transmit two pages of text (3,600 bytes) within 3)1 seconds
20. A computer connected to the Internet must have 1)IP address
Algorithmic programming language- a formal language used to write, implement, and study algorithms. Unlike most programming languages, an algorithmic language is not tied to the computer architecture and does not contain details related to the design of the machine.
To study the basics of algorithmization, the so-called Russian algorithmic language(school algorithmic language), using words in Russian that are understandable to schoolchildren.
An Algol-like algorithmic language with Russian syntax was introduced by academician A.P. Ershov in the mid-1980s, as the basis for a “machineless” computer science course.
Basic function words of the algorithmic language
Description of the algorithm
- alg(algorithm)
- arg(argument)
- res(result)
- beginning(beginning) — the beginning of the algorithm
- con(end) - end of the algorithm
- given— source data in any form
- necessary— the goal of the algorithm
Data types:
- intact(whole)
- things(real)
- Sim(character)
- lit(letter) - string
- log(logical)
- tab(table) - to denote an array
- lengths(length) - number of array elements
Designation of conditions
- If
- otherwise
- choice
- value
Cycle designation
- nc(start of cycle)
- kts(end of cycle)
- Bye
Logical functions and values for constructing expressions
Input Output
- input
- conclusion
General view of the algorithm
1
2
3
4
5
6
alg name of the algorithm (arguments and results)
| given conditions for applicability of the algorithm
| necessary purpose of the algorithm
beginning description of intermediate quantities
|
sequence of commands (body of the algorithm)
con
Part of the algorithm from the word alg to the word beginning is called a heading, and the part enclosed between the words beginning And con- body of the algorithm.
In a sentence alg after the name of the algorithm, the characteristics are indicated in parentheses ( arg, res) and value type ( intact, things, Sim, lit or log) all input (arguments) and output (results) variables. When describing arrays (tables), a special word is used tab, supplemented by boundary pairs at each array element index.
In the algorithm entry, keywords are usually underlined or in bold. To highlight logical blocks, indentations are used, and paired words of the beginning and end of the block are connected by a vertical bar.
Basic algorithmic structures
A detailed description of the main algorithmic structures is given in this article. Below are templates for composing these structures in algorithmic language.
Incomplete fork
| If condition
| | That actions
| All
Full fork
1
2
3
4
5
| If condition
| | That actions 1
| | otherwise actions 2
| All
Branching
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| choice parameter
| | at value value 1
| | |
actions 1
| | at value value 2
| | |
actions 2
| | otherwise
| | |
default actions
| All
Loop with precondition
| nts for now condition
| |
actions
| kts
Loop with postcondition
| Test
Lesson 38
Test
"Algorithmization and programming"
Attention! The test contains questions and code elements from Pascal!
First option
Part 1.
1. What does an assignment sign look like in programming?:
- <=
2. What is the name of an algorithmic design that consists of sequential actions that follow each other in a strictly ordered order?
- Following
- Branching
- Repetition
3. What algorithm is shown in the picture?:
- Following
- Branching
- Repetition
4. Select the correct program entry :
- program Yakov_petrovich;
- program Yakov petrovich;
- program Yakov Petrovich;
- program_Yakov_Petrovich;
5. Which command can be used to find out the remainder of division of a number? aonb:
Part 2.
1. Write down the value of the variable b
a:=4;
x:=10;
a:= x-a*2;
x:=a*2-x;
2. What will happen as a result of executing this algorithm? Write down your answer :
a:=5;
b:=7;
if a>b then b:= a+b-28
elseb:= a* b-30;
3. What will happen as a result of executing this algorithm? Write down the value you get for variable b
a:=7;
b:=22;
a:= b div a;
b:= b mod a;
4. What value of b will be obtained after executing the algorithm? Write down the answer. (If you need to round your answer, round to the nearest tenth)
a:=3;
b:=90;
for i:=1 to 4 do
b:=b/a;
- program cup_of_tea;
- var a, b, c, y , x: real;
- begin
- writeln('Please enter three numbers');
- readln(a,b,c);
- y:=a;
- if b>y then y:=b;
- if c>y then y:=c;
- if ab) or (a>c) then x:=a;
- if ba) or (b>c) then x:=b;
- if ca) or (c>b) then x:=c;
- writeln(y+x);
- end.
- What is the name of the program? Write
- Write down what type of variables is used in the program.
- Write down the names of the variables used.
- On which line does the program receive data from the user? Write the line number
- What will be displayed if the user enters the values: 6, 9, 3
Part 3. Write a program.
Three numbers are entered. Print the smallest number.
Second option
Part I
1. The design of an algorithm in which, as a result of checking the fulfillment of a condition, various actions can be performed is called:
- Following
- Branching
- Repetition
2. Not equal in pascal it is written:
3. Which entry is correct:
- write (Set variables a and b);
- write (‘ Set Variables a and b’);
- write (‘ Set Variables ’, a and b);
- write ( Set Variables , ‘a and b’);
4. The block diagram shows the algorithmic design:

- Linear algorithm
- Branching algorithm
- Repetition algorithm
5. A command in pascal that allows you to read data received from the user:
- write
Part 2.
1. What value will the variable k have after executing this algorithm?:
a:=2;
k:=4;
a:= k+a*3;
k:=a/2-k;
2. Write down the value of the variable b after executing a fragment of the algorithm:
a:=7;
b:=5;
if a>b then b:= a+b+5
elseb:= a* b-3;
3. Write down the value of the variable b after executing a fragment of the algorithm:
a:=4;
b:=15;
a:= b div a;
b:= b mod a;
4. Write down the value of the variable b after executing a fragment of the algorithm:
a:=2;
b:=5;
for i:=1 to 5 do
b:= a* b;
5. Review the algorithm and answer the questions:
program stocking;
var a, b, c, y: real;
begin
writeln('Enter three numbers');
readln(a,b,c);
y:=a;
if b>y then y:=b;
if c>y then y:=c;
writeln( y) ;
end.
- Write the name of the program.
- What type of variables is used in the program.
- How many variables are used in the program, indicate their names.
- Rewrite the line where the program receives data from the user.
- What will be displayed if the user enters the values: 5, 8, 2.
Part 3. Write a program.
Given two integersaAndb ( a< b). Print in ascending order all the integers located between a andb(including the numbers themselvesaAndb), as well as the numberNthese numbers.