What is an information system. Information systems: definition of information systems, classification, use, examples What is an information retrieval system
State portals, websites
- ESIA. Unified identification and authentication system - esia.gosuslugi.ru
- EPSU. Unified portal of public services - gosuslugi.ru
- Public services portal of St. Petersburg - gu.spb.ru
- Portal of state and municipal services of the Leningrad region - gu.lenobl.ru
- Portal of state and municipal services of the city of Moscow - mos.ru
- EFRSDYUL. Unified Federal Register of Information on the Activity of Legal Entities - fedresurs.ru
- Federal Tax Service. Electronic services - nalog.ru
- FIAS. Federal information address system - fias.nalog.ru
- GIS housing and communal services - dom.gosuslugi.ru
- Software register. Unified register of Russian programs for electronic computers and databases (Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications) - reestr.minsvyaz.ru
- Unified Register of Prohibited Sites (Roskomnadzor) - eais.rkn.gov.ru
- NAP register. Register of copyright infringers - nap.rkn.gov.ru
- Register of information prohibited by law 398-FZ (Roskomnadzor) - 398-fz.rkn.gov.ru
- GISP Industry. State information system of the Industrial Development Fund - gisp.gov.ru
- KIO. Committee of Property Relations of St. Petersburg - commim.spb.ru
- FSIS CS. Federal State Information System of Pricing in Construction - fgiscs.minstroyrf.ru
- GIS USRZ. Unified State Register of Expert Review Conclusions of Design Documentation for Capital Construction Projects - egrz.ru
- DOM.RF. Unified information system for housing construction - nash.dom.rf
- GIS ESGFC. Portal of state and municipal financial audit - portal.audit.gov.ru
- EISUX. Unified information system for personnel management of the state civil service - gossluzhba.gov.ru
- The official website of the Russian Federation for posting information about bidding - torgi.gov.ru
- EIS. Unified information system in the field of procurement - zakupki.gov.ru
- AIS GZ. Automated information system for state procurement of St. Petersburg - start.gz-spb.ru
- AIS GZ: Electronic store. AIS subsystem of the State order of St. Petersburg - estore.gz-spb.ru
- Portal 223. Portal of AIS Civil Protection of St. Petersburg - 223.gz-spb.ru
- Moscow supplier portal - market.zakupki.mos.ru
- PIK EASUZ. Contract execution portal of the Unified Automated Procurement Management System of the Moscow Region - pik.mosreg.ru
- EIS GOZ. Unified Information System of State Defense Order
- EGISSO. Unified state information system for social security - egisso.ru
- AISGZ LO. Electronic store - zakupki.lenreg.ru
- Electronic store of the Moscow region - market.mosreg.ru
Reporting systems
- Rosprirodnadzor. Federal Service for Supervision of Natural Resources - rpn.gov.ru
- Rosfinmonitoring. Reporting to the Federal Service for Financial Monitoring - portal.fedsfm.ru
- FGIS EIAS FTS of Russia Unified Information Analytical System - eias.ru
- IAS FST of St. Petersburg. Unified information analytical system - web.spbeias.ru
- Rostekhnadzor. Reporting to the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision - gosnadzor.ru
- Housing and communal services of St. Petersburg. Portal of Housing and Communal Services of St. Petersburg - gilkom-complex.ru
- GZHI SPb. Reporting to the State Housing Inspectorate of St. Petersburg
- AS AKOT. Federal State Information System for recording the results of a special assessment of working conditions (FSIS SOUT) - akot.rosmintrud.ru
- Rostrud. Register of declarations of conformity of working conditions - declaration.rostrud.ru
- Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Personal account for financial markets - cbr.ru
- ESOD. A unified data exchange system with external subscribers of the Central Bank of Russia - portal4.cbr.ru
- GIS Energy Efficiency. Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation - gisee.ru
- Energy passport, GIS subsystem Energy efficiency - passport.gisee.ru
- EGAIS Forest. Unified state automated information system for accounting of wood and transactions with it - lesegais.ru
- Rosnedra. Personal account of the subsoil user - lk.rosnedra.gov.ru
News agencies for information disclosure
- AK&M. Analysis, Consulting and Marketing - disclosure.ru
- Interfax-TsRKI. e-disclosure Center for Corporate Information Disclosure. ru
- PRIME. Economic Information Agency - disclosure.1prime.ru
- SCREEN. System of comprehensive disclosure of information and news - disclosure.skrin.ru
Electronic document management systems
- SMEV. System of interdepartmental electronic interaction (certificate of an authorized person) - smev.gosuslugi.ru
- Uniform State Health Information System. Unified state information system in the field of healthcare - portal.egisz.rosminzdrav.ru
- UIIS Sotsstrakh - Unified integrated information system FSS "Sotsstrakh" (Electronic sick leave) - cabinets.fss.ru
- ESSK. Unified system of the construction complex of St. Petersburg - essk.gov.spb.ru
- AIS Project declarations for shared construction of the Ministry of Construction of Russia - dol.minstroyrf.ru
- Urban planning portal of St. Petersburg - portal.kgainfo.spb.ru
- AIS GATI. State Administrative and Technical Inspectorate of St. Petersburg - xc.gati-online.ru
- FAU Glavgosexpertiza of Russia - gge.ru
- State Autonomous Institution Lenoblgosekpertiza. Department of State Expertise of the Leningrad Region - loexp.ru
- Gosstroyzhilnadzor NAO. State Inspectorate for Construction and Housing Supervision of the Nenets Autonomous Okrug - stroy.adm-nao.ru
- State Autonomous Institution "Office of State Expertise of the Republic of Bashkortostan" - lk.expertizarb.ru
- State Autonomous Institution "Office of State Expertise of the Republic of Buryatia" - personal.ekspbur.ru
- Center for Construction Audit and Support - csas-spb.ru
- FBU ROSGEOLEXPERTIZA - rgexp.ru
- GIS APK LO. Geographic information system of the agro-industrial complex of the Leningrad region - gisapk.lenreg.ru
- Rosimushchestvo. Interdepartmental portal for state property management -mvpt.rosim.ru
- FSIS of the Russian Accreditation Service - fsa.gov.ru
- ARM MUNICIPAL. Municipal automated workstation system
- CONTROL. State automated information system - gasu.gov.ru
- GIIS Electronic budget. Subsystem "Budget planning" - ssl.budgetplan.minfin.ru
- FSIS TP. Federal State Information System of Territorial Planning - fgis.economy.gov.ru
- GIS GMP. State information system on state and municipal payments - gis-gmp.kck.ru
- Federal Customs Service of Russia. Personal account of a foreign trade participant - edata.customs.ru
- AIS Foreign trade information. Support for foreign trade participants (Ministry of Industry and Trade) - non-tariff.gov.ru
- FIPS. Federal Institute for Industrial Property (Rospatent) - 1.fips.ru
- FAS Russia. Filing applications and complaints to the Federal Antimonopoly Service
- Rospotrebnadzor. Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare - rospotrebnadzor.ru
- IS Rossvyaz. Personal account of the telecom operator - is.rossvyaz.ru:8081/rossvyaz/
- Russian public initiative - roi.ru
- Notary EIS. Unified information system of notaries of Russia - fciit.ru
- Local government self-government portal. Local government portal - app.fciit.ru/oms
- Register of notifications of pledge of movable property - reestr-zalogov.ru
- Information system Numeral-PNU - numeral.su
- AS SEP. Automated system of electronic vehicle passports - elpts.ru
- Providing CASCO and OSAGO insurance policies in electronic form
- ROSGOSTRAKH. Personal account - my.rgs.ru
- AIS NSSO. National Union of Liability Insurers - nsso.ru
- Supreme Court of the Russian Federation - vsrf.ru
- GAS Justice. Service "Electronic Justice" - ej.sudrf.ru
- Information system My Arbiter - my.arbitr.ru
- Moscow City Court. Moscow City Court - mos-gorsud.ru
- FSSP. Federal Bailiff Service - fssprus.ru
- Traffic police Online appeals to the State Traffic Inspectorate - traffic police.rf
- SMAO. Self-regulatory interregional association of appraisers - smao.ru
- Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation. Conclusion on the state historical and cultural examination
- State Registration Bulletin - vestnik-gosreg.ru
- IS State Bibliography. Russian Book Chamber, ITAR-TASS branch - online.bookchamber.ru
- OEC. System for accepting legal deposits of printed publications in electronic form - oek.rsl.ru
- EGISU R&D. Unified state information system for recording research, development and technological work for civil purposes - rosrid.ru
- Moscow State University. Moscow State University named after. Lomonosov - cpk.msu.ru
- AIS Electronic voucher. Federal Agency for Tourism - russiatourism.ru
- To the Far East.rf - nadalnivostok.rf
- Petroelectrosbyt. EDI with JSC "Petersburg Sales Company" - pesc.ru
- EDI with PJSC Rostelecom
- EDI with State Unitary Enterprise "Vodokanal of St. Petersburg"
- 1C-EDO. Electronic document management system
- Synerdocs. Electronic document management system
- ATI-DOKI - d.ati.su
- Case. Electronic document management system
- Diadoc. Electronic document management system with counterparties
- INFINITUM. Electronic document management system of a specialized depository
- Rosinvoice. Electronic document management system - docs.roseltorg.ru
- Sbis. Electronic document management system
- EDI SPHERE. Electronic document management system
- Edisoft. Electronic document management system
- EDO PORTAL. Electronic document management system (EXITE)
- Sberbank Leasing - e-leasing.sberleasing.ru
- First Expert Bureau (PEB) - 1expb.ru
- ASTO OGV Krasnodar Territory - asto-23.ru
- EDI with Mosenergosbyt JSC
- OFD platform. Fiscal data operator
- BIFIT EDO. Electronic document management system
- EDI LeraData
- FSIS ARSHIN. Metrology information system of Rosstandart - fgis.gost.ru
- IS EPS. Electronic mail system - zakaznoe.pochta.ru
- Various corporate information systems for secure document management
It is worth considering this issue from different points of view, which will create an overall picture. Experts say that it is an interconnected set of tools, personnel and methods used to store, process and provide information necessary to solve specific tasks.
Basic moments
When considering, it must be said that it can have different scales and purposes. There are other features as well. Systems may differ in the extent to which they cover different areas of the company’s activities; they may be intended not only for maintaining warehouse or accounting records, but also for finance, production accounting and document control of the enterprise.
Regardless of their purpose, they all have a whole set of properties that have become common to them. The use of computers is essential for processing information in any modern system. They are tools and technical base in combination with specialized programs installed on them. If we talk about what an information system is, then it should be noted that its basis can be called tools developed for storing and accessing data. They are intended for use by the end user, who should not be a computer specialist. This includes client applications designed to provide an intuitive interface.

Types of ICs
Such systems are divided into documentary and factual. The first ones are focused on solving problems related to production management, accounting and other similar ones. The latter are focused on finding unambiguous answers to queries, as well as solving a given problem in only one way. These can be heterogeneous reference and information systems, search systems, and also those engaged in operational data processing. Documentary information systems are designed to solve problems that do not provide unambiguous answers to questions. Here we can give an example that has become increasingly popular in enterprises recently. Mixed type of IP is allowed.

Scale
Speaking about what an information system is, it is worth touching on such an important issue as its scale. It is customary to distinguish between individual or desktop IS, network IS, which includes several users, as well as the largest – enterprise-scale. It is quite difficult to imagine a modern company without using such a system. It doesn’t matter in what area the enterprise’s activities are concentrated, its size is not so important, its IP in any case serves as the core that ensures effective management of production, trade or timely, high-quality provision of services. With its help, the solution of management problems is simplified, it is possible to free some employees from solving various routine matters, the likelihood of errors is reduced, the number of paper documents is reduced, and there are also opportunities for significant cost reduction. For this reason, any modern enterprise is distinguished by the fact that everything related to the information system and ensuring its smooth functioning has become the subject of special control by management personnel.

City cadastral information system
IS urban cadastre is one of the ways to ensure information transformation of cadastral data on objects of different types of property in a populated area. It is a complex of technical means and software, material and labor resources, which are aimed at creating information about real estate objects and its full presentation in the form of tangible documents.
The city information system plays a very important role in providing data, since it serves as an effective means of creating an information space that is used to manage social, business, economic and other activities in it. In the current socio-economic conditions, the creation of such a space becomes possible only on the basis of absolute automation of processes such as the collection, processing, storage and updating of cadastral data on real estate. In addition, the provision of information systems provides access to all specified data, operational exchange between government and commercial structures of various kinds, services and organizations of the city.

The need for such a structure
At the moment, certain state, commercial and municipal organizations (land markets, mortgage banks, real estate privatization committees, tax inspectorates, insurance companies and others) are almost unable to fulfill their direct responsibilities without organizing the timely exchange of cadastral information that is reliable during this period of time. That is why the development of an information system of this kind makes it possible to solve not only the problems of protecting property rights and taxation, but also other issues.
Non-cadastral tasks
Prompt, complete and high-quality information provision of bodies managing the city, commercial, economic and other structures and individual citizens with complete and reliable information about the physical condition of real estate of various forms of ownership and other elements of the urban environment;
Analysis of the use of infrastructure, natural, labor, material, technical means and resources of the city, their distribution by type of ownership, etc.;
Work on the preparation of urban planning and architectural projects, design of utility networks and other things.

Difficulties at work
The design of information systems of this kind has become necessary due to the fact that until recently there were no analogues on the domestic market capable of solving such complex problems. There are no similar solutions abroad either, but in recent years the intensification of work in this area is simply amazing. The first Russian development in this area was the AIS GK, created by the Novosibirsk branch of the Russian Scientific Research Center "Earth". It is aimed at providing a variety of structures with reliable cadastral information: administration, privatization committee, insurance bureaus, tax inspectorates, institutions and enterprises, mortgage, land and investment banks, as well as individuals who own real estate.
Features of data accounting
It is important to understand that certain services and organizations of the city are capable of being not only passive consumers of cadastral information, but also shaping it, having a huge impact on the formation of the urban information space. It is for this reason that the development of AIS GC was carried out taking into account the possibility of using software products of similar users, and also provided for the safety of their fleet of technical measuring instruments. The unified information system was developed taking into account all these features.

Construction principles used
Modularity in terms of construction, which makes it possible to ensure the normal functioning of each individual element, and therefore of their entirety as a whole;
They have a very flexible software architecture, which allows you to include new subscribers in the network and exclude them from it without reducing the operability, reliability and performance of the entire structure, and also does not require any reconfiguration;
Data is fully protected from loss due to failures or unauthorized access to the information system;
The classification and coding of data on elements of the urban environment is unified;
Information is entered in a unified format, which is made possible through the use of system configuration tools provided by the operating system and network DBMS;
The results of geodetic changes are processed in a fully automated mode, regardless of what methods were used to collect them;
The information in the database is presented in topological integrity, it is possible to edit all types of cadastral data;
Operational control of the reliability and correctness of data in all operations with them.
Such a unified information system is capable of solving not only cadastral problems directly, but also many others associated with the development of plans for the development of territories and their redevelopment, environmental protection, rational placement of housing facilities, modeling of transport flows, property management and much more. In addition, such a system easily incorporates user devices, tools and computers.
Alternative options
The school information system represents a completely new approach to education. With the help of important elements, timely provision of data is achieved. For example, an element such as an electronic diary is used to post information about grades and homework, allowing teachers to quickly interact with students. This includes a student portfolio that demonstrates their activities in and outside of school. The school information system supports the use of personal privacy settings through a personal account. Parents can quickly receive reliable information not only about academic performance, but also about homework.
So, all this allows you to understand what an information system is and how it helps in solving many important issues.
Information system is a system of software, hardware and organizational support that solves the problems of information support for various spheres of human activity. Thus, an information system includes not only running software applications, but also computers, communication equipment, databases, as well as personnel servicing the system and interacting with it according to certain regulations.
There are quite a few ways to classify information systems, but each of them characterizes only certain aspects of it. For example, information systems are divided into automated systems operating under human control and participation; And automatic systems, operating without human intervention. Large information systems can include both automated subsystems and subsystems operating in an automatic or even completely autonomous mode. Also, information systems are classified according to their architecture, scope of application, regulations for use, etc. In this section, I want to dwell on the classification of information systems according to their purpose and requirements for their mode of operation.
Classification of information systems
Information retrieval systems. Actually, everything is clear from the name: a regular user of such a system has the opportunity to search and view the information he needs. An example is, such as Google or Yandex.
Data processing systems. Such systems, in addition to information retrieval functions, allow you to change the data under their control. Here we can already distinguish the following types of information systems:
- Automated control systems (ACS)
A fairly wide class of information systems created to manage a large enterprise. Management systems can be of different scales: from an automated management system for the entire enterprise (ACS), to the management of individual technological processes (APCS), financial management or accounting automation. Enterprise level management systems include components of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) class software systems used for planning and information support of production management processes. Examples of ERP: domestic product “1C Enterprise” and foreign SAP ERP, from SAP AG (Germany).
- Dispatch systems
Dispatch systems are part of management systems and are used for remote control over the use of production assets (equipment) of an enterprise and operational management of these assets. The peculiarities of such systems are that they must provide a centralized monitoring mode for all observed objects, through the rapid exchange of information with these objects and the consolidation of this information on central control input/output devices. Based on such data, the dispatcher makes decisions regarding the operational management of technological processes in which dispatch objects are involved.
- Decision support systems or expert systems
Expert systems belong to the class of artificial intelligence systems. They work with knowledge bases and are able to draw certain conclusions based on this knowledge. Decision support systems are capable of simulating real situations and predicting their development based on the mathematical models embedded in them. Such systems can also be part of, since they are an indispensable tool for solving planning problems.
Systems that allow organizing the collection, storage and visualization of spatial data. Spatial data are objects described not only by a set of attributes, but also by geometry. In GIS, point geometry is distinguished when only the location of the object is important (pillar, tree), linear geometry when the length and linear configuration of the object is also important (various overpasses) and areal geometry, which allows you to fully represent the object in the GIS context (forests, lakes , buildings). Visualization of spatial data in GIS is most often done in the form of two-dimensional graphic maps. Maps are usually created and configured for different scales and, as a result, with different degrees of detail, so the same objects on one scale can be represented by points, and on another - by area objects. Some GIS use their own file formats to store data, and some use . Geographic information systems allow you not only to edit and view spatial data, but also to perform spatial queries on it, for example, select all objects in a certain territory or select all intersecting objects of a particular class. These capabilities are classified as GIS spatial data analysis tools. The most famous, at least in Russia, are GIS offered by ESRI (ArcGIS), Intergraph (Geomedia) and MapInfo Corporation (MapInfo).
- Computer-aided design (CAD) systems
Systems designed to automate engineering design processes. In English, the abbreviation CAD (computer-aided design) is used to refer to these systems. Using CAD, electronic versions of various types of engineering documentation are created, most often represented by drawings of design objects in two or three dimensions. The most famous representative of CAD in Russia is the AutoCAD software product from Autodesk.
- Database management systems (DBMS)
Systems of this class most often act as database subsystems of other information systems. From their name everything is clear: they are used to manage large amounts of structured data, and their tasks include adding, deleting, editing data in the information warehouse and processing. There are desktop (Microsoft Access) and distributed, capable of managing large enterprise data volumes (Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle).
- Content management systems (, Content management system)
The purpose of these information systems is to provide the administrator with the ability to enter various information through predefined user forms, place (publish) this information in accordance with specified templates and organize user access to it in a free mode or with pre-registration. Quite a lot is created using a CMS. The most famous of them are WordPress, Joomla and Drupal. Often, users of such systems don’t even need to - the CMS will create the required Internet page for them, and they will only need to select the type of page (news, review, article, etc.), enter text and click something like “Publish” . Of course, the functionality of more or less serious information systems of this class is not limited to this. The most famous commercial CMS of domestic production is 1C-Bitrix.
- Operating Systems
System software representative. System and application software differ from each other in the way they use computer hardware resources: system software uses resources through firmware built into these same resources, and application software through software interfaces of the system software. Operating systems are designed to manage everything and plan the use of its resources by application programs. The most well-known representatives of operating systems are Microsoft Windows and UNIX-class systems and the like, such as Linux, Mac OS, Android and others.
- Real-time systems
Real-time systems are systems whose quality of operation is determined not only by the fact that their functions work correctly from the point of view of the logic embedded in them, but also complete their work within the established time frame. A real-time system cannot afford delays in responding to intended external influences. In other words, such a system can interrupt ongoing calculations if they cannot adequately process the signals coming to it in real time. In fact, this aspect of information systems already relates to operating modes, and not to their purpose, since a real-time system can be of various kinds, including. Dispatch systems operating in real time belong to the class of SCADA systems (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition), which are required to exchange data with dispatch objects strictly in accordance with established time limits.
If this article helped you understand what an information system is, and you are interested in where you can order the development and implementation of automated information systems to suit your requirements, then the site below should help you with this.
itconcord.ru - creation of information systems for your business.
Information and information technologies and technical means that ensure its processing."
One of the broadest definitions of IS was given by M. R. Kogalovsky: “an information system is a complex that includes computing and communication equipment, software, linguistic tools and information resources, as well as system personnel and provides support for a dynamic information model of some part of the real world to satisfy information needs of users".
The ISO/IEC 2382-1 standard defines it as follows: “An information system is an information processing system that works in conjunction with organizational resources, such as people, hardware and financial resources, that provide and distribute information.”
Russian GOST RV 51987 defines an information system as “an automated system, the result of which is the presentation of output information for subsequent use.”
IN in the narrow sense An information system refers to only a subset of IS components in a broad sense, including databases, DBMS and specialized application programs. An IS in the narrow sense is considered as a hardware and software system designed to automate the targeted activities of end users, providing, in accordance with the processing logic embedded in it, the possibility of obtaining, modifying and storing information.
In any case, the main task of IS is to satisfy specific information needs within a specific subject area. Modern information systems are de facto unthinkable without the use of databases and DBMS, therefore the term “information system” in practice merges in meaning with the term “database system”.
Ideally, a unified corporate information system should operate within the enterprise, satisfying all existing information needs of all employees, services and departments. However, in practice, the creation of such a comprehensive IS is too difficult or even impossible, as a result of which an enterprise usually operates several different IS that solve separate groups of tasks: production management, financial and economic activities, etc. Some tasks are “covered” simultaneously by several IS, Some tasks are not automated at all. This situation is called “patchwork automation” and is quite typical for many enterprises.
Classifications of information systems
Classification by architecture
According to the degree of distribution they are distinguished:
- desktop (desktop), or local IS in which all components (DB, DBMS, client applications) are located on one computer;
- distributed (distributed) ICs in which components are distributed across several computers.
Distributed information systems, in turn, are divided into:
- file-server IS (IS with file-server architecture);
- client-server IS (IS with client-server architecture).
In file server IS, the database is located on the file server, and the DBMS and client applications are located on workstations.
In client-server IS, the database and DBMS are located on the server, and client applications are located on workstations.
In turn, client-server ISs are divided into two-link And multi-link.
Classification by degree of automation
Classification by the nature of data processing
Based on the nature of data processing, information systems are divided into:
- information and reference, or information retrieval information systems, in which there are no complex data processing algorithms, and the purpose of the system is to search and provide information in a convenient form;
- Data Processing IC, or decisive IP, in which data is processed using complex algorithms. Such systems primarily include automated control systems and decision support systems.
Classification by area of application
Since ISs are created to satisfy information needs within a specific subject area, each subject area (field of application) has its own type of IS. It makes no sense to list all these types, since the number of subject areas is large, but the following types of IS can be cited as an example:
- Economic information system is an information system designed to perform management functions at an enterprise.
- Medical information system is an information system intended for use in a medical or treatment-and-prophylactic institution.
- Geographic information system - an information system that provides collection, storage, processing, access, display and dissemination of spatially coordinated data (spatial data).
Classification by task coverage (scale)
- Personal The IS is designed to solve a certain range of problems for one person.
- Group IS is focused on the collective use of information by members of a work group or unit.
- Corporate IS ideally covers all information processes of the entire enterprise, achieving their complete consistency, redundancy and transparency. Such systems are sometimes called integrated enterprise automation systems.
Notes
see also
Literature
- William S. Davis, David C. Yen The Information System Consultant's Handbook. Systems Analysis and Design. - CRC Press, 1998. - 800 pp. - ISBN 0849370019
- Kogalovsky M.R. Advanced technologies of information systems. - M.: DMK Press; IT Company, 2003. - 288 p. - ISBN 5-94074-200-9
- Kogalovsky M.R. Encyclopedia of Database Technologies. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2002. - 800 p. - ISBN 5-279-02276-4
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- Financial Dictionary
Information system- Information system (Information system) is a system for collecting, storing, processing, converting, transmitting and updating information using computer and other equipment. Thus, the elements of this system are non-material... ... Economic and mathematical dictionary
According to the definition of the Federal Law on Information, Informatization and Information Protection of January 25, 1995, an organizationally ordered set of documents (arrays of documents) and information technologies, including the use of computing tools... ... Legal Dictionary
1) an organizationally ordered set of documents (arrays of documents) and information technologies, including the use of computer technology and communications that implement information processes; 2) infrastructure, organization,… … Dictionary of emergency situations
The totality of information contained in databases and the information technologies and technical means that ensure its processing. Dictionary of business terms. Akademik.ru. 2001 ... Dictionary of business terms
Information system- (English information system) in the Russian Federation, an organizationally ordered set of documents (arrays of documents) and information technologies, incl. using computer technology and communications that implement information processes. IN… … Encyclopedia of Law
INFORMATION SYSTEM- an organizationally ordered set of documents (arrays of documents) and information technologies, including the use of computer technology and communications that implement information processes... Legal encyclopedia
Information system- 2.49 information system: A system that organizes the processing of information about the subject area and its storage.
10. Information systems
1. Information systems: definition, purpose of creation, structure.
2. Basic principles of IS development
3. Classification of information systems.
4. Systems of classification and coding of economic information.
IP classes: MR I, MRP II, ERP
1. Information systems: definition, purpose of creation, structure.
Information- this is some information, knowledge about objects and processes of the real world. Economic information is usually displayed in the form of documents.
Document - is a material medium of information that has legal force and is drawn up in the prescribed manner.
System is a complex of interconnected means acting as a single whole. Each system is characterized by structure, input and output flows, purpose and limitations, and the law of operation.
System covers a complex of interrelated elements that act as a single whole in achieving set goals.
Each system includes components
1. The structure of the system is the set of elements of the system and the relationships between them.
2. Functions of each element of the system
3. Input and output of each element and the system as a whole.
4. Goals and limitations of the system and its individual elements (achievements: reducing costs and increasing profits)
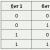
Each system has the properties of divisibility and integrity.
IP ensures the collection, storage, and processing of information about the facility, supplying employees of various ranks with information for the implementation of management functions.
EIS is system, functioning which consists in collecting, storing, processing and disseminating information about the activities of any economic entity in the real world.
EIS are designed to solve problems of data processing, office automation, searching for information and individual tasks based on artificial intelligence methods (from lectures).
Information system (IS) is a software and hardware complex designed for automated collection, storage, processing and delivery of information. Typically, information systems deal with large volumes of information that have a fairly complex structure. Classic examples of information systems are banking systems, transport ticketing systems, etc.
IS always specializes in information from a certain area of the real world: economics, technology, medicine, etc. The part of the real world displayed in the IC is called subject area . Therefore, economic IP is IP whose subject area is economics. In this sense, it acts as an information model of the subject area.
Any management system for an economic object has its own information system, called an economic information system.
Economic Information System (EIS) - these are a set of internal and external flows of direct and feedback information communication of an economic object, methods, means, specialists involved in the process of information processing and the development of management decisions.
The information system is an information service system for employees of management services and performs technological functions for the accumulation, storage, transmission and processing of information. It develops, is formed and functions in accordance with the regulations determined by the methods and structure of management activities adopted at a specific economic entity, and implements the goals and objectives facing it.
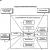
IP structure
The most common division of EIS subsystems is the separation of supporting and functional parts. The functional part is actually a model of the facility management system. In relation to control systems, a sign of structuring can be the functions of object management, according to which the EIS consists of functional subsystems. The supporting part of the EIS consists of information, technical, software, organizational, legal and other types of support.
Regardless of the characteristics, any EIS consists of functional and supporting parts. The functional part is determined by the set of tasks to be solved, identified by certain types of activities of various economic entities (by function).
The supporting part is a set of interconnected means of a certain type that ensure the functioning of the system as a whole or its individual elements. The supporting subsystems include: information support of IO, technical support of TO, mathematical support of MO, legal support of Prav.O, software software, organizational support of Org.O, technological support of Tech.O
IO is a set of a unified system for classifying and encoding information, unified documentation systems, information flow diagrams circulating in organizations, as well as a methodology for constructing a database. IO is divided into extra-machine and intra-machine.
A non-machine unified documentation system, as well as a classification and coding system for accounting information.
In-machine – documents and arrays of documents located in computer memory in the form of libraries, archives, databases, knowledge bases.
TO is a set of technical means intended for the operation of an IS, as well as the corresponding documentation for these means and technological processes.
Tech.O - focused on the selected information technology for entering, registering, transferring, processing and issuing effective information. (centralized, distributed, decentralized)
Software – includes: general system and special software products, as well as technical documentation (OS, shells, programs...)
Mat.O. – a set of mathematical methods, models, algorithms for the implementation of the goals and objectives of the IS, as well as the functioning of a complex of technical means.
Org.O is a set of methods and means that regulate the interaction of workers with technical means and with each other in the process of development and operation of IS.
Right. – a set of legal norms that determine the creation of legal status and functioning of IP, regulating the procedure for obtaining the transformation and use of information. (from lectures)
The structure of information includes the following concepts: information space, subject area, object, object instance, object properties, interaction of objects and interaction properties. To describe a subject area means to list objects and the relationships between them, and then describe them with attributes and constituent units of information.
The structure of economic information is quite complex and can include various combinations of information sets that have a certain content. An information set is understood as a group of data characterizing an object, process, or operation. Based on their structural composition, information sets can be divided into:
requisites,
indicators,