What is the difference between the memory of the laptop. Select the RAM.
(English), we went through the basic concepts and characteristics random access memory. In this article we want to touch upon topics that are often controversial, and try to understand the following myths and statements:
- All DDR3 memory is the same
- You just need to add more RAM
- There are only a few manufacturers of DIMMs
- Support for DDR-3200 means that you can use any RAM
- When installing different modules RAM runs at the speed (timings) of the slowest DIMM
- Cheaper to buy two sets of DIMMs than one large and expensive set
- RAM is faster when all slots are busy
- RAM faster than 1600 MT / s does not give a performance boost
- The volume of 8 GB is enough for the next ten years
- You will never be able to use 16 GB of memory
- I do not use all available memory, so additional memory will not accelerate
- 64-bit OS allows to use any amount of RAM
- 1.65V RAM may damage Intel processors
- Dual-mode doubles the data transfer rate, that is, RAM runs twice as fast
Myths about RAM | All DDR3 memory is the same
One this topic deserves a separate article, but we will try to discuss it briefly and denote several theses.
- Remember the line of Kingston Fury RAM, which is not equipped with an XMP profile and instead uses plug and play technology. The modules have a reasonable price, look beautiful, are equipped with multi-colored radiators and are aimed at users of old systems that would like to update RAM. But since this memory is based on PnP, it will work only with some chipsets: H67, P67, Z68, Z77, Z87 and H61 from Intel, along with AMD A75, A87, A88, A89, A78 and E35. Also here you can add Z87 and Z97. The list of chipsets is taken from the company's website.
- The chips themselves also differ:
- Most of today's RAM uses high-density 4Gb memory chips, and in the old DDR3 chips are installed at a lower density of 2Gbps. Old memory controllers can only work with low-density chips. One of our editors recently discovered that none of the motherboards on P55 logic wanted to work with its 8 GB modules. And if you install a memory with different characteristics, then the module can not decide or lose stability.
- Memory chips are produced by many companies that adhere to their own specifications. Each line of chips is tested or subjected to binning, and in accordance with the quality of the chip is marked and allocated to different series.
Usually, we recommend checking with data from RAM manufacturers who spend a lot of time testing memory on various motherboards. Manufacturers of motherboards also provide lists of certified vendors (QVL) of RAM, whose products they tested on a particular motherboard. But usually these lists indicate a small number of producers whose memory was in the laboratory. Therefore, it is better to check with the list of the memory manufacturer. you can find many useful advice and recommendations on RAM modules for hotel platforms and motherboards, as well as information on their speed and compatibility with different processors.
Myths about RAM | You just need to add more RAM
JEDEC is an association of electronic device manufacturers and developers who set industry standards for widespread adaptation among their members. Since some RAM manufacturers exceeded JDREC's maximum of DDR3-1600 CAS 11 (and later CAS 9) and offer more tight timings and higher data rates, mixing different RAM modules turned out to be not such an easy task as originally intended.
Simply put, mixing RAM modules from different sets does not guarantee a stable operation, even if you have two identical sets of the same model line. We want to add that DIMMs that do not work well together often, but not always, can be made to work by adjusting the voltage and / or timings. For an article "DDR3 memory: how to improve system performance?" two companies instead of a single set of 32 GB RAM with a speed of 2400 MT / s sent us a pair of identical sets of modules in a configuration of 2 x 8 GB. Initially, they did not work together, but with minor adjustments we achieved a positive result.
What is the problem? After all, the modules have the same frequencies, timings and voltage.
DRAM basically consists of memory chips soldered to the printed circuit board. In the process of manufacturing a RAM of a certain model, the manufacturer can spend a certain amount of printed circuit boards, and then switch to new PCBs from another production lot, which as a result may affect a number of characteristics.
The same can happen with solder. The manufacturer can start using a different type that has slightly modified conductive properties.
Also, the crystals themselves can be different. In the process of production, the chips are binning, that is, sorting according to their quality.
Let's look at this concept from a theoretical point of view. In one production lot, there may be, say, 1000 memory chips that are separated or passed through binning. 200 chips the manufacturer can classify as entry-level chips, 350 slightly better, 300 chips even better and 150 first-class chips. Then they sell these chips to different manufacturers of memory modules.
If you buy memory modules DDR3-1866 from several companies, then, most likely, you will get different PCBs, solder with different conductive properties and, quite possibly, chips of different levels from different manufacturers.
The memory chips themselves are produced by several different companies, which only aggravates the compatibility problem. Probably, you already understand why mixing different RAM modules often causes problems.
Also, we noticed that most new lines of RAM use chips with a density of 4 Gbit, while the old lines are 2 Gb.
Myths about RAM | There are only a few manufacturers of DIMMs
This is both a myth and an error. There are several companies that manufacture memory chips and many manufacturers of RAM modules. There are RAM modules made by one or more companies for other companies. For example, AMD Radeon RAM produces Patriot and VisionTek.
Myths about RAM | Support for DDR-3200 means that you can use any RAM
To use expensive memory standard 3200 MT / s you need a processor that will be able to cope with such a high data transfer rate. Otherwise, the memory will only work in modes 1333, 1600 or 1866.
In the time of Intel LGA 775 processors, CPU and RAM overclocking was carried out, first of all, at the expense of FSB (system bus). Let's say you have a Q6600 processor and your motherboard supports 1066 MHz FSB. In this case, the processor will operate at a native frequency of 2.4 GHz, and memory at a speed of 1066 MT / s. If you want to overclock the processor by raising the FSB frequency to 1333, it will run at 3 GHz and the memory in 1333 MT / s mode. In other words, the memory speed was limited by the FSB frequency limit. The memory controller was in the chipset, more often in the north bridge motherboard, and also worked on the FSB frequency.
Today, the memory controller moved to the CPU. So the main driver of memory at the advertised frequencies is the CPU. Processors based on the Haswell architecture are designed for DDR3-1600 memory, and middle and top-level chips that do not belong to the K series, as a rule, can operate quite stably with memory up to 1866 - 2133 MT / s. The K-series processors can be overclocked, and their controllers support modules with increased data transfer speed, focused on enthusiasts.
The current line of FX processors from AMD supports "up to 1866 MT / s per channel DIMM". However, you may encounter problems when starting memory in the 1866 mode on the processors of the initial, and sometimes average, level. This is partly due to the fact that the FX memory controller is optimized for DDR3-1333 (according to BIOS and Kernel Programming Guide). Like any other processor, FX chips can be overclocked to work at speeds even higher than DDR3-1866, but this will negatively affect stability.
Myths about RAM | When installing different modules RAM runs at the speed (timings) of the slowest DIMM
Suppose you have a DDR3-1600 CAS 9 module and you add another module, but already 1866 CAS 9. This can lead to the fact that RAM will work on the settings specified motherboard by default, that is, 1333 CAS 9 or 10 (many AMD motherboards use the default 1066). Or both modules will work in 1600 CAS 9 mode (10 or even 11) if DOCP, EOCP, XMP or AMP technologies were enabled before installing the DDR3-1866 module.
But you can also set the parameters manually. Typically, in such scenarios, we would try the 1866 mode at 10-10-10-27, increasing the voltage a little, about + 0.005 V. Depending on the results, you can adjust the memory controller voltage.
Myths about RAM | Cheaper to buy two sets of DIMMs than one large and expensive set
Even if you buy two identical sets, there is no guarantee that they will work together. The RAM modules, which are sold in one set, have been tested for compatibility. Manufacturers do not guarantee the performance of mixed sets, even if they use the same models of memory modules.
Customers often do this with high-speed modules and rely on XMP in the configuration. When XMP is enabled, the motherboard can read the profile of the two RAM slots and set the secondary timings appropriately, but the tRFC timings for the two modules can be set to 226, while the four modules require a value of 314. This problem is difficult to detect because users rarely go into the settings of secondary timings.
Myths about RAM | RAM is faster when all slots are busy
Two RAM slots give less memory controller load than four. Less power is required, the memory controller needs less voltage for stable operation, and RAM usually runs a little faster, although it is not noticeable. The same applies to three- and four-channel motherboards. Users are often mistaken, believing that four DIMMs (often sold as four-channel sets) always work in four-channel mode, although dual-channel motherboards in principle can not work like this.
Myths about RAM | RAM faster than 1600 MT / s does not give a performance boost
The validity of this statement depends on several factors. For processors with a built-in graphics core or APU, this is completely incorrect, because the video core uses system memory, and the faster it is, the better!
Most RAM tests measure the speed of reading, writing, and copying. Many game tests when changing RAM 1600 to 2133 show an increase in the frame rate from 3 to 5 FPS. This is due to the fact that in most games RAM is mainly used as a channel for transferring information to the GPU, and also as a buffer for frequently used data. The fact remains that the RAM can slightly increase the FPS. Since the price difference between the 1600 and 2133 memory is not always large, sometimes buying a faster RAM can be justified.
In addition, the WinRAR archiver takes data from RAM and compresses it in RAM before writing to disk. When the DDR3-1600 memory is replaced by 2400, the speed increase in tests using WinRAR can reach 25 percent. There are many other applications that use memory extensively: editing video, working with images, CAD and so on. Even a small speed advantage will save time if you work in such applications.
If you use a PC in an office single-task mode, for example, take notes, then browse the web, then watch the video, then you do not need a faster RAM. If you prefer to work in multitasking mode, for example, you have a lot of browser tabs open at the same time, while you are working with large tables or watching videos in the window, or working with images and performing virus checking in the background, then faster memory can bring certain benefits.
You can check it yourself by running several similar applications with a memory of 1600 MT / s, and then with a faster RAM. When downloading multiple applications, run a benchmark, for example, SiSoftware Sandra and simultaneously perform a large file backup using WinRAR. While these tasks are being completed, go through the open Windows windows, then check the results of Sandra and the time of the backup.
Myths about RAM | The volume of 8 GB is enough for the next ten years
If you really do not like multitasking, then 8 GB is enough. But this does not apply to gamers and enthusiasts. Five years ago it was enough 2 GB, then 4 GB and so on.
Another fact: computer manufacturers often stint on RAM. For example, when 2 GB was enough, they installed 1 GB. Today 6 to 8 GB of RAM is considered the norm and 16 GB is also not uncommon, so it's unlikely that the 8 GB level will last as a standard. Games use more and more RAM. If you collect a new system and you want it to remain relevant in a few years, we recommend 16 GB of RAM.
Myths about RAM | You will never be able to use 16 GB of memory
This misconception is a continuation of the previous one, but it is more relevant to users of applications that use memory intensively, as well as those who work with large volumes of files and data. The more RAM you have, the more data it can hold for instant re-access, instead of accessing the file on the hard disk or the network for a re-boot.
Many people use more than 20 GB of memory on the system at almost the same time almost every day, and this becomes the norm among Tom's Hardware forum participants who often discuss the possibility of maximizing the performance of their 8 and 16 GB RAM sets.
Remember also that manufacturers conduct a lot of research and get in touch with software developers and users. Therefore, the fact that modern motherboards are developed taking into account support for 32 GB RAM, 64 GB and 128 GB (and more), of course, have their own reasons.
Myths about RAM | I do not use all RAM, so additional memory will not accelerate
In some situations, increasing the amount of RAM can speed up the execution of certain processes. Many programs regulate the amount of data stored in memory, depending on the amount of available RAM, so that more RAM saves time by storing more frequently used data in RAM (rather than on the hard disk). This can be especially useful when you are working on projects with a variety of images or videos, CAD, GIS, with virtual machines etc. Another advantage of a large amount of RAM is the ability to create a RAM disk for downloading games, applications and other data. Such a disk has its hidden flaws, but many users are delighted with this feature.
Myths about RAM | 64-bit OS allows to use any amount of RAM
Many people believe that you can use an infinite amount of RAM with a 64-bit operating system, but it's not. As an example, we give the limitations on the amount of RAM in Windows 7:
| RAM Limitations in Windows 7 | ||
| x86 (32-bit) | x64 (64-bit) | |
| Windows 7 Ultimate | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Professional | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | 16 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | 8 GB |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 GB | does not exist |
And in Windows 8:
| RAM Limit in Windows 8 | ||
| x86 (32-bit) | x64 (64-bit) | |
| Windows 8 Enterprise | 4 GB | 512 GB |
| Windows 8 Professional | 4 GB | 512 GB |
| Windows 8 | 4 GB | 128 GB |
Myths about RAM | Memory with a voltage of 1.65 V can damage Intel processors
For its processors Intel recommends memory with a voltage of 1.50 V and a certain data rate. For Haswell, this is DDR3-1600. However, the fact that Intel also certifies RAM (even DDR3-1600), which works at voltages of 1.60 and 1.65 volts, is confusing. Keep in mind that the voltage 1.60 - 1.65V is considered the norm for RAM standard DDR3-2133 and higher.
Most memory with a lower data rate (for example, DDR3-1333 and 1600) use a voltage of 1.50 V or less. We recommend to refrain from buying RAM at such speeds if its voltage is 1.65V, since this could mean that the manufacturer used the cheapest and substandard memory chips. Why do RAM with good chips generally need a voltage of 1.60 -1.65 V? To further protect ourselves from future problems, we would recommend not to buy DDR3-1866 memory, the voltage of which exceeds 1.50V, unless it has low latency timings (CL7 or CL8).
Myths about RAM | Dual-mode doubles the data transfer rate, that is, RAM runs twice as fast
This is another misconception. When you install two slats in a two-channel mode, the memory controller does not perceive RAM as two separate 64-bit devices, but as a single 128-bit device. Theoretically, this should double throughput, but in practice the speed increase is 20-50 percent on Intel processors and slightly less on AMD chips.
This article was written with the participation of many members of the forum, but there are too many of them to list all. We would also like to thank the remarkable employees of such companies as Corsair, G.Skill and Team Group, whose knowledge and experience in this field have helped us a lot.
As always, comments and constructive criticism of the article are welcome.
Date of publication:
25.06.2009
As you know, RAM puts a big component in the performance of the computer. And it is clear that users are trying to increase the amount of RAM to the maximum.
If 2-3 years ago there were literally several types of memory modules on the market, now they are much larger. And it became more difficult to understand them.
In this article, we'll look at the various notations in the marking of memory modules, so that you can more easily navigate in them.
First, we introduce a number of terms that we need to understand the article:
- a "memory stick" - a memory module, a circuit board with memory chips on board, installed in a memory slot;
- one-sided plank - the memory bar, in which the memory chips are located on the 1 side of the module.
- two-sided plank - the memory bar, in which the memory chips are located on both sides of the module.
- RAM (Random Access Memory, RAM) is a random access memory, in other words, RAM. This is volatile memory, the contents of which are lost when there is no power.
- SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) - synchronous dynamic random access memory: all modern memory modules have such a device, that is, they require constant synchronization and updating of the content.
Consider markings
- 4096Mb (2x2048Mb) DIMM DDR2 PC2-8500 Corsair XMS2 C5 BOX
- 1024Mb SO-DIMM DDR2 PC6400 OCZ OCZ2M8001G (5-5-5-15) Retail
Scope
The first notation in the line is the amount of memory modules. In particular, in the first case it is 4 GB, and in the second case - 1 GB. True, 4 GB in this case are implemented not by one memory bar, but by two. This is the so-called Kit of 2 - a set of two bars. Typically, these sets are purchased to install the bars in a two-channel mode in parallel slots. The fact that they have the same parameters will improve their compatibility, which has a positive effect on stability.
Type of shell
DIMM / SO-DIMM is the type of the memory strap body. All modern memory modules are available in one of the two specified designs.
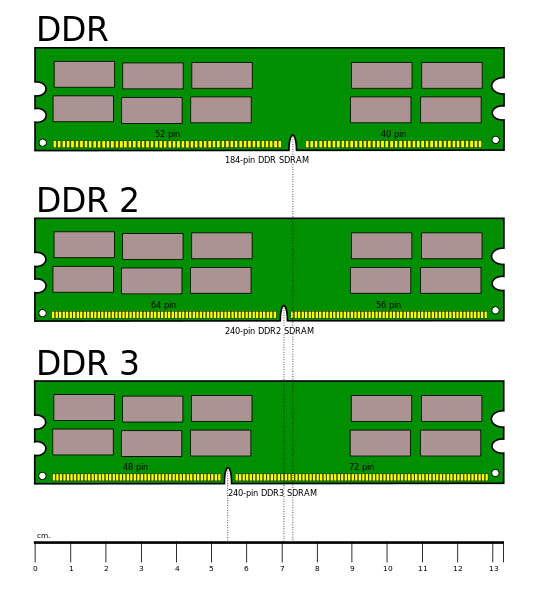
DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) - a module in which the contacts are arranged in a row on both sides of the module.
Memory type DDR SDRAM is available in the form of 184-pin DIMM-modules, and for memory type DDR2 SDRAM produced 240-contact strips.
In laptops memory modules of smaller dimensions are used, called SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM).
Memory type
The type of memory is the architecture by which the memory chips themselves are organized. It affects all the technical characteristics of memory - performance, frequency, voltage, power, etc.
At the moment, 3 types of memory are used: DDR SDRAM, DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM. Of these, DDR3 - the most productive, least consuming energy.
Data rates for memory types:
- DDR: 200-400 MHz
- DDR2: 533-1200 MHz
- DDR3: 800-2400 MHz
The figure indicated after the type of memory is frequency: DDR400, DDR2-800.
Memory modules of all types differ in power supply and connectors and do not allow to be inserted into each other.
The frequency of data transmission characterizes the memory bus potential for data transmission per unit of time: the higher the frequency, the more data can be transmitted.
However, there are still factors, such as the number of memory channels, the width of the memory bus. They also affect the performance of memory subsystems.
The term memory bandwidth is used to comprehensively evaluate the capabilities of RAM. It also takes into account the frequency at which the data and bit capacity of the bus and the number of memory channels are transmitted.
Bandwidth (B) = Frequency (f) x Memory bus width (c) x Number of channels (k)
For example, if you use 400 MHz DDR400 memory and a dual-channel memory controller, the bandwidth will be:
(400 MHz x 64 bit x 2) / 8 bit = 6400 MB / s
At 8 we were divided to transfer Mbit / s to MB / s (in 1 byte 8 bits).
Memory Speed Standard
In the notation for understanding the speed of the module, the memory bandwidth standard is also indicated. It just shows how much bandwidth the module has.
All these standards begin with the letters PC and then there are figures indicating the memory bandwidth in MB per second.
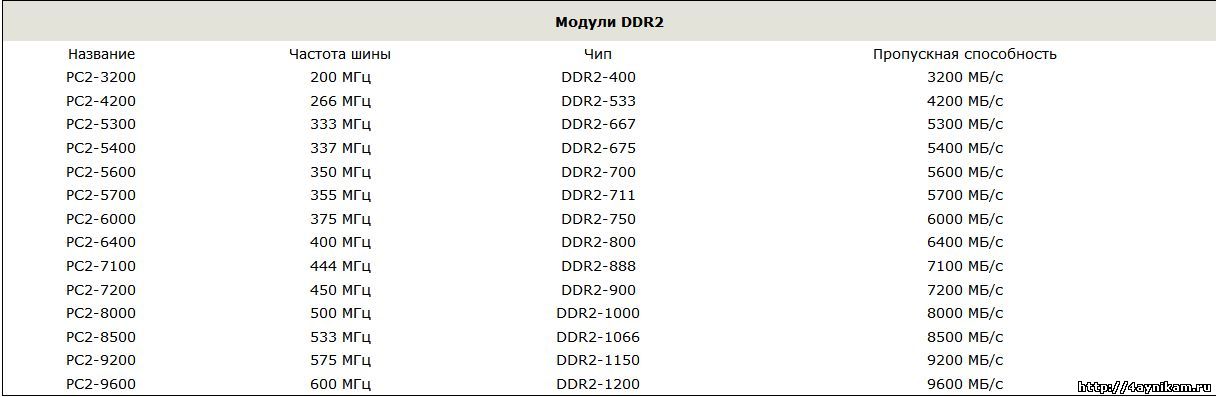
| Module name | Bus frequency | Type of chip | |
| PC2-3200 | 200 MHz | DDR2-400 | 3200 MB / s or 3.2 GB / s |
| PC2-4200 | 266 MHz | DDR2-533 | 4200 MB / s or 4.2 GB / s |
| PC2-5300 | 333 MHz | DDR2-667 | 5300 MB / s or 5.3 GB / s 1 |
| PC2-5400 | 337 MHz | DDR2-675 | 5400 MB / s or 5.4 GB / s |
| PC2-5600 | 350 MHz | DDR2-700 | 5600 MB / s or 5.6 GB / s |
| PC2-5700 | 355 MHz | DDR2-711 | 5700 MB / s or 5.7 GB / s |
| PC2-6000 | 375 MHz | DDR2-750 | 6000 MB / s or 6.0 GB / s |
| PC2-6400 | 400 MHz | DDR2-800 | 6400 MB / s or 6.4 GB / s |
| PC2-7100 | 444 MHz | DDR2-888 | 7100 MB / s or 7.1 GB / s |
| PC2-7200 | 450 MHz | DDR2-900 | 7200 MB / s or 7.2 GB / s |
| PC2-8000 | 500 MHz | DDR2-1000 | 8000 MB / s or 8.0 GB / s |
| PC2-8500 | 533 MHz | DDR2-1066 | 8500 MB / s or 8.5 GB / s |
| PC2-9200 | 575 MHz | DDR2-1150 | 9200 MB / s or 9.2 GB / s |
| PC2-9600 | 600 MHz | DDR2-1200 | 9600 MB / s or 9.6 GB / s |
| Memory type | Memory frequency | Cycle time | Bus frequency | Data transfer per second | Name of the standard | Peak data rate |
| DDR3-800 | 100 MHz | 10.00 ns | 400 MHz | 800 million | PC3-6400 | 6400MB / s |
| DDR3-1066 | 133 MHz | 7.50 ns | 533 MHz | 1066 million | PC3-8500 | 8533MB / s |
| DDR3-1333 | 166 MHz | 6.00 ns | 667 MHz | 1333 million | PC3-10600 | 10667MB / s |
| DDR3-1600 | 200 MHz | 5.00 ns | 800 MHz | 1600 million | PC3-12800 | 12800MB / s |
| DDR3-1800 | 225 MHz | 4.44 ns | 900 MHz | 1,800 million | PC3-14400 | 14400MB / s |
| DDR3-2000 | 250 MHz | 4.00 ns | 1000 MHz | 2,000 million | PC3-16000 | 16000MB / s |
| DDR3-2133 | 266 MHz | 3.75 ns | 1066 MHz | 2.133 billion | PC3-17000 | 17066MB / s |
| DDR3-2400 | 300 MHz | 3.33 ns | 1200 MHz | 2,400 million | PC3-19200 | 19200MB / s |
The tables indicate the peak values, in practice they may not be achievable.
Manufacturer and its part number
Each manufacturer gives each product or part its internal production label, called P / N (part number) - the part number.
For memory modules from different manufacturers, it looks something like this:
- Kingston KVR800D2N6 / 1G
- OCZ OCZ2M8001G
- Corsair XMS2 CM2X1024-6400C5
On the site of many memory manufacturers, you can learn how to read their Part Number.
Modules KingstonvalueRAM family:
Modules Kingston family HyperX (with additional passive cooling for overclocking):
By marking OCZ, you can understand that this is a 1 GB DDR2 module, with a frequency of 800 MHz.
By marking CM2X1024-6400C5 It is clear that this is a 1024 MB DDR2 module of PC2-6400 standard and delays of CL = 5.
Some manufacturers instead of the frequency or memory standard specify the time in ns access to the memory chip. By this time, you can understand what frequency is used.
This is what Micron does: MT47H128M16HG-3. The digit at the end indicates that the access time is 3 ns (0.003 ms).
According to the well-known forum T = 1 / f the frequency of the work of the chip f = 1 / T: 1 / 0.003 = 333 MHz.
Frequency of data transmission is 2 times higher - 667 MHz.
Accordingly, this module DDR2-667.
Timings
Timings are delays in accessing memory chips. Naturally, the smaller they are, the faster the module works.
The fact is that the memory chips on the module have a matrix structure - they are represented as matrix cells with the row number and the column number.
When accessing the memory cell, the entire line in which the desired cell is located is read.
First, you select the desired row, then the desired column. At the intersection of the row and the column number, the desired cell is located. Considering the huge amount of modern RAM, such memory arrays are not intricate - they are divided into pages and banks for faster access to memory cells.
First, the memory bank is accessed, the page is activated in it, then it works within the current page: the choice of the row and column.
All these actions occur with a definite delay relative to each other.
The main timings of RAM are the delay between the supply of the line number and the column number, called the full access time ( RAS to CAS delay, RCD), the delay between the supply of a column number and the receipt of cell contents, called the runtime ( CAS latency, CL), the delay between reading the last cell and supplying a new line number ( RAS precharge, RP). Timings are measured in nanoseconds (ns).
These timings and go one after another in the order of performing operations and are also indicated schematically 5-5-5-15 . In this case, all three timings are 5 ns, and the general duty cycle is 15 ns from the moment the line is activated.
The main timing is considered to be CAS latency, which is often abbreviated CL = 5. It is he who "brakes" the memory to the greatest degree.
Based on this information, you can choose the right memory module.
A lot of readers on our site are interested in questions that are somehow related to the choice of RAM and our site has a very big desire to answer everyone. That in the process of obtaining knowledge you were interested, this article is presented by the author in the form of a fascinating story from which you learn everything about the computer's RAM!
You will learn not only how to choose and buy the memory of a quality manufacturer, but also how to install the RAM modules into your computer and much more, for example:
- How much RAM do you need for a modern computer for the comfortable operation of all resource-intensive applications, for example: modern games at maximum settings, video processing programs, sound, etc. What should a powerful modern computer be?
- (click on the link and read a separate article).
- (click on the link and read a separate article)?
- What way out of the situation does the operating system find when there is a shortage of RAM?
- Does the computer benefit from an excess of RAM?
- Do I need to completely disable the swap file if you have a large amount of physical RAM, for example 16 -32 GB?
- How much dual-channel mode of operation of RAM is better than single-channel mode. What is better to buy, one 8GB memory bar or two 4 GB slats?
- How to choose the right memory modules for dual-channel operation?
- What is the frequency of RAM and can I install memory slots with different frequencies in the computer?
- What is the latency (timings) of RAM? Can I install memory slots with different timings in the computer?
- What is the difference between the slats of RAM used on laptops from ordinary RAM?
- Nowadays, DDR3 memory is actively used, and are there any DDR4 memory cards?
- If you have an old computer and want to buy DDR2 memory, then think about it several times, because DDR2 memory is expensive, maybe it's better for you to replace the motherboard, the processor and change the RAM to DDR3.
- How to choose the manufacturer of RAM and whether all the RAM is made in China?
- Do you need overclocking of RAM and how much will the performance of RAM in overclocking?
- Is it necessary to have a heatsink?
- What is a memory controller, why is it needed and where is it located?
- What does the ECC memory label mean?
How to choose RAM
Friends, in the last article we discussed the issue of choice with you and I was thinking about what kind of article to write next. It seems to be logical after the processor to choose the motherboard for it, but I usually do it differently. After choosing a processor, I choose the memory and video card, I do not know why, it's probably so simple and you can estimate how much to expect about it, since the choice of the motherboard is the most difficult part of choosing a computer configuration. In view of this, I decided not to deviate from my chosen tradition and devote this article to the choice of RAM (RAM). As this site is dedicated to the repair of personal computers, the choice of RAM will be considered, not only for new computers, but for older PCs.
Like the choice of processor, the choice of RAM is not at all a difficult task, probably even easier. But, as elsewhere, there are some nuances. Often the choice of RAM is reduced to its current price and the amount that you are willing to spend. Recently, the trend of price changes for RAM modules is very ambiguous. A few years ago there was a real boom in the increase in the amount of RAM in personal computers. And it was connected not so much with the growth of requirements of modern applications and operating systems, but with an incredible reduction in the price of it.
Memory bar for 4 gigabytes (GB) could be purchased for only $ 25 and even cheaper. As a result, exclusively for marketing purposes (for greater attractiveness and increased sales of computers), this very memory began to be "thrust" into new computers in huge volumes. So, the cheapest system unit, worth about 200-250 $ necessarily had 4 GB of memory, and the average for 300-350 $ - all 8 GB. At this, sellers in stores made a big accent, while keeping silent that this amount of memory of this PC to implement (use fully) will never succeed, since the rest of the "stuffing", such as the processor and video card left much to be desired. This, in fact, was a kind of cheating buyers or, if beautifully formulated, - a marketing move ...
Unfortunately, the days have passed when it was possible to "swagger" zatarivatsya operative on most do not indulge, and now the price of it has increased significantly. It seems that we were again "hooked on the needle" of technical progress ... But does it really need a large amount of RAM?
How much RAM do you need for a modern computer?

I must say that until recently, I was fond of modern computer games. Therefore, I always tried to keep my PC in topical technical condition. Probably, since when in 1997 I assembled my first full-fledged PC, not a single year passed, that I would not spoil myself with the purchase of a new video card, processor or memory.
In those old (by computer standards) times there was a certain division of the use of computers components operating system. The games were only needed powerful video card, a little RAM, and the processor had almost no value, since all calculations were made by a video card that has both its own processor and its memory.
To encode a video, on the contrary, powerful processor and a sufficient amount of RAM, and the video card did not matter, etc. Modern gaming applications "learned" enough to use "idle" before this powerful components of modern computers, such as the processor and RAM.
If we are talking about using a PC as a gaming and entertainment platform, then, until recently, I did not come across games that could even at the maximum graphics settings load at least 3 GB of memory by 100%. But in some cases, the total memory load was approaching this figure, despite the fact that the game itself consumed about 2 GB, and the rest of other applications, such as Skype, antivirus, etc.
Note: Note that this was not about 4 GB, namely about 3 GB. The fact is that 32-bit operating systems (OS) Windows can not use more than 3 GB of RAM and therefore "surplus" simply "do not see" ... It is fair to say that for 32-bit OSs built on the Linux kernel, there are no such hard limits. So, friends, there's no point in putting more than 4GB of memory on a 32-bit "Windows", they just will not be used.
For not very new, but also relatively old systems, on which you can put a lot of memory, the use of a 64-bit OS, in some cases, can be problematic. Since 64-bit versions of drivers for some equipment may simply not exist.
Not so long ago, just at the time of the total cheapening of memory, I bought in addition to my 4 GB as much. But it was caused not by its lack, but by the fact that on my, quite powerful motherboard, due to some misunderstanding) there were slots for the already almost obsolete DDR2 memory and I was afraid that even a little bit and it might completely disappear or wildly to rise in price, and here such "a freebie" ... After that I have passed to 64-bit operational system as otherwise this acquisition would look not so it is reasonable). I also need to consider that I have a fairly powerful 4-core processor and an expensive modern graphics card, thanks to which I can play games at very high graphics settings, at which the consumption of RAM is the maximum.
If you have a PC of the initial or intermediate level, then you will have enough 4 GB of RAM, as you can play comfortably in modern games only at low or medium settings, which do not require large amounts of memory. In such conditions, the installation say 8 GB of RAM is money thrown to the wind. But if your PC is powerful enough and is playable, then I would recommend still installing 8 GB, as there is some tendency to gradually increase the consumption of RAM by modern games.
So, for example, the recently released game Call of Duty: Ghosts simply refused to run if it found that you have less than 6 GB of RAM installed. Again, for the sake of justice, it should be noted that folk craftsmen made a fix, allowing to bypass this limitation at start-up and the game worked.
As for 64-bit operating systems, then you should know that it, like all 64-bit applications, consumes exactly 2 times more memory than 32-bit ones. Here it is completely justified by the technology of addressing memory and significantly improves performance.
What should be a fast computer

We will not go into details, but you should understand that in order to feel the increase in speed, the following conditions must be observed:
The central processor (CPU) must have a 64-bit architecture, the operating system must be 64-bit.
The application you want to use to improve the performance of certain operations must be 64-bit, the data that is processed must be streaming (converting video, archiving), as the speed increase is achieved by processing more information in one pass. In this case, the increase will be very significant - up to 2 times. Under such conditions, using the Intel processor (with a longer pipeline), you will get the maximum possible performance of such operations. But, as is known, in games data is transmitted in small portions (since it is impossible to predict the next step of the user), therefore, even in those games where there are 64-bit versions of the game engine, there will be almost no growth. And yet the decisive role of the video card in them has not gone anywhere.
As for professional applications, in such areas as video editing, 3D modeling, design, experts in these areas know exactly what hardware and how much memory they need. Usually this is from 16 GB or more. And if, say, 3D-modeling does not have streaming data processing, then simply the volume and quality of models can be so high that it "stupidly" needs a lot of RAM to place this model.
If you are not a professional, but really like to convert video, then you will have enough and 4-8 GB.
Truly huge RAM sizes can be claimed in scientific systems and highly loaded servers. In the latter, for example, it is quite common to consider the amount of memory from 64 GB. But the memory there is not cheap - server (with parity checking and automatic correction of errors), because failures on them are not allowed.
Well, and for example, I will bring the situation from my real life. When I was trained in network technologies and system administration, I often had to emulate a large number of simultaneously operating operating systems and network equipment. Such bundles as 5-10 running in VirtualBox (or VMware) OS + as many emulated network devices in GNS can eat decent RAM. And it's good if, in addition to the powerful "process" supporting modern virtualization technologies, there will be 8-16 Gb "operatives", otherwise brakes are provided ...
Why you can not disable the swap file
What happens when there is a shortage of RAM? Yes, it's very simple - the OS, to compensate for the lack of memory, begins to actively use hDD (the so-called paging file). By the way, God forbid you to turn it off. The system's operation is very deeply tied to the swap file and from its disconnection there will be more problems than good. As a result, not only does the CPU work, but also the hard disk.
Conclusion one - the memory should be enough, if it is not enough the computer starts to terribly braked, but its excessive excess does not give any increase in productivity.
What is RAM
What kind of memory does not happen ...

A card with memory chips is usually called a memory module (or "bar"). There are one-sided and two-sided memory modules. On the first chips are placed on one side of the printed circuit board, on the second - from two sides. What's better? I do not know) There is an opinion that two-way modules are better "chasing", about what this means, read on in this article. On the other hand, the smaller the chips, the higher the reliability of the module. I have repeatedly met cases when one side of the chips refused on the bar and the computer saw only half of its volume. But now I would not focus on this.
The main thing that you need to know is that if there are several memory modules in the computer, it is desirable that everyone be either one-sided or two-sided. Otherwise, memory does not always work well together and does not work at full speed.
To date, the most modern is the memory type DDR3, which replaced the older DDR2, and it in turn is an even older one - DDR. A new, more modern DDR4 memory has already been developed, but it has not yet reached the masses. Further we will not go deep.
When assembling a new PC, you should select only the latest memory standard. At the moment this is DDR3.
Sometimes replacing the motherboard and purchasing a new type of memory is equivalent to adding an old type of RAM to the old card.
The new memory will also be much cheaper than the older DDR2, which greedy manufacturers and sellers "hold" (hold) a high price, as it is not enough and for those who want to upgrade the PC there is simply no other choice than to agree to such draconian conditions. In this case, it is worthwhile to think, and can slightly add and buy more promising components? And if you still sell the old, and generally in the plus you can get out, if you're lucky of course)
It will work on its native frequency on any computer. In principle, the speed of the computer does not greatly affect the memory frequency. For example, in games this gain will be absolutely indistinguishable, and in some other applications it will be noticeable more. But the difference in price, for example, in comparison with DDR3 PC3-12800 memory (1600 MHz) will be very small. Here I usually follow the rule - if the price is slightly higher (1-3 $) and the processor supports a higher frequency, then why not - we take a faster memory.


Can I install memory slots with different frequencies in the computer?
The frequency of RAM does not have to coincide, the motherboard will set the frequency for all slats to the slowest module, but very often the computer with slats of different frequencies is unstable. For example, it may not even turn on.
Timings
The next parameter of memory speed is the so-called delays (timings). Roughly speaking, this is the time that has elapsed from the moment of access to memory until the time it was given the necessary data. Accordingly, the lower the timing - the better. There are dozens of different delays in reading, writing, copying and various combinations of these and other operations. But the main, which can be guided by only a few.
Timings are indicated (though not always) on the label of the memory modules in the form of 4 digits with hyphens between them. The first and most important is latency, the rest are derivatives of it.
Delays depend on the manufacturing quality of memory chips. Accordingly - higher quality-lower timings-higher price. However, it should be noted that timings significantly less impact on performance than memory frequency. Therefore, I rarely attach importance to this, only if the price is approximately the same you can take memory with smaller timings. Usually, modules with ultra-low timings are positioned as top-end, come complete with radiators (which we will talk about later), in a beautiful package and are much more expensive.

Marking of the main types, memory modules, their frequency and typical latency (CL)
DDR - obsolete (at all)
DDR-266 - PC2100 - 266 MHz - CL 2.5
In single-channel mode, data is written first into one memory module, and when its volume is exhausted, it starts to be written to the next available module.
In the two-channel mode, data recording is parallelized and recorded simultaneously on several modules.
Here, friends, the use of dual-channel mode significantly increases the speed of memory. Actually, the memory speed in the two-channel mode is up to 30% higher than in the single-channel mode. But in order for it to work it is necessary to observe the following conditions:
The motherboard must support dual-channel operation with RAM
The memory modules must be 2 or 4
The memory modules must be either one-sided or all two-sided
If any of these conditions are not met, the memory will work only in single-channel mode.

It is desirable that all the bars would be as identical as possible: they had one frequency, latency, and even had one manufacturer. Otherwise, no one will be able to give any guarantees of the operation of the dual-channel system. Therefore, if you want your memory to work in the fastest possible mode, it is very desirable to purchase immediately 2 identical memory slots, because after a year or two you will not find this exactly.
Another question is if you need to increase the amount of memory on the old computer. In this case, you can try to find the most similar memory module to the one that you already have. If you have 2, and there are 2 more free slots on the motherboard, you will have to search for 2 more of the same modules. The ideal, but not always economical option - to pass the old memory as used and buy 2 new identical modules of a larger volume.
Of course, if your old computer is very weak, then there can be no big increase from the two-channel mode. In this case, you can put any module, but it's better to choose the most suitable one, that would exclude a possible conflict with the old modules and the complete inoperability of the computer. Try to negotiate with the seller in advance about the return or bring the systemist to him and let him try to find a suitable module.
Memory Controller
It should be noted that earlier the memory controllers were in the chipset (the set of logic) of the motherboards. In modern systems, memory controllers are located in processors. In this regard, the two-channel memory operation mode has 2 more submodes: Ganged and Unganged.
In the coupled mode, the memory modules work in the same way as in the old motherboards, but in Unganged, each processor memory controller (in modern processors there are 2 of them) can work separately with each bar. This mode can be set in Computer BIOS, but it is usually selected by the processor automatically. If the slats are identical - then Ganged (but not necessarily), if different - then only Unganged. In any case, the memory will work in two-channel mode. But I still recommend buying and installing at once 2 identical modules, this will eliminate the distortions in their parameters and improve compatibility.
The dual-channel mode of RAM operation has only one drawback - two memory slots cost slightly more than one of the same volume. Therefore, many shops and private assemblers save and put one bar. As a result, we have a modern computer that does not work at full speed.
Some modern expensive motherboards, which usually have 6 slots for memory modules, can work even in a three-channel mode.
By the way, if you have 2 or 3 memory slots, then in order for two-channel or three-channel mode to work, all these slots need to be inserted into slots of the same color.

Some memory modules for desktops in their marking have the abbreviation ECC.
This is memory with parity control, the technology used in server systems. Do not pay any attention to this, as in desktop PC this technology is not critical and, in most cases, does not work at all. It's the same marketing move.
Memory slots
There's nothing to talk about. Each type of DDR, DDR2, DDR3 memory has its own connector on the motherboard of the same name (DDR, DDR2, DDR3). You do not insert one type of memory into another type of connector, since there is a special protrusion (key) in the motherboard slot,
Which should coincide with the slot on the memory module board. This is just done in order not to accidentally confuse and install the bar into the wrong connector and, as a result, not to disable both the memory and, possibly, the motherboard. When buying memory, you need to know exactly what type of motherboard supports it.
About the heatsinks of RAM
Some memory modules are equipped with so-called radiators, which are lining from aluminum plates, sometimes painted for copper or other colors, on both sides of the board. These overlays are connected to the memory chips through special thermal pads that are designed to better transfer heat from the chips to the radiators. Radiators can have additional ribs to increase the cooling area and even better heat dissipation.
In practice, memory chips during normal operation are heated slightly and do not require additional cooling. Gaskets between chips and radiators do not transmit heat as well as thermal paste between the processor and the cooler. In addition, in the free space between the board and the radiators there is an air layer that prevents natural cooling and eventually gets clogged with dust, which is difficult to clean out from there. Such a design provides for active cooling by means of an additional fan or a good organization of airflow inside the housing. In addition, such modules can often cost more.

So, who needs such joy, you ask? Well, ask me)
The answer is: enthusiasts, who are always very few, who want to disperse everything, overtake everyone, etc. Besides - it's just beautiful) Yes, friends, if you consider yourself to this group of users, then this is the memory for you! Because such a cooling system will be effective only at sufficiently high heating as a result of acceleration with increasing voltage and mandatory additional blowing. Remember - conventional memory, working in the normal mode, radiators are not needed.
An example of the proper use of memory with heat sinks in a powerful system

Overclocking RAM
Overclocking is a slang word in computer vocabulary, which implies manual installation of more aggressive parameters of electronic components, such as processors, memory and video cards than are provided by the manufacturer. Such parameters are usually the frequency (in processors there is still a multiplier). With a particularly high acceleration for relatively stable operation of these components, the voltage is also increased. As a result, higher heating of elements takes place, which requires improved cooling. The so-called overclocking is possible due to a certain stock, which the manufacturer has built, that the product would work stably, and not on the edge of its capabilities, or specially for advanced users. In any case, this event makes the entire system work less stable and shortens the life of the overclocked components . If you still decide to experiment, then first thoroughly study all aspects and act strictly according to the instructions. By the way, if components fail due to overclocking, you may lose warranty.
Manufacturers of RAM
Like other memory accessories, many manufacturers make it. And, as always, they have a different quality. I recommend paying attention to the following brands with the optimal price / quality ratio: AMD, Crucial, Goodram, Hynix, Kingston, Micron, Patriot, Samsung, TakeMS, Transcend.

The brands for enthusiasts are: Corsair, G.Skill, Mushkin, Team. These companies produce a large range of modules with radiators and improved technical characteristics. I recommend to avoid cheap Chinese brands: A-Data, Apacer, Elixir, Elpida, NCP, PQI and other little known manufacturers.
Memory modules that are not made in China deserve special mention. Currently, there are not many such, for example modules that are labeled as Hynix Original and Samsung Original are made in Korea. The quality of such modules is considered higher, they cost a little more, but usually have a longer warranty (up to 36 months).
In fairness, it should be noted that even if you purchased the memory of a well-known and well-proven brand, this, unfortunately, does not mean that you will not get a marriage or damaged during transportation modules. Of course, in the production of top brands in the individual packaging of the marriage (damage) will be less than the cheapest modules that are transported and sold "scattered".

Memory module in individual packaging

How to choose a memory for a new computer
First of all, choose the most modern of the types of memory used. For today it is DDR3. Decide on the volume that you need. Briefly summarizing this article, I will give general recommendations on the minimum amount of RAM for different PCs:
For office or weak home PC - 2 GB
4. It is better to choose the most identical strips (one-sided or two-sided), with the same frequency and latency. The ideal option is to sell the old memory as a used and install a new one in the right amount.
5. If you put the memory at a higher frequency than your processor or motherboard supports, it will run at a lower frequency.
Do right choice with us friends, and no dust to you nor a breakdown)
Comparing two types of RAM. Today, we offer you to get acquainted with the advice that concerns the ways of correct choice of RAM modules for a certain model of the motherboard.
Determine the appropriate module RAM for the motherboard
The amount of RAM is one of the important indicators of any PC. It determines how many programs a user can run on his computer simultaneously and without significant loss of quality and performance.
To determine which memory supports a particular motherboard, you need to go to the official site of the device manufacturer and see the data: type, frequency and volume of RAM.
However, if you do not know which motherboard you have installed and because of this there are difficulties, we suggest that you perform the following actions:
- Download and run on your PC hardware. We recommend using CPU-Z.
- A new window will open. To find out the model of the motherboard, go to the "Mainboard" tab. We look at the first two parameters.
- Also in the "Memory" tab you can find out which RAM bar is already installed.
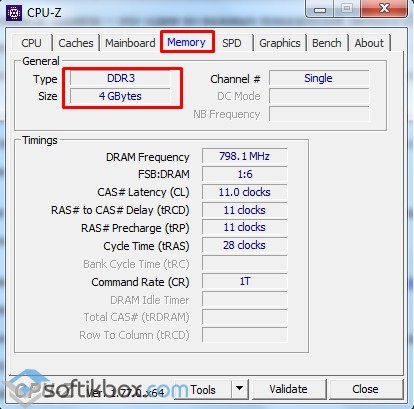
- Data about the motherboard (make and model) is copied and pasted into the search string. We choose only the official website of the manufacturer.

- On the specifications page of the motherboard we are looking for a section on RAM. We look, what type of operative memory is compatible with it. Also, the manufacturer always indicates the maximum amount of RAM and the permissible operating frequencies.

IMPORTANT! Some motherboard manufacturers provide a complete list of RAM modules on their site, indicating the manufacturer and model of the component.
After you have learned the compatible RAM module, it is worth considering the following recommendations:
- If you already have one RAM bar, the second one should be selected with exactly the same parameters.
- The amount of RAM should not exceed the maximum, which is indicated on the site of the motherboard manufacturer.
- If you install two RAM slots with different operating frequencies, they will operate at the maximum frequency, but the SLOW module itself.
- If you install memory slots with higher frequencies on the motherboard, the modules will only work on the frequencies that the board and processor support.
My respect dear visitors of the site. In the last article I wrote about that. Now, knowing what it is and for what and how it serves, many of you are probably thinking about acquiring a more powerful and productive RAM for your computer. After all, increasing the performance of your computer with additional memory RAM is the simplest and cheapest (in contrast to for example a video card) method of upgrading your pet.
And ... Here you stand at the window with the packages op. There are a lot of them and they are all different. There are questions: And what kind of memory to choose?How to choose the right RAM and not to lose?What if I buy an operative, and then it will not work? These are quite reasonable questions. In this article I will try to answer all these questions. As you already understood, this article will take its worthy place in the series of articles in which I wrote about how to choose the right components of the computer ie. iron. If you did not forget, there were articles there:
—
—
—
This cycle will continue and continue, and in the end you can already assemble for yourself a super in every sense super computer (unless of course finances will allow :))
In the meantime learn how to choose the right RAM for your computer.
Go!
RAM and its main characteristics.
When choosing the RAM for your computer, you must necessarily build on your motherboard and processor because the RAM modules are installed on the motherboard and it also supports certain types of RAM. In this way, the relationship between the motherboard, the processor and the RAM is obtained.

Learn about how what kind of RAM does your motherboard and processor support? you can visit the manufacturer's website where you need to find the model of your motherboard, as well as find out which processors and RAM they support. If you do not, then it turns out that you bought a super modern operating system, and it is not compatible with your motherboard and will dust anywhere in your closet. Now let's go directly to the main technical characteristics of RAM, which will serve as a kind of criteria for choosing RAM. These include:
So I listed the main characteristics of RAM, which should pay attention first of all when buying it. Now we will open each of them in turn.
Type of operative memory.
For today in the world the most preferable type of memory are memory modules DDR(double data rate). They differ in time of release and of course with technical parameters.
- DDR or DDR SDRAM (in translation from English Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory - synchronous dynamic memory with random access and twice the data transfer rate). Modules of this type have 184 contacts on the bar, they are powered by a voltage of 2.5 V and have a clock frequency of up to 400 MHz. This type of RAM is already obsolete and is used only in old motherboards.
- DDR2 A type of memory that is widespread at the time. It has 240 contacts on the PCB (120 on each side). Consumption unlike DDR1 is reduced to 1.8 V. The clock frequency ranges from 400 MHz to 800 MHz.
- DDR3 - the leader in performance at the time of this writing. Distributed no less than DDR2 and consumes a voltage of 30-40% less, in contrast to its predecessor (1.5 V). It has a clock speed of up to 1800 MHz.
- DDR4 - a new, super modern type of RAM, ahead of its counterparts in terms of both performance (clock frequency) and voltage consumption (and therefore less heat generation). Support for frequencies from 2133 to 4266 MHz is being announced. At the moment, these modules have not yet entered mass production (they promise to be released in mass production in mid-2012). Officially, the fourth generation modules operating in the mode DDR4-2133 at a voltage of 1.2 V were presented at the exhibition CES, Samsung on January 04, 2011.
The amount of RAM.
About the amount of memory I will not write much. I will only say that it is in this case that the size matters 🙂
All several years ago, operative memory in the amount of 256-512 MB satisfied all the needs of even cool gaming computers. At the present time, for normal operation, only the operating room system windows 7 requires 1 GB of memory, not to mention applications and games. Superfluous RAM will never be, but I'll tell you a secret that 32-bit windows uses only 3.25 GB of RAM, even if you install all 8 GB of RAM. More about this you can read.
The dimensions of the bars or the so-called Form factor.
Form - factor - this standard sizes modules RAM, the design type of the RAM slots themselves.
DIMM (Dual InLine Memory Module - two-sided type of modules with contacts on both sides) - mainly intended for desktop stationary computers, and SO-DIMM used in laptops.

Clock frequency.
This is still an important technical parameter of RAM. But the clock frequency is also on the motherboard and it is important to know the operating frequency of the bus of this board, since if you bought for example a RAM module DDR3-1800, and the slot (connector) of the motherboard supports the maximum clock frequency DDR3-1600, then the RAM module as a result will work at the clock frequency in 1600 MHz. In this case, all kinds of failures and errors in the system operation are possible.
Note: The frequency of the memory bus and the frequency of the processor are completely different concepts.

From these tables it can be understood that the bus frequency multiplied by 2 gives the effective memory frequency (indicated in the "chip" column), i.e. gives us the data transfer rate. About this, we are told by the name DDR (Double Data Rate) - which means twice the data transfer rate.
I will give for clarity an example of decoding in the name of the RAM module - Kingston / PC2-9600 / DDR3 (DIMM) / 2Gb / 1200MHz, where:
- Kingston - manufacturer;
- PC2-9600 - the name of the module and its bandwidth;
- DDR3 (DIMM) - type of memory (form factor in which the module is executed);
- 2Gb - the volume of the module;
- 1200MHz - Effective frequency, 1200 MHz.
Throughput.
Throughput - the characteristics of the memory on which the system's performance depends. It is expressed as the product of the system bus frequency by the amount of data transmitted per clock cycle. Bandwidth (peak rate of data transfer) is a complex indicator of the possibility RAM, it takes into account data transmission frequency, bit capacity and the number of memory channels. The frequency indicates the capacity of the memory bus per clock - more data can be transmitted at a higher frequency.
The peak is calculated using the formula: B = f * c, where:
B is the throughput, f is the transmission frequency, and c is the width of the bus. If you use two channels for data transmission, multiply everything by 2. To get the digit in bytes / c, you need to divide the result by 8 (because in 1 byte 8 bits).
For best performance bandwidth of the RAM bus and processor bus bandwidth must coincide. For example, for an Intel core 2 duo E6850 processor with a 1333 MHz system bus and a throughput of 10600 Mb / s, you can install two modules with a throughput of 5300 Mb / s each (PC2-5300), in total they will have a system bus bandwidth (FSB) of 10600 Mb / s.
The bus frequency and throughput are denoted as follows: " DDR2-XXXX"and" PC2-YYYY"Here" XXXX "stands for the effective memory frequency, and" YYYY "for the peak bandwidth.
Timing (latency).
Timing (or latency) - these are the time delays of the signal, which, in the technical characteristics of RAM, are recorded as " 2-2-2 " or " 3-3-3 ", etc. Each digit here expresses a parameter.In order, this is always" CAS Latency"(runtime)," RAS to CAS Delay"(full access time) and" RAS Precharge Time"(precharge time).
Note
So that you can better understand the concept of timings, imagine a book, it will be our operational memory, to which we are addressing. Information (data) in the book (RAM) is divided into chapters, and chapters consist of pages that in turn contain tables with cells (such as in Excel tables). Each cell with data on the page has its coordinates vertically (columns) and horizontal (rows). The RAS signal (Raw Address Strobe) is used to select the line, and the CAS (Column Address Strobe) signal is used to read the word (data) from the selected row (ie to select the column). The full cycle of reading begins with the opening of the "page" and ends with its closing and recharging, because otherwise the cells will be discharged and the data will be lost.
Here is the algorithm for reading data from memory:
- the selected "page" is activated by the RAS signal;
- data from the selected line on the page is transferred to the amplifier, and the data transfer requires a delay (it is called RAS-to-CAS);
- a CAS signal is used to select (column) a word from this line;
- the data is transferred to the bus (where from go to the memory controller), while also there is a delay (CAS Latency);
- the next word goes without delay, since it is contained in the prepared line;
- after the call to the line is completed, the page closes, the data is returned to the cells and the page is reloaded (the delay is called RAS Precharge).
Each digit in the designation indicates how many bus cycles the signal will be delayed. Timings are measured in nano-seconds. Figures can have values from 2 to 9. But sometimes a fourth (eg 2-3-3-8) is added to these three parameters, called " DRAM Cycle Time Tras / Trc"(Characterizes the speed of the entire memory chip as a whole).
Sometimes it happens that sometimes a crafty producer points out in the performance characteristic only one value, for example " CL2"(CAS Latency), the first timing is equal to two bars, but the first parameter does not have to be equal to all timings, and maybe less than others, so keep this in mind and do not fall for the marketing course of the manufacturer.
An example for clarifying the effect of timings on performance: a system with 100 MHz memory with timings 2-2-2 has about the same performance as the same system at 112 MHz, but with 3-3-3 delays. In other words, depending on the delay, the performance difference can reach 10%.
So, when choosing it is better to buy the memory with the least timings, and if you want to add the module to the already installed one, then the timings for the purchased memory must coincide with the timings of the installed memory.
Modes of memory.
RAM can work in several modes, if of course such modes are supported by the motherboard. it single-channel, two-channel, three-channel and even four-channel modes. Therefore, when choosing RAM, it is worth paying attention to this parameter modules.
Theoretically, the speed of the memory subsystem in the two-channel mode is increased by 2 times, three-channel mode - by 3 times, etc., but in practice with the two-channel mode, the performance gain, unlike the single-channel mode, is 10-70%.
Let's consider the types of modes:
- Single chanell mode (single-channel or asymmetric) - this mode is activated when only one memory module is installed in the system or all modules differ in memory size, frequency of operation or manufacturer. It does not matter which connectors and what memory to install. All memory will work at the slowest speed of the installed memory.
- Dual Mode (two-channel or symmetrical) - in each channel the same amount of RAM is installed (and theoretically, the maximum data rate is doubled). In dual-channel mode, the memory modules work in pairs in the 1st, 3rd and 2nd with the 4th.
- Triple Mode (three-channel) - in each of the three channels the same amount of RAM is installed. Modules are selected by speed and volume. To enable this mode, the modules must be installed in 1, 3 and 5 / or 2, 4 and 6 slots. In practice, by the way, this mode is not always more efficient than dual-channel, and sometimes even loses to it in data transfer speed.
- Flex Mode (flexible) - allows you to increase the performance of RAM when installing two modules of different sizes, but the same frequency of operation. As in the dual-channel mode, memory cards are installed in the same name connectors of different channels.
Usually the most common option is dual-channel memory mode.
For work in multichannel modes there are special sets of memory modules - the so-called Kit Memory (Kit-kit) - this set includes two (three) modules, one manufacturer, with the same frequency, timings and memory type.
Appearance of KIT-kits:
for dual-channel mode

for three-channel mode

But the most important thing is that such modules are carefully selected and tested, by the manufacturer, for operation in pairs (triples) in two- (three-) channel modes and do not assume any surprises in operation and tuning.
Manufacturer of modules.
Now on the market RAM well-proven manufacturers such as: Hynix, amsung, Corsair, Kingmax, Transcend, Kingston, OCZ…
Each company has its own product for each product. marking number, which, if properly decoded, you can find for yourself a lot of useful information about the product. Let's try to decipher the marking of the module Kingston family ValueRAM (see the picture):
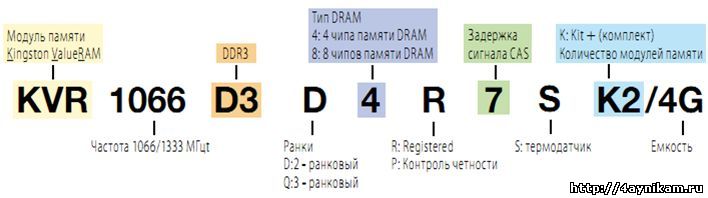
Explanation:
- KVR - Kingston ValueRAM ie. manufacturer
- 1066/1333 - working / effective frequency (Mhz)
- D3 - memory type (DDR3)
- D (Dual) - rank / rank. The two-logger module is two logical modules that are soldered on the same physical one and use the same physical channel in turn (needed to reach the maximum amount of RAM with a limited number of slots)
- 4 - 4 DRAM memory chips
- R - Registered, indicates stable operation without failures and errors for as long as possible continuous time interval
- 7 - signal delay (CAS = 7)
- S - temperature sensor on the module
- K2 - Kit (kit) of two modules
- 4G - the total volume of the whale (both slats) is 4 GB.
I will give one more example of marking CM2X1024-6400C5:
From the marking it can be seen that this dDR2 module volume of 1024 MB standard PC2-6400 and delays CL = 5.
Brands OCZ, Kingston and Corsair recommend for overclocking, i.e. have the potential for overclocking. They will be with small timings and a reserve of clock frequency, plus they are all equipped with radiators, and some even with coolers for removing heat, because when overclocked, the amount of heat increases significantly. The price for them will naturally be much higher.
I advise you not to forget about fakes (there are a lot of them on the shelves) and buy RAM modules only in serious stores that will give you a guarantee.
Finally:
That's all. With the help of this article, I think you will not be wrong when choosing the RAM for your computer. Now you can choose the right operative for the system and increase its performance without any problems. Well, and those who buy RAM (or have already bought), I will devote the following article, in which I will describe in detail how to install RAM in the system. Do not miss…
The First Distribution Company carts store will deliver your cartridges for 2 hours to anywhere in Moscow. You only need to place an order.