Optimal processor frequency for a laptop. Processor clock speed: myths and misconceptions. Online and cache memory
The processor (CPU or CPU) is the central link of almost every modern device. It is capable of simultaneously performing any calculations and executing commands of various programs. Mostly, the CPU depends on how fast and productive the computer or laptop will be. It is his choice that gives further direction to the process of selecting the remaining components.
This figure is informative. To estimate how much autonomy you need to find the laptop with the lowest consumption in the series and compare it with the one you want to take for games. You will be surprised to find that the one you want to buy in reality will have a double energy consumption, so the maximum autonomy is 2 and a half hours.
The same goes for the cooling system. Conclusion? This laptop is not very good. It gets really hot. But why should you play on your laptop? 90% of those who buy their laptop for games do not use it outside the home. Most buy their laptop to play in bed or lack of space. I have friends who never took a laptop out of the bedroom, and some never dropped it from the table. Why did you get a gaming laptop at the expense of the desktop? On the desktop, you did not have so many problems with cooling or performance, and with the same money you created a much better system.
Choose a processor for a computer or laptop is not a difficult matter. First you need to determine the goals for which it is purchased. After, you need to understand the main parameters of its central "brain".
Types of sockets of processors AMD, Intel and frequency of the system bus
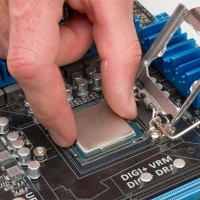 A socket is a processor socket for connecting to the motherboard (see photo). Today, most motherboards are manufactured either for Intel CPUs or for AMD. It is important to know that the CPUs of these brands are not interchangeable - their sockets differ both in form and electrically.
A socket is a processor socket for connecting to the motherboard (see photo). Today, most motherboards are manufactured either for Intel CPUs or for AMD. It is important to know that the CPUs of these brands are not interchangeable - their sockets differ both in form and electrically. By the type of connector they are divided into classes. Each such class consists of models with sockets of the same form. In this case, it is possible to insert them on the same motherboard. The main thing is that its chipset has the appropriate support.
Also, when buying a CPU, for example, with an LGA1155 connector, the motherboard should be purchased with a similar socket. Over time, new connectors began to have an increasing number of contacts, which led to a constant increase in the frequency of the bus - the speed of communication between the CPU and the motherboard. Thus, the more modern the type of the socket, the higher the frequency of the bus. It is the same as the clock frequency, measured in hertz. The higher this value, the faster the process of information exchange. It is best to choose a CPU with a bus frequency of 1.6 GHz or higher.
At the time of writing the article, Intel's most popular is the LGA1155 socket. For more powerful servers with a CPU Core i7 or Xeon, a LGA1366 connector is made. The last development was the LGA2011 socket. It is used in some Ivy Bridge CPUs. Although the price of similar CPU drops, but motherboards with such a connector are very expensive. There is no need to overpay for a small increase in productivity.
AMD has compatible "+" series sockets. For example, the most popular AM3 + connectors are also suitable for AM3. This allows you to expand the possibilities for improving the CPU. Sockets FM1 and FM2 were developed for the CPU AMD Fusion, which have a powerful integrated graphics, an excellent solution for those who do not want to spend money on a discrete graphics card.
CPU clock speed: choose for games and daily tasks
 The clock frequency is the total number of actions a CPU can perform in one second. This characteristic is measured in hertz (Hz). For example, the clock frequency of 1.8 GHz per second is the performance of 1 billion 800 million operations. The higher this number, the faster the CPU will work. Therefore, you should choose a CPU with a higher clock speed.
The clock frequency is the total number of actions a CPU can perform in one second. This characteristic is measured in hertz (Hz). For example, the clock frequency of 1.8 GHz per second is the performance of 1 billion 800 million operations. The higher this number, the faster the CPU will work. Therefore, you should choose a CPU with a higher clock speed. To launch office applications, comfort video viewing in Full HD resolution and listening to music, it's enough to have a dual-core CPU with a frequency of about 1500-2000 MHz. For modern games and multimedia tasks, the clock frequency from 2000-2500 MHz will be required - 4-6 or 8-core (according to the requirements of the programs).
Please note, modern models from Intel are equipped with proprietary technology Turbo Boost. This is an automatic increase in the nominal frequency at the request of the operating system (see photo).
Cache memory of the processor: choose the desired volume
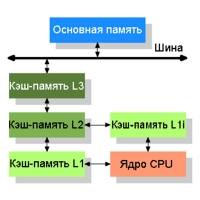 The cache is the super-fast CPU memory in which the executable program data is loaded. The larger the cache size, the faster this data will be processed.
The cache is the super-fast CPU memory in which the executable program data is loaded. The larger the cache size, the faster this data will be processed. Currently there are 3 levels of cache memory:
L1 - the fastest memory, because it has the smallest size (8-128 KB);
L2 - slower than L1, but larger than (128-12288 KB);
L3 is the slowest memory. It has the largest size or may be completely absent (0-16384 Kb). The latter is possible for specially executed processors or specific servers.
When the CPU is selected, the L3 cache must be calculated in such a way that each core has a volume of at least 1 MB. It should be borne in mind that in the characteristics it is indicated completely on the whole processor. Proceeding from this, it is not necessary to purchase a 4-core CPU with a level 3 cache memory of less than 4 MB.
Number of processor cores: more is not always better
 The core is called a small-sized crystal, made of silicon. Its area is approximately 1 square centimeter. It contains the CPU implemented with the help of the smallest logical elements. At the moment, the clock speed of the CPU can not be raised higher, because its value has reached the maximum value. Therefore, manufacturers have moved to increase the number of cores.
The core is called a small-sized crystal, made of silicon. Its area is approximately 1 square centimeter. It contains the CPU implemented with the help of the smallest logical elements. At the moment, the clock speed of the CPU can not be raised higher, because its value has reached the maximum value. Therefore, manufacturers have moved to increase the number of cores. The advantage of multi-core is especially evident when you simultaneously run resource-intensive multitasking programs, but only those that support this feature. Therefore, if the CPU has 4 cores, and the running program is developed only for the use of 2, the remaining 2 will not be used. In the opposite case, for example, optimized for four cores game Ghost Recon demonstrate a confident superiority over the dual-core mode (see photo).
Therefore, when choosing a CPU for everyday tasks, it is more important to rely not on the number of cores, but on the indicator of its clock frequency and the amount of cache memory. However, when buying a computer or laptop for games, it is better to purchase a modern quad-core version.
Processor size: 32 and 64 bits
The number of bits of information processed by the CPU during a single clock cycle is characterized by the bit depth. It can have a value of 8, 16, 32 and 64. Nowadays all major programs are designed for 32-bit or 64-bit architecture.When choosing a computer or laptop, you should take into account that 32-bit systems support the memory no more than 3.75 GB. 64-bit allows you to transfer the amount of RAM more than 4 GB, which is necessary for modern applications, where 4 GB is already a minimum.
Graphical core of the processor, heat dissipation and technology
 In addition to a number of conventional cores, the CPU can be additionally equipped with a kernel that has the capabilities of graphical calculations. This significantly reduces the workload of an integrated graphics processor or a discrete graphics card. The latest development of models with a graphics core is quite capable of replacing budget variants of video cards. They support video in Full HD mode, as well as low-power games.
In addition to a number of conventional cores, the CPU can be additionally equipped with a kernel that has the capabilities of graphical calculations. This significantly reduces the workload of an integrated graphics processor or a discrete graphics card. The latest development of models with a graphics core is quite capable of replacing budget variants of video cards. They support video in Full HD mode, as well as low-power games. For desktop computers, Intel has released similar hybrid models of the Clarkdale family, and for mobile devices - Arrandale. Still there is a cheaper option - Lynnfield. The graphical decision of the company in Sandy Bridge CPU was rather weak. It was significantly inferior to similar developments of competitors - ARM or AMD Llano. Therefore, for the new CPUs Ivy Bridge, the architecture of the graphics core was changed, which improved its performance.
Heat dissipation, a parameter that determines how much the CPU is heated during operation, is called heat dissipation (TDP). Its unit of measurement is considered to be watt. By the value of heat generation, you can select the appropriate cooling system. For example, if the TDP CPU is 75W, then the cooler needs to be selected of the same power, and better even slightly higher.
For notebooks and netbooks, heat dissipation should not exceed 45W, because they do not have the ability to use bulky cooling systems. This characteristic is also taken into account in those cases when a more silent system is selected, which lasts longer from the battery.
If you choose between the same models that have different heat dissipation, you should buy one with this value less.
A set of specific commands aimed at increasing the performance of the CPU is called technology. For example, SSE4 technology includes 54 commands that improve the process of working with more serious programs. These include 3-dimensional modeling, powerful games, as well as processing audio and video files.
If you plan to use the above programs, the selected central CPU should support similar technologies.
In conclusion: AMD and Intel - which processor is better
 Models from Intel are preferable to AMD, because they are more correctly operated by other internal components and some applications, although in general, Intel is more expensive than AMD. Objectively, for expensive devices, the choice of a system based on Intel is more justified, and AMD is a good option for budget solutions.
Models from Intel are preferable to AMD, because they are more correctly operated by other internal components and some applications, although in general, Intel is more expensive than AMD. Objectively, for expensive devices, the choice of a system based on Intel is more justified, and AMD is a good option for budget solutions. Intel also produces Atom processors with a twice-reduced cache compared to Core, but Atom has its advantages - it's lower power consumption. According to the testimony, when solving different types of tasks, different CPUs show different results: some are faster in games, others in multimedia applications. Therefore, the choice is made based on the needs of the owner.
Employees of simple offices work with easy text and graphic editors, and also carry out a small surfing on the Internet. It is enough for them to stop their choice on modern, besides not very expensive series. These include Pentium Dual-Core models from Intel or Phenom II X2 (AMD).
For home use, including modern games and watching videos in high definition, you will need a more productive 2-core CPU with the highest possible clock speed. It can be Core i3 5xx, 6xx (Intel) or Phenom II X2 5xx (AMD).
When installing the most demanding toys, you need to choose a 4-core CPU of a higher price category, for example, Core i5 750 (Intel) or Phenom II X4 95x.
If you run programs designed for professional occupations with 3D graphics or media applications, they require processing a very large amount of data. For such purposes it is recommended to select a model with at least 6 cores. Here the models Core i7 8xx, 9xx (Intel) or Phenom II X6 (AMD) are suitable.
If you are serious about choosing a laptop, but for sure carefully choose each component. We will tell you about some of them so that you can freely navigate in all variety of choice. Today our story will be about the processors.
The processor for a laptop is his heart. Suppose you will indecently have a lot of RAM, a powerful video card, but if the processor is weak - everything will be slow. This problem was faced by many users of the first generations of netbooks - they added memory to 2 GB, but the processor was still single-core. As a result, they had to spend long minutes in anticipation that the processor now prochuhayetsya and run the program. A sad sight.
Which processor to choose a laptop? Intel! Why am I not talking now about AMD, because they are used quite widely in desktop computers? Yes, because the laptop - this is not your desktop computer. And the processors from AMD are heated. The less space, the worse cooling. The worse cooling is, the more brakes and the probability of failure of not only the processor, but also other components of the laptop, which are unlucky to be near. Of course, I will say a little about the AMD processors at the end of this article, but seriously, guys ... Do not be fooled at low cost. Then you will be more expensive.
Intel has Core processors, but Celeron and Pentium.
– Celeron - are cheap, but so braked that well, its nafig. We do not buy. There are single-core and dual-core.
– Pentium - the last generation can be very productive, look for them on the architecture Broadwell and Skylake. There is also an index Nxxx - that's not a very good option, although almost all budget laptops are completed with them. The fact is that these "Pentiums" were originally created for tablets, so they will not have much performance either. However, if you do not have very large inquiries - well, there's no need to wander around (do not open many tabs), you can reply to the mail - maybe you will have enough. But it's better to take a full Pentium, even a low-voltage (with U index) - and it will be more productive. These processors have two to four cores.
Core Processors
– Core i3 (dual-core) - the minimum level of performance for those who want to be comfortable. But! The old i3 may be weaker than the new "Pentium"! This is especially true for low voltage versions with a U-letter. To help us, check with it whenever you want to check how productive this or that chip is, and which processor is best for your laptop.
– Core i5 (there are dual-core, but in the last generation there are also quad-core) - the golden mean. But with the current crisis laptops with core i5 are for 40,000 rubles, and not everyone can afford it. The most unproductive of i5 will provide excellent work with everyday and not very tasks (for example, with video editing). Well, the most powerful on the shoulder is almost everything - and heavy games, and AutoCAD.
– Core i7 (if for desktops i7 are only quad, then laptops can have two and four cores - in the first case it's a low-voltage processor, which saves you the battery charge) - this is for enthusiasts. For those who want to play games or work with powerful programs. By the way, often i7 can be found on ultrabooks - thin and light imaging laptops. Along with a solid-state drive such laptops provide exceptional performance. So these processors will suit those who just want a laptop to fly.
Intel processors are divided into generations, and I'll tell you about those that are currently relevant. In addition to Core, you can find both Celeron and Pentium in them.
Sandy Bridge - the second generation of Core processors
They have an index Core i3 / i5 / i7 2ххх. Released were already in 2011, but in fact, many users still use them and are quite satisfied. Take a closer look at these processors if you are not going to buy a new laptop. And some shops, by the way, now periodically throw out junk somewhere from the dustiest corners of their warehouses. Do not be scared of these processors, they are very good in performance. Bad only in energy efficiency, but a notebook of such prescription is still, most likely, the battery will be killed, so it will only work from the network.
Ivy Bridge - third generation Core
Core i3 / i5 / i7-3xxx. The platform seemed to be better, but somehow it did not catch on. Yes, the processors have become more energy efficient, yes, the performance of top models has increased, but no "wow-effect" ever happened. This generation of good low-voltage processors, providing a long battery life.
Haswell - the fourth generation of Core
Core i3 / i5 / i7-4xxx. Here there was a real breakthrough. This architecture has become very popular almost immediately - and is still popular. There are a lot of laptops with Haswell processors on the market, and we strongly recommend them to buy. They are cheaper than the newer Skylake, but at the same time their performance and energy efficiency is at a very high level.
Broadwell - the fifth generation of Core
Core i3 / i5 / i7-5xxx. Here again somehow everything is not very fused. Few manufacturers decided to install these processors in their notebooks, although it was in this generation that the Core M processors for the first time appeared, designed for installation in extremely thin and light - and at the same time expensive - laptops or tablets. The fact that they did not go to the masses is explained solely by their nicheness, although these processors are really good. Waiting for them to perform miracles of performance is certainly not worth it, but they perform their basic tasks perfectly, especially as a solid-state drive usually paired with them.
Skylake - the sixth generation of Core
Core i3 / i5 / i7-6xxx. Well, plus the Core m3 / m5 / m7. The latter, like last year's Core M, have high energy efficiency and are installed in thin and light notebooks. In other respects, this architecture turned out to be very good. Although it should be noted that laptops on Skylake are still expensive, but if you want to buy the device for years to come - definitely prefer this platform. It is quite efficient, and if you do not pursue strong power, then choose low-voltage processors - the laptop will last longer from the battery. In this generation, by the way, mobile quad-core Core i5 for the first time appeared.
Well, now about the code symbols of Intel processors. Immediately after i3 / i5 / i7 comes the figure denoting the generation. Core i5- 3 340M - the third generation processor, that is Ivy Bridge. The next three figures are performance within a generation. M means "mobile processor". QM - Quad-core mobile processor. HQ - Quad-core processor for powerful gaming laptops and workstations. U - processors with increased energy efficiency, but not so powerful. Well, there's more Y - it's very little consuming processors, but their performance is even lower than that of U.
And finally - a couple of words about AMD. If you really want to, you can, but only under your responsibility. Choose processors A6, A8 and A10 (in order of increasing performance) and stay away from A4 and, God forbid, E1 and E2.