What is the Internet modem. Analog modems.
Modulator modulates, that is, changes the characteristics of the carrier signal in
according to changes in input information signal .
Demodulator performs the reverse process. A special case of a modem is a widely used peripheral device for a computer, allowing it to communicate with another computer equipped with a modem via a telephone network ( telephone modem) or cable network (cable modem).
Modem Types
By execution:
1
. external - connect to Com or USBport, usually have an external unit
food (there are USB modemseating from USB, and LPT modems
(manufacturer - Prolink)).
2. internal - set inside computerin slot ISA, PCI, PCMCIA

3. embedded - are inside the device, for example laptop.

Another classification is to divide modems into normal and voice.
Voice stocked connectors under headphones and microphone and allow to communicate in
mode " internet phone»Via the Internet.
According to the principle of work:
hardware - all signal conversion operations, support for physical
exchange protocols are made by a computer built into the modem (for example, with
using DSP controller). Also present in the hardware modem Rom, at
which recorded the firmware that controls the modem

Windows modems - hardware modems, devoid ROMwith firmware.
The firmware of such a modem is stored in the memory of the computer to which
A modem is connected. It works only with drivers, which are usually
were written exclusively for operating systems of the MS Windows family.
semi-software (Controller based soft-modem) - modems in which part of the functions
the modem is performed by the computer to which the modem is connected.
software(Host based soft-modem) - all signal coding operations,
error checking and protocol management are implemented in software and
produced by the central processor of the computer. In this case, the modem is
analog circuit and converters: ADC, DAC, interface controller (for example USB).
Type:
Analog - the most common type of modem for ordinary dial-up telephone lines
ISDN - modems for digital switched telephone lines
DSL - used to organize dedicated ( non-switcheda) lines using a regular telephone network. Difference from switched modems in signal coding. Usually, it is allowed to use the telephone line in the usual manner simultaneously with data exchange.
Cable - used to exchange data on specialized cables
- for example, on cables of collective television systems.
Radio
Satellite
Plc- use the technology of data transmission over household wires
electrical network, i.e. usually by wiring 220 volt.
More widely used now:
internal software modem
external hardware modem
embedded in laptops modems.
Composite devices
1. I / O ports - schemes intended for data exchange between
telephone line and modem on the one hand, and a modem and computer - with
other. To interact with analog telephone line is often used
transformer.
2. Signal processor (Digital Signal Processor, DSP). Normally modulates outgoing
signals and demodulates incoming digital level in accordance with
used by the data transfer protocol.
It contains software "filling" modem - firmware - BIOS.
It can also perform other functions.
3. The controller controls the exchange with the computer..
The controller is a special chip that accepts information,
passed through DSP Her appointment is data compression and error correction.
Codec (Digital-Analog Coder-Decoder). Translates digitalsignals (ready to
sending data) to analogand sends them over the phone lines. Data,
coming to your PCthrough the Internetpasses inverse transform and
after that it is transferred to the controller for processing and DSP processor.
4. Memory chips:
ROM - non-volatile memory in which the control firmware is stored
Modem - firmware, which includes a set of commands and data to control the modem, all supported communication protocols and an interface with a computer. Modem firmware update is available in most modern models, for which
serves a special procedure described in the user manual.
To enable flashing for storing firmware flash memory (EEPROM).
Flash memory makes it easy to update modem firmware, correcting errors
developers and expanding device capabilities. In some models of external modems, it is also used to record incoming voice and fax messages when the computer is turned off.
NVRAM - non-volatile electrically reprogrammable memory in which modem settings are stored. The user can change the settings, for example using the set AT commands.
Modem AT commands Huawei for Hiperterminal read
Ram— rAM modem, used for buffering received and transmitted data, operation of compression algorithms and others.
Types of modems
It should be recognized that the classical scheme described above is not used in all modems.
In cheap internal devices may be absent 1
or 2 chips.
Softmodem. In him missingcontroller chip, and its functions
shifted to the central processor. This is reflected only in a slight fall.
speeds but not in health modem.
Winmodem. In him dSP chip missingits functions are performed by
special BY, work oriented under Windows OS.
The advantage of the models described above is low price. They are used for household purposes,
but inferior in performance to full-fledged modems.
According to the protocol
Protocol - languagethrough which 2 modemsestablish a connection.
It determines the type and speed of information transfer.
1. V.34.Allows you to receive information at speeds up to 33,600 bits per second (bps);
2. V.90, x2 and k56flex.Support work with speed 57,600 bps The V.90 protocol is universal. x2 and k56flex are “private” developments of individual firms;
3. V.92.The protocol is adopted in 2000
However, the main thing for users not protocol, and the speed of reception and transmission of data.
Analog modems
cannot fully satisfy this need in contrast to abelian
modems. The minimum speed of work on the Internet - 28 800bit / s. V.90 protocol
theoretically allows you to work at speed 57,600 bpsbut reality does not justify it.
Recommendations for analog modems.
For sustainability and good quality the work of these models need additional
microcircuits and software
who are responsible for error correction and
regulation of the signal level.
Modemshould be connected directly to the telephone line in front of the phone, otherwise the connection
will break off.
Cable modemsdo not require the implementation of the above tips.
There are still modems with additional features, this-
Fax modem- allows the computer to which it is attached to, send and receive
fax images to another fax modem or regular fax machine.
Voice modem- has a function digitizing signal from the telephone line and play any sound in line. Some voice modems have built-in microphone. This allows you to: transmit voice messages in real time to another remote voice modem and receive messages from it and play them through the internal speaker; the use of such a modem in the answering machine mode and for the organization of voice mail.
How to configure the modem and the Internet read
How to set up Wi-Fi in Windows XP read
That's all I wanted to tell you about modems.
A strict classification of modems does not exist due to the diversity of both the modems themselves and the fields of application and their modes of operation. Conventionally, modems can be classified by design, scope, functionality, type of channel used, transmission method, intellectual capabilities, etc.
By design modems are divided into external, internal, portable, group.
External Modems are available in a separate package and have a built-in or remote power supply. Their advantages: the presence of the light indication on the front panel, and recently LCD, which makes it easy to determine its state; The controls are located on the front panel, which allows you to control the modem and change its configuration. On the rear panel of the modem are connectors for connecting to a power source, a computer’s serial port, a telephone line (LINE), and also for connecting a telephone set (PHONE). Modems are equipped with an internal loudspeaker, sometimes there is a volume control. Disadvantages of external modems: an additional outlet for the power supply is required, additional space on the desktop, foreign-made modems are sometimes designed to be connected to an electrical network with a voltage of 110-115 V, which requires replacement of the power supply.
Interior A modem is an expansion card that is inserted into the appropriate slot of the system bus of a computer motherboard. Such modems do not have their own power supply and receive power from the device in which they are installed. On the rear panel of the modems there are connectors for connecting a communication line and a telephone. Advantages: they do not need to be turned on / off, do not occupy standard COM ports of a computer, are cheaper than an external modem, etc. Disadvantages: the need for a free slot motherboard, an increase in the load on the power supply, the absence of an external indication, the complexity of the installation, and the restart of the entire computer when the modem hangs.
Portable Modems are designed for use with Notebook computers. This modem is similar to the external, only a reduced size. It has a stronger case and universal power (from the mains through an adapter, from a 12-volt car network and from an internal battery. Modems appeared that connect to a laptop computer through a special connector through which it also receives power. Disadvantages: such modems are much more expensive other modems with similar capabilities.
Group (rack) Modems are a collection of individual modems arranged in a common unit and having a common power supply, display and control devices. These are professional modems. And they are inserted not into the computer, but into a special modem rack, called the modem manager.
By scope Modems can be divided into several groups:
for dial-up telephone channels - such modems should be able to work with PBX, distinguish between their signals and transmit their dialing signals;
for dedicated (leased) channels;
for physical connecting lines (bandwidth is not limited to 3400 Hz and depends on cable type and length);
for digital transmission systems - connect to digital channelssuch as ISDN;
for cellular communication systems - they support special modulation and error correction protocols, which allow to efficiently transmit data in the conditions of cellular channels with a high level of interference and constantly changing parameters;
for packet radio networks, several radio modems use the same radio channel in the multiple access mode;
for local radio networks - such radio modems provide data transmission over short distances (up to 300 m) with high speed (2-10 Mbit / s), comparable to the transmission speed in wired local networks;
cable modems — used to transmit channels cable tv; transmission speed can reach 10 Mbps.
Consider the types of modems by function.
Fax modems. To increase the functionality of a classic modem, fax exchange with fax machines and other fax modems is almost always added. Virtues fax modems:
1. saving thermal paper
2. The message file is slightly better read than the fax,
3. sending a fax using a modem is faster
4. you can program the sending of several faxes at a specified time,
5. incoming documents are more convenient to process as files.
Voice modems (VOX) run as an extension to fax modems. These modems receive voice messages from the telephone network, recording them as a computer file, and also play previously formed voice files into the telephone network. The file can be output to the computer speaker, to a separate handset connected to the modem or to the handset of a telephone set, if you use a special switch.
Svd modemsallow you to transfer data and simultaneously carry on a conversation using a handset connected to a modem, and in duplex mode.
Speed Modems -these are SR modems and cable modems. They use completely different transmission protocols than on telephone lines. SR-modems They are used for data transmission over short distances, i.e., when it is possible to connect two terminal devices with a direct cable and there is no need to "squeeze" into the standard width of the telephone channel. This allows you to increase data transfer speeds up to 80 kbps over a distance of 15 km, and for good twisted-pair cable and shorter distances, the speed can go up to 2 Mbps. Cable modems Cable channels are used for transmission (transmission speed reaches 10 Mbps).
Radio modems instead of telephone wires, they use radio as the medium for transmitting information. In them, instead of a telephone connector, there is an antenna connector where the antenna is inserted. It is the same as the classic modem: it connects to a computer through a standard RS-232 interface. A whip antenna (up to 30 cm) is connected to the antenna connector, or if a longer range is needed - antenna cable, amplifier and directional antenna. In addition, the radio modem contains a radio transceiver. They are used in cases when laying a telephone or cable line is difficult. The main difference between radio modems is that they are oriented to work in a single radio channel with many users, and not in a point-to-point channel.
Cell modems used for mobile cellular radiotelephony. They do not contain transceivers in their composition, but use transceivers included in a cell phone, transmitting their signals to them. The speed of data transmission and facsimile information in such a radio channel is up to 14.4 kbps (without their compression). These modems are portable and are housed in a rugged case. They are used on noisy and unstable lines: satellite, rural and intercity.
By transfer methodmodems are divided into asynchronous and synchronous. Transmission via the DTE-DCE interface can be synchronous and asynchronous. The modem can work with the computer in asynchronous mode and simultaneously with the remote modem - in synchronous mode and vice versa. Then we can say that the modem works in synchronous-asynchronous mode. Most often, synchronization is implemented in one of two ways, related to how the clock generators of the sender and receiver work: independently from each other (asynchronously) or consistently (synchronously).
Asynchronous transfer mode it is used when the transmitted data is generated at random times (by the user). In this case, the receiving device must restore synchronization at the beginning of each received symbol. To do this, each transmitted character is supplied with an additional start and one or more stop bits.
With synchronous transfer method A large number of characters or bytes are combined into separate blocks or frames. The entire frame is transmitted as one chain of bits without any delay between eight-bit elements. In order for a receiving device to provide different levels of synchronization, the following requirements must be met:
the transmitted sequence must not contain long sequences of zeros and ones, so that the device can allocate clock frequency sync.
each frame must have reserved sequences of bits or characters that mark its beginning and end.
On intellectual possibilities modemsare:
without control system;
supporting a set of AT commands; (allows the user to control the characteristics of the modem and communication parameters).
with support for V.25bis commands; (allows you to control the connection and autoplay modes).
with a proprietary command system; (specialized industrial modems).
supporting network layer protocols; (allow the administrator to manage network elements and modems from a remote terminal).
Questions
The main functions and types of modems.
Data transfer protocols.
Hardware external and internal modems.
Goals and objectives of studying the topic:getting an idea of signal conversion devices - modems, analog and digital modems, modem communication protocols, modem design.
Having studied the topic, the student should:
know the concept and essence of modulation and demodulation, analog and digital modems, modem communication protocols, modem design
have an idea of modems as negotiation devices digital signals computer with analog telephone line signals, modem communication protocols, as a set of rules and procedures for data transmission in a communication channel, compression protocols and error correction during data transmission.
Studying the topic, you need to focus on the following concepts: modem, modulation and demodulation, analog and digital modem, asynchronous and synchronous modem, modem communication protocols, modem design.
7.1. Basic Functions and Modem Types
When computers are located far from each other and cannot be connected with a standard network cable, the connection between them is established using signal conversion devices. The UPS transforms the signals from the terminal equipment into a form suitable for their transmission over the used communication channels, and vice versa, the signals coming through the communication channel convert them to the form perceived by the terminal equipment. Models are usually used as UPSs. In a networked environment, modems serve as a means of communication between individual networks or LANs and the individual world.
Modem Is a device of direct (modulator) and reverse (demodulation) signal conversion, to the form adopted for use in a particular communication channel.
Modulation–Change any parameter of the signal in the communication channel (modulated signal) in accordance with the current values of the transmitted data (modulating signal).
Demodulation - is the inverse transform of the modulated signal into a modulating signal.
The modem performs the functions of data termination equipment. In the quality of the equipment in the communication channel is usually a computer in which there is a transmitter. The transceiver is connected to the modem via one of the serial ports of the computer and the RS-232C serial interface, which provides a speed of at least 9.6 kbit / s over a distance of 15 km. Exist different types modems, since each type of transfer rate requires different data transfer methods, but first of all they can be divided into:
analog;
digital.
Analog modems
Uhthese are currently the most common modems. They are used to transmit information over analog communication lines.
Taking the synchronization of communication as a criterion, modems can be divided into:
Asynchronous;
synchronous.
Depending on which modulation type is used in the modem, there are modems with:
frequency modulation;
phase modulation;
quadrature amplitude modulation.
With frequency modulation In accordance with the current values of the modeling signal, the frequency of the physical signal changes at a constant amplitude. In the simplest case, the values of 1 and 0 data bits correspond to two frequencies, for example, 980 and 1180 Hz, as was the case in one of the first V.21 data transfer protocols. Frequency modulation is very noise-resistant, because only a signal amplitude is distorted during transmission.
With phase modulation the modulated parameter is the phase of the signal at constant frequency and amplitude; the noise immunity of the phase-modulated signal is also stable.
With quadrature amplitude modulation both the phase and the amplitude of the signal change simultaneously with the transmitted data.
Asynchronous communication - The most common form of data transfer. The reason for this popularity is that the asynchronous communication method uses standard telephone lines.
With the asynchronous method, data is transmitted in sequential streams.
Each character — a letter, number, or character — is decomposed into a sequence of bits. Each of these sequences is separated from each other by the start and stop bits. The receiving computer uses the start and stop bits to control synchronization, thereby preparing to receive the next byte of data.
This type of communication is not synchronized. The sending computer simply transfers the data, and the receiving computer checks the data to make sure that they are received without errors. With asynchronous communication, the control information is about 25% of the transmitted data.
For error control during asynchronous communication, a special bit is used - the parity bit. The check and error correction scheme that accepts it is called parity. In parity checking, the number of unit bits sent and received must match.
Synchronous communicationbased on synchronization scheme agreed between devices. Its purpose is to select bits from the group when transmitted by blocks. These blocks are called frames. Special characters are used for synchronization. The transfer ends at the end of one frame and begins again at the next frame.
This method is more efficient than asynchronous transfer. In case of an error, the synchronous recognition and error correction scheme simply repeats the frame transmission.
Digital modems
Developing digital data transmission technologies that provide significantly higher transmission speeds and quality of communication, providing users with significantly better service, require the use of modems of a different class — digital. Digital modems can be more properly called network adapters, because of classical modulation — there is no signal demodulation — the input and output signals of such a modem are pulses. For digital modems generally accepted standards of work in general, and speed standards in particular, has not yet been developed.
Digital modems are used only in digital communication systems. They provide much higher transmission speeds and communication quality. When working with digital lines, a synchronous modem is used, and not asynchronous.
Digital modems are available to work in specific digital technologies:
cable modems to work with networks through switching cable television;
cellular modems to work in a cellular telephone system;
fiber optic modems for work on fiber-optic communication channels;
satellite radio modems to receive data via satellite;
power modems for work in networks through the power supply system of computers.
NETWORK CARDS
Instead of a modem in local networks You can use network adapters (network cards). Made in the form of expansion cards that are installed in the connector of the motherboard.
Network adapters can be divided into two groups:
adapters for client computers;
adapters for servers.
In adapters for client computers, much of the work of receiving and transmitting messages is switched to a program running on a PC. Such an adapter is simpler and cheaper, but it additionally loads the central microprocessor of the machine.
Adapters for servers are equipped with their own processors that perform all the necessary work.
The following devices are used as interface devices for a computer with data transmission equipment and with terminal devices:
line adapters;
data transmission multiplexers;
connected processors.
Today, our everyday speech includes a lot of technical terms, the meaning of which people, far from the problems associated with electronic technologies, sometimes do not understand well.
One of these concepts is a modem, a device that you may have, or you need in order to have it all the time. Let's see what a modem is and how it works.
The word "modem" is an abbreviation, or acronym, formed from two words: "Modulator-DEMODulator", which describe the functions of the device in a language understandable to specialists. That is, with the help of a modem, the electrical signal going in one direction is modulated, and the incoming signal is demodulated, and thus the computer is connected to the Internet.
Modems today are widely used in various fields of activity where an accurate and often secure data transmission system is needed. Everyone knows, in addition to computer, telephone modems. These devices are used in military affairs, providing communication command centers with tracking devices, military units, etc.
In fact, any modem is a device that converts a computer binary code into analog voltage fluctuations (in a telephone modem) or in radio waves (in a modem wireless connectivity), if your computer sends a packet of data, and the reverse transformation - if it receives data from the server. This allows to provide high accuracy of data transmission and communication quality, since the digitized signal is transmitted with much less noise than analog.
By design, modems are:
External - in a separate case, with its own power supply and connecting to a computer via a COM port;
Built-in - representing a board located inside the computer;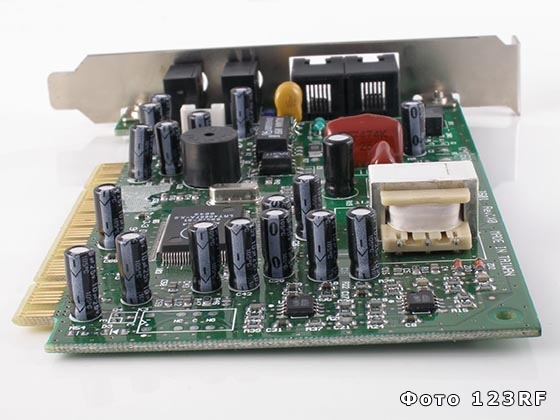 
- software, or card - having only a signal conversion device, and its processing is performed by a computer processor. These modems are connected via USB input.
By the principle of data transmission today there are several of the most common types of modems.
1. A telephone or Dial-up modem transmits information to the Internet using a wired telephone line, and at the time of transmission the telephone signal cannot be transmitted.
2. The ADSL modem transmits information over the telephone wire, but does not interfere with the passage of telephone signals.
3. USB modem - small external deviceconnected via uSB port and transmitting information using cellular networks.
4. 3G-modem - today provides the fastest mass data exchange using 3G technology. In order for a 3G modem to be used, a 3G cellular system is required.
Experts advise: if you lost your internet connection via a modem, you need to consistently perform the following steps:
1. Check if the modem is connected to the computer.
2. Check if there is a network receive signal.
3. Check if there is enough money in the account to pay for the Internet connection.
4. If all of the above items are met, and the reason for the lack of a signal is not found, you should call the provider and report the problem. Often, it can be eliminated without the departure of a technician, by changing the modem settings.
Quite often non-specialists confuse modem with router, however it’s different devices. If the modem is used to convert the passing signal, then the router is needed to distribute the incoming signal to several devices. 
Part modern routers both the modem and the router are included, so the router is a modem of complicated construction. It receives a signal from the server, sorts it and sends it to computers, tablets or phones connected to it, to each device a data packet intended for it.
Using a router, we have the ability to connect to the same Internet cable several different computers and work on each one offline.