Accounting software receipts. Cost accounting software
We bought work program (non-exclusive rights) for estimators (our MUP provides services for the production of estimates), for 2 jobs, costs 77 TR, including: the cost of software components is 24.0 TR; the cost of the database components is 44.0 tr., the cost of the protection keys (in the contract are goods), the rest is the services for the departure of a specialist. Question: to credit as bps? One amount of 24 + 44? Do they account for expenses of the simplified taxation system?
Answer
In accounting, the cost of software components and databases must be considered as part of future expenses. If in the documents for the program the cost of the program and the databases are indicated separately, then they should be taken into account in two separate amounts. When this is done the wiring:
Debit 97 Credit 60 (76) - fixed one-time payment for using a computer program;
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 44 ...) Credit 97 - expenses for the purchase of a computer program are written off.
In tax accounting, the costs of purchasing the program are taken into account at the time of payment.
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbuch System.
Use Rights
If an organization has acquired the right to use a computer program under a license agreement (non-exclusive right, license), then this right may be exclusive or non-exclusive.
If the organization has been granted an exclusive license, it is the only one who uses a computer program within the framework of the rights transferred to it. For example, a program for management accounting has been developed for the organization. Under the contract, the organization has exclusive rights to use the program in its business activities, and the developer has exclusive rights to it. In such a situation, the developer does not have the right to provide a computer program for others to use, and the organization has no right to manage the computer program in a way other than using it in its activities.
However, the program can be used under a simple (non-exclusive) license. Then the original owner of the program retains the right to enter into license agreements with other organizations.
This procedure follows from the articles and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Program accounting is not part of IA
If the conditions on the recognition of a computer program as part of intangible assets are not met, and also if it is received for use under a licensing agreement, reflect the cost of its acquisition in the composition:
- expenses of future periods, if a fixed amount is established for the use of a computer program, which is transferred at a time; *
- current expenses, if for the use of a computer program periodic payments are listed. For example, the monthly payment amount depends on the number of copies of the computer program sold.
In accounting, make the following entries:
Debit 97 Credit 60 (76)
- fixed one-time payment for using a computer program; *
Debit (20, 23, 25, 26, 44 ...) Credit 60 (76)
- periodic payments for the use of a computer program are taken into account.
After putting the computer program into operation, the expenses for its acquisition, which are considered as expenses of the future periods, shall be written off. The procedure for writing off expenses related to several reporting periods is determined by the organization independently. For example, a one-time one-time payment for using a computer program can be charged by an organization at regular intervals during the period approved by the manager. The applied option of write-off of expenses of future periods (Clause and PBU 1/2008). Write off the cost of acquiring a computer program, recorded as expenses for future periods, reflect the postings: *
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 44 ...) Credit 97
- written off expenses for the purchase of a computer program. *
Glavbukh advises: in accounting policies for accounting purposes, fix the same procedure for writing off expenses relating to several reporting periods, as well as in tax accounting. In this case, accounting organizations will not arise.
In addition, if the organization transferred the rights to use a computer program (under a license agreement), it is recognized as an intangible asset obtained for use. Such a computer program note on the off-balance account. This is stated in PBU 14/2007. The chart of accounts does not provide for a separate off-balance sheet account for accounting for intangible assets received for use. Therefore, the organization must independently open an off-balance account and fix it in accounting policies for accounting purposes. For example, it could be account 012 “Intangible assets acquired for use”:
Debit 012 "Intangible assets received for use"
- the cost of rights to a computer program received for use (on the basis of a license agreement) has been taken into account. *
Sergey Razgulin,
If the organization has chosen the object of taxation income, the cost of purchasing a computer program does not affect the single tax. With this object of taxation do not take into account any costs ().
If an organization pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses, the cost of purchasing a computer program reduces the tax base in the following order.
If an organization acquires exclusive rights to computer programs or the rights to use them under a license agreement, then write down such expenses at a time (, NK RF).
An example of reflection in accounting and taxation of expenses for the acquisition of non-exclusive rights to a computer program. The organization applies the simplified text. Single tax pays on the difference between income and expenses *
In April of this year, CJSC Alfa acquired a copy of a computer program for bookkeeping at a price of 24,000 rubles. (under license agreement). Exclusive rights to the organization’s computer program are not owned. In May, the program was paid for and installed on the accountant’s computer.
The cost of acquiring a computer program refers to several reporting periods. According to the accounting policy in accounting, such expenses are written off evenly during the period approved by the order of the head of the organization. The period for writing off expenses for the purchase of a computer program by the order of the head of the organization is set to 12 months (the term of the license agreement).
The accountant "Alpha" made the following entries in the account.
In April:
Debit 97 Credit 60
- 24 000 rubles. - included the cost of purchasing a computer program.
Debit 60 Credit 51
- 24 000 rubles. - paid for a computer program.
From May of this year to April of the following year, the accountant reflected in the accounting for the write-off of the cost of a computer program by posting:
Debit 26 Credit 97
- 2000 rub. (24 000 rub.: 12 months) - the cost of the computer program is written off.
When calculating the single tax, the accountant took into account the cost of purchasing a computer program in the amount of 24,000 rubles. in May.
The costs associated with the acquisition of non-exclusive rights to computer programs (under licensing agreements), as well as the costs associated with updating programs, write off one-time (, NK RF). *
If an organization acquires a computer program with a computer, the cost of the program from the cost of the computer is not necessary to allocate. If the computer is purchased without minimum software, the cost of purchasing and installing such programs should be included in the original cost of the computer as the cost of bringing it to a usable condition (, RF TC). Such explanations are contained in the letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia,. Despite the fact that these letters relate to the general system of taxation, they may also be guided by organizations in the simplified textbook ().
Sergey Razgulin,
acting State Counselor of the Russian Federation 3rd Class
* So highlighted part of the material that will help you make the right decision.
Software is an integral attribute of any enterprise, because it is software that ensures the full functioning of not only computer equipment, but also some types of production equipment. In the article, we will use examples to consider the specifics of accounting for non-exclusive software rights.
In modern practice, the most common way to use software is to issue non-exclusive rights to an object of intellectual property. The transfer of rights is executed by a license agreement, according to which the copyright holder transfers to the licensee the right to use the software. The terms of such an agreement stipulate that an organization receives a non-exclusive right to use the program, that is, the copyright holder can transfer the right to the software of any other organization.
In accounting, non-exclusive rights to software obtained under a license agreement are not recognized as IA objects.
Accounting software required for the operation of the OS
A number of fixed assets cannot function without appropriate software (for example, computer operating systems). In such cases, the cost of the purchase of non-exclusive rights to the software are reflected in the costs associated with bringing the asset to a condition that is usable.
Purchase of software with equipment
Producer LLC acquired production equipment at a price of 651,000 rubles, VAT 99,305 rubles. with a useful life of 18 months. The equipment operates with the help of special software, the acquisition of non-exclusive rights to which was issued by a license agreement. The cost of the rights to the software under the contract is 34,500 rubles, VAT 5,263 rubles. Hardware and software is accounted for as a single entity.
The accountant of Producer LLC reflected these operations in the following way:
| Dt | Ct | Description | Amount | Document |
| 08/4 | 60 | Received equipment from the supplier (651,000 rubles. - 99,305 rubles.) | 551 695 rub. | Packing list |
| 19 | 60 | Reflected in the accounting of VAT on the cost of equipment | 99 305 rub. | Packing list |
| 08/4 | 60 | Reflected in accounting software receipt (34 500 rubles. - 5 263 rubles.) | 237 rub. | License agreement |
| 19 | 60 | Reflected in VAT accounting of the cost of non-exclusive rights to software | 5 263 rub. | License agreement |
| 68 VAT | 19 | VAT deductible (RUB 99,305 + RUB 5,263) | 104 568 rub. | Invoice |
| 01 | 08/4 | (551 695 rub. + 237 rub.) | 580 932 rub. | The act of commissioning the OS |
| 02 | Accrued monthly depreciation amount (580 932 rubles / 18 months) | 32 274 rub. | Depreciation statement |
Reflecting the cost of repairing and reinstalling software
LLC "Aegis" uses the 1C system for accounting. The non-exclusive right to 1C is executed by a license agreement. 10/02/2015 software failed due to a breakdown. .2015 the breakdown was fixed:
1C restoration costs - 74,000 rubles, VAT 288 rubles;
costs of reinstallation - 12,400 rubles, VAT 1,892 rubles.
In the account of LLC "Aegis" the following transactions were made:
Purchase of antivirus software
In order to ensure information security, Ryabina LLC acquired antivirus software. The license agreement provides for the provision of non-exclusive rights to the antivirus for a period of 5 years. One-time payment under the contract is 24,500 rubles, VAT is 3,737 rubles, monthly payments for software maintenance are 1,240 rubles, VAT is 184 rubles.
In the account of the company "Ryabina" the following transactions were made:
| Dt | Ct | Description | Amount | Document |
| 012 | Takes into account the cost of non-exclusive rights to the object of intellectual property (antivirus software) | 24 500 rub. | License agreement | |
| 97 | 60 | Reflects a one-time payment for the right to use the software (24,500 rubles - 3,737 rubles) | 20 763 rub. | License agreement |
| 20 | 60 | Reflects the amount of the monthly payment for software maintenance services (1240 rubles - 184 rubles) | 1 056 rub. | License agreement |
| 19 | 60 | Reflects the amount of VAT under the license agreement (3737 rubles. + 184 rubles.) | 3 921 rub. | Invoice |
| 20 | 97 | Reflects the monthly amount of expenses for the right to use the object of intellectual property (20 763 rubles / 5 years * 12 months) | 346 rub. | License agreement |
To operate a computer, one or another operating system is needed (MSDOS, Unix, Windows, Vista). In almost all cases, the budget (autonomous) institution does not receive exclusive rights for such programs. They remain with the developer. Consider cost accounting software.
Licensed software can be supplied in two versions:
- OEM version (provided with the computer as a pre-installed version);
- "boxed" version (set by the user independently, for example, from a disk).
The main distinctive feature of the OEM version is that, under the terms of the license, they cannot be transferred to another personal computer. In this case, the OEM version of the software installed on a specific computer cannot function separately from it (it represents a single entity with it). Therefore, the cost of such software should be included by the institution in the original cost of the asset acquired.
Expert opinion
In accordance with paragraph 47 of the “Instructions for the use of a single chart of accounts of accounting ...” approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01.12.2010 N 157n, in order to determine the initial value of the asset of the fixed asset when it is purchased for a fee, actual investments are formed not only from sums paid in accordance with the contract to the supplier (seller), but also other expenses of the institution related to the acquisition (creation, manufacture) of the asset.
At the same time, experts of authorized bodies, explaining the issues of taxation of profits (see the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 25, 2009 No. 03-03-06 / 2/105, letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 13, 2011 No. KE-4-3 / 7756, dated 29.11. 2010 N ShS-17-3 / 1835), note the following:
- the operation of computer technology is to use specific properties of material objects in order to ensure that an organization uses in production or management of consumer qualities of certain software products;
- if computer equipment is acquired without any minimal software, then a material object cannot be used in any way. In this case, the cost of acquiring rights to the necessary software is the cost of bringing the object to a usable state. Such software is an integral part of the hardware;
- in the case of the acquisition in the organization of trade of computer equipment with the appropriate software that allows you to implement the consumer properties of this computer technology publicly declared by the seller, the allocation of the cost of such software from the cost of technology is not required;
- if, when purchasing a fixed asset with a program, the license agreement for the program does not provide for payment of remuneration to the right holder in the form of periodic payments, the amount of such remuneration is included in the original cost of the acquired fixed assets and is written off through the depreciation mechanism.
The above arguments, in our opinion, can be taken into account and the budget institution for accounting purposes. Moreover, such an approach essentially corresponds to the provisions of the International Public Sector Accounting Standards (IPSAS), the content of which is taken as a basis for reforming public sector accounting in the Russian Federation (see, in particular, paragraph 14 of IPSAS 17 " Real estate, buildings and equipment, paragraph 7 of IPPAS (IPSAS 31, Intangible Assets). Thus, software pre-installed on the server or computer purchased by the institution and being an integral part of such a carrier (fixed asset) must be included in its original cost.
A. Semenyuk, an expert of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT; V. Pimenov, reviewer of the service of legal consulting GARANT
The “boxed” version of the software can be installed on any other computer or purchased separately from it. Therefore, the cost of its acquisition can be taken into account in future expenses (the corresponding analytical accounts of the account 0 401 50 000 "Expenses of future periods") with subsequent inclusion in the expenses of the current year in the manner prescribed by the accounting policies of the institution (paragraph 66 of the Instructions for use of the Unified Plan). accounting records for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, government bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state governmental (municipal) institutions, approved. by order of the Russian Finance Ministry of 01.12.2010 number 157n)). They are reflected in the article 226 "Other expenses" of KOSGU. In addition, the cost of such a version is reflected on off-balance account 01 “Property acquired for use” in the valuation reflected in the purchase and sale agreement. Similarly, purchase costs should be reflected. additional programspurchased for computer facilities of an institution (for example Microsoft Office, Nero, Outlook Express, Mozilla thunderbird, Opera, etc.).
EXAMPLE
At the expense of a subsidy for the implementation of a government job, the institution acquired a computer. The equipment will be used in the main activity of the institution, which is not subject to VAT. The cost of a computer was 53,100 rubles. (including VAT - 8100 rubles.). It belongs to especially valuable property. In addition, the institution purchased the operating room. windows system Xp. Its cost is 2714 rubles. (including VAT - 414 rubles.). Under the contract with the supplier, the pre-installed operating system is paid for by the institution separately. After the computer was commissioned, the institution acquired additional software - Microsoft Office. The cost of its purchase amounted to 3776 rubles. (including VAT - 576 rubles.).
To simplify the example, the procedure for off-balance accounting of funds of the institution is not given.
Situation 1
Institution acquired OEM version operating system and the "boxed" version of additional software. Operations on the purchase of equipment and programs will be reflected in the accounting records:
DEBIT 4 106 21 310 CREDIT 4 302 26 730
- 2714 rubles. - the costs of obtaining the right to use the operating system and accounts payable to the supplier (including “input” VAT) are taken into account;
- 2714 rubles. - services on granting the right to use the operating system from the personal account of the institution in the treasury were paid;
The initial cost of the computer will be:
53,100 + 2714 = 55,814 rubles.
When you include the purchased property in the composition of fixed assets in the account make an entry:
- 55 814 rubles. - The purchased computer is included in the fixed assets of the institution.
The cost of additional software will be reflected in the records:
- 3776 rubles. - included the cost of purchasing additional software;
DEBIT 4 302 26 830 CREDIT 4 201 11 610
- 3776 rubles. - services paid for granting the right to use additional software from the personal account of the institution in the treasury;
DEBET 01
- 3776 rubles. - the increase in off-balance account 01 is reflected in the amount of expenses for payment of the right to use additional software.
Subsequently, the cost of purchasing additional software in the amount of 3776 rubles. included in the expenses of the current fiscal year in the manner prescribed by the accounting policies of the institution.
Situation 2
The agency purchased a "boxed" version of both the operating system and additional software. Operations on the purchase of equipment and programs will be reflected in the accounting records:
DEBIT 4 106 21 310 CREDIT 4 302 31 730
- 53,100 rubles. - taken into account the cost of acquiring a computer and payables to the supplier (including the "input" VAT);
DEBIT 4 302 31 830 CREDIT 4 201 11 610
- 53,100 rubles. - computer paid from the personal account of the institution in the treasury;
DEBIT 4 101 24 310 CREDIT 4 106 21 310
- 53,100 rubles. - the purchased computer is included in the fixed assets of the institution;
DEBIT 4 401 50 226 CREDIT 4 302 26 730
- 6490 rubles. (2714 + 3776) - expenses for the acquisition of the right to use the software and accounts payable to the supplier (including “input” VAT) are taken into account;
DEBIT 4 302 26 830 CREDIT 4 201 11 610
- 6490 rubles. - paid services to provide the right to use the software from the personal account of the institution in the treasury.
DEBET 01
- 6490 rubles. - the increase in off-balance account 01 is reflected in the amount of expenses for payment of the right to use the software.
Subsequently, the cost of acquiring software in the amount of 6490 rubles. included in the expenses of the current fiscal year in the manner prescribed by the accounting policies of the institution.
The software necessary for work of the technician, can fail. In such a situation, the cost of its restoration and reinstallation may be regarded as the cost of repairing the asset (in Substate 225 "Works, property maintenance services" of the KOSGU). They are reflected in the current expenses of the institution.
EXAMPLE
The facility uses the water supply system included in the OS. It is used in the main activities of the organization, not subject to VAT. The system cannot function without special software. As a result of a breakdown, it failed. The cost of services for its restoration, provided by an outside organization, were:
59 000 rub. (including VAT - 9000 rubles.) - the cost of restoration;
26 550 rub. (Including VAT - 4050 rubles.) - The cost of reinstalling.
These costs are paid by subsidies for the implementation of goszadaniya. To simplify the example, the procedure for off-balance accounting of funds of the institution is not given.
The cost of restoring the system will be reflected in the records of the institution records:
- 59 000 rub. - expenses for payment of services of a third-party software recovery organization (including “input” VAT) are taken into account;
DEBIT 4 109 60 225 (4 109 70 225, 4 109 80 225 ...) CREDIT 4 302 25 730
- 26 500 rub. - expenses for payment of services of a third-party organization for software reinstallation (including “input” VAT) are taken into account;
DEBIT 4 302 25 830 CREDIT 4 201 11 610
- 85 500 rub. (59 000 + 26 500) - paid for the restoration and reinstallation of software from the personal account of the institution in the treasury.
The software complex 1C is used by almost all accountants to keep financial records of their enterprises. This is a very powerful and convenient complex, which includes many programs specially adapted for use in enterprises and companies engaged in various activities. There are versions for trade, industrial, building, agricultural, educational, budgetary, municipal and many other institutions and companies.
Posting programs in 1C is different from the reflection of the purchase of ordinary goods.
Since the program is complex and not the easiest, even the most experienced accountant may not be able to understand the technical intricacies of making certain operations for their accounting in financial records. In this article we will consider how the purchase of software 1C should be correctly reflected in the menu of the program itself. That is, you and we will learn in the program menu to indicate that it was purchased for use in the enterprise. This is very important, because if this is not done, or done incorrectly, problems may arise when checking the financial records of your activities.
Be warned immediately that our goal is to show the process from a technical point of view so that you know what and where to click. We will not delve into the subtleties of accounting, there are other specialized resources for this.
Brief legal information
Let's start with a brief legal note. According to Russian law, software belongs to an intangible asset. But, in the case of 1C, the program is an intangible asset only for the company 1C, which developed it and benefits from its sale. Since the company that acquired the license did not acquire the right to distribute and does not benefit from this material gain, the purchase operation of this software cannot be reflected as an acquisition of intangible assets.
By purchasing the 1C program, you acquire the non-exclusive right to use the product of intellectual activity. That is, your rights are limited, as the license only allows you to use the software on a certain number of computers without the right to change the program code and receive additional profits from resale or other operations. Accordingly, in order to reflect the posting of the program, you need to specify the procedure as other services related to production.
Another point worth mentioning is the period during which the cost of the purchase of intangible rights will be taken into account. According to the law, there are several options for such accounting. If the term is not specified in the contract, the owner either chooses such a period independently, or any unlimited contracts are considered to be concluded for a period of five years. We will not recommend you which option is better, for this consult with lawyers or more experienced fellow accountants. In one of the letters, 1C recommended that the term of the contract be two years.
After a short legal derogation, consider how the procedure takes place from the technical side. The whole process will be considered on latest version 1C: Accounting 8. If you use previous versionThe procedure may vary.
The reflection of the purchase program
To enter the data correctly, you should have the following documents:
- License agreement.
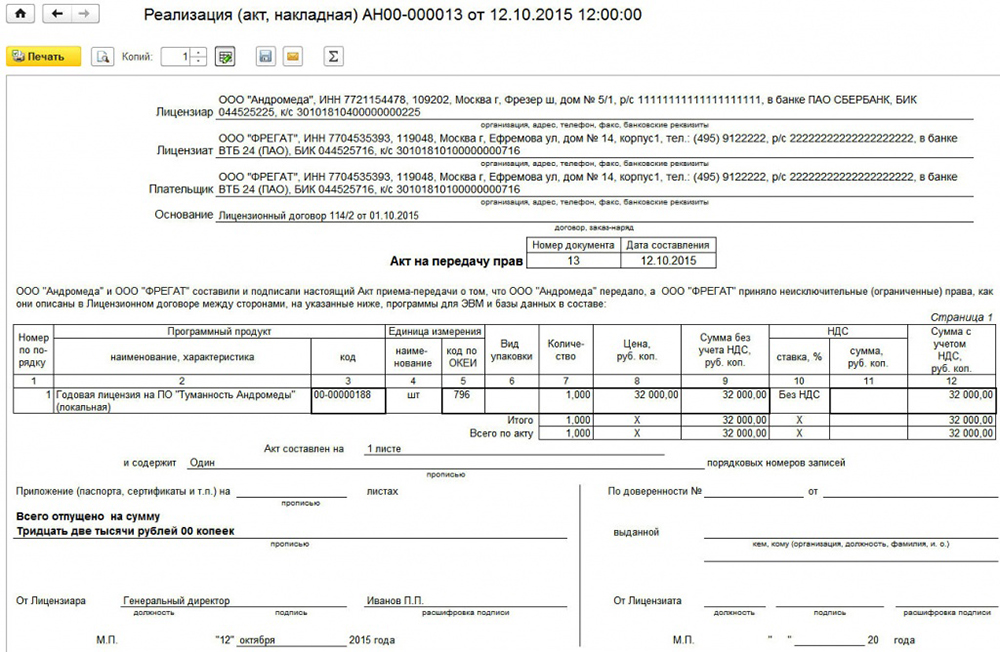
- The act of acceptance and transfer of rights to use the software.
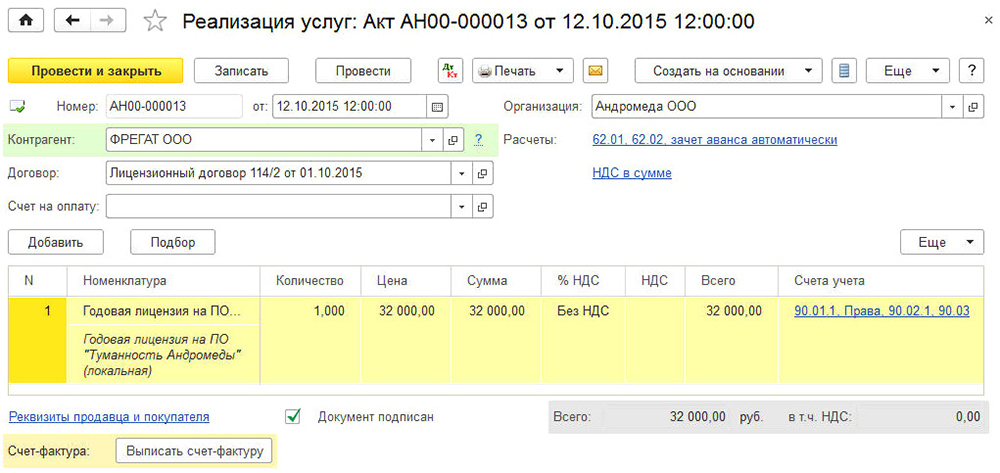
For example, you bought the program 1C and one-time transferred to the seller’s account the amount of 13 thousand rubles. You need to specify and configure such operations and payments:
- Directly purchase software.
- Write-off of expenses for future periods.
It will be more convenient to first create the expense of the future period, and only then - the purchase of the program. Let's get started
- Launch the main menu of the program by logging into it under your account.
- On the right side of the screen, select in the menu Directories - Deferred expenses - Create. In the form that opens, you will need to fill in the correct data.
- Indicate the following indicators:
- Name - enter the name of your regular expense, for example, 1C: Accounting 8.
- Group - can be left empty.
- View for NU - Other (select from the list).
- Type of asset in the balance sheet - Other current assets (select from the list).
- Amount - enter the amount of the purchase, for example, 13,000 rubles.
- Recognition of expenses - by month.
- The period of cancellation - the first date, specify when you bought the product, and the second - the end of the contract. For example, you bought the program on 02/17/2017 with a contract validity period of two years. That means you need to specify 02/17/2019.
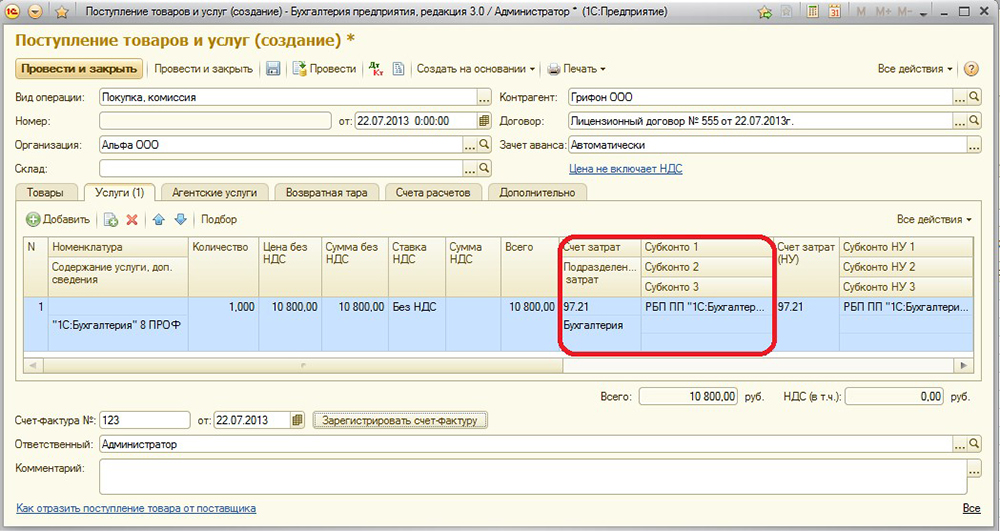
- The cost account is 26. Click on the icon of the drop-down list - Show all, enter 26 in the search field, highlight the desired item with the cursor, click the "Select" button in the upper part of the window.
- Cost Items - Read Costs. Choose the same way as the expense account.
- Confirm your entry by clicking “Record and close”.
- In the side menu, go to Shopping - Receipt (acts, invoices) - the "Receipt" button with a green plus - Services (act).
- Specify the following data:
- Act № from - enter the data specified in the act of reception and transmission of rights to use the software obtained during the transaction.
- Do not fill in the number, as it is calculated by the program automatically, and specify only the date. You can choose the same as in the act.
- Organization - select the name of the company in whose name the contract was executed.
- Counterparty - the name of the company with which you entered into an agreement reflecting the purchase of rights to use. First you need to create it. Click on the list icon and click on the green plus sign. Enter the name of the company, if it is in the register of enterprises, all data will be entered automatically. Otherwise, add all the information manually. Confirm your entry with the “Record and close” button.
- Contract - in the list of available, click the green plus, in the window that opens, enter the type, number, date and name of the contract, specify the organization and the counterparty.
- Fill in the table with the details:
- click the Add button, then you will see the fields in the Nomenclature column become active.
- Click on the bottom field “Service Content”, enter the name of the program, for example, 1С: Accounting 8.
- In the next column, specify the price of 13,000 rubles.
- In the last column indicate the account of the account - 97.21 - click on the link in the form of red arrows.
- In the opened window in the “Cost Account” line click on the drop-down list - Show all - enter 97 in the search - select 97.21 “Other expenses for future periods” - click “Select” in the top menu bar.
- In the line “Future expenses”, select the one you created at the very beginning (steps 2–4).
- In the line Cost Division - “Main costs”.
- Information about calculations will appear in the menu for adding an act, which is automatically displayed by the program. If you wish, you can change them, but if everything suits you, finish by entering with the button “Post and close”.
- In the future, every month, when it is closed, there will be an automatic accounting of funds for the right to use the program. The first month will take into account the number of days, and in the future the amount will be divided into equal parts.