User Account Management. Correction of user and group configuration files. Password expiration
In one of my articles I already wrote that you can add and change the properties of user accounts through the “Control Panel” - “User Accounts”. but this method more suitable for ordinary users. But the system administrator will be more convenient to manage accounts through the console "Computer Management" - "Local users and groups."
To get to the “Computer Management” console, right-click on the “My Computer” icon on the desktop and select “Management”. Next, expand the “Utilities” section and select “Local users and groups”.
The snap-in “” is designed to create new users and groups, manage accounts, assign tasks and reset user passwords. 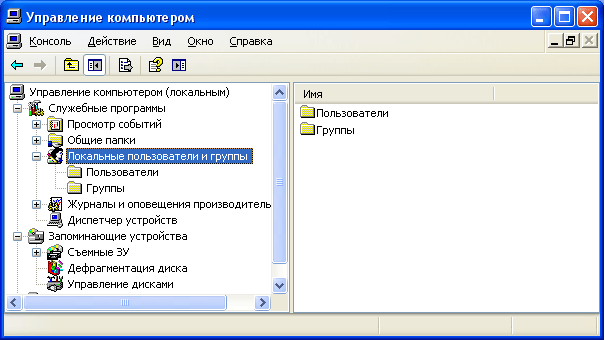 Local user
- This is an account that can be granted certain permissions and rights on your computer. The account always has its name and password (the password may be empty). You can also hear a different user account name - accountt
, and instead of “username” often say login
.
Local user
- This is an account that can be granted certain permissions and rights on your computer. The account always has its name and password (the password may be empty). You can also hear a different user account name - accountt
, and instead of “username” often say login
.
The “Local Users and Groups” snap-in node displays a list of user accounts: embedded accounts (for example, “Administrator” and “Guest”), as well as the accounts you have created for real PC users. 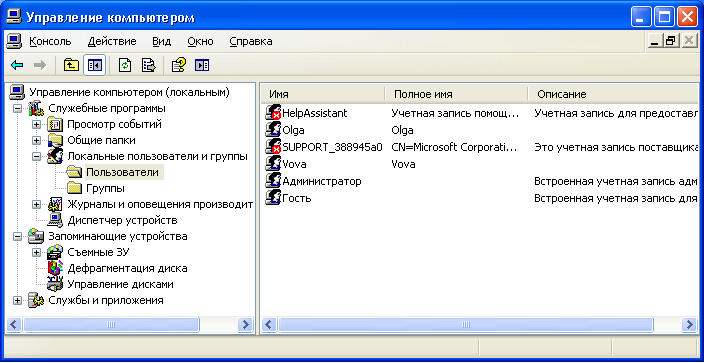 Built-in user accounts are created automatically when installing windows and can not be deleted. When creating a new user, you will need to give him a name and password (preferably), as well as determine which group he will belong to. new user. Each user can belong to one or several groups.
Built-in user accounts are created automatically when installing windows and can not be deleted. When creating a new user, you will need to give him a name and password (preferably), as well as determine which group he will belong to. new user. Each user can belong to one or several groups.
The node displays both built-in groups and those created by the administrator (i.e., you). Built-in groups are created automatically when you install Windows. 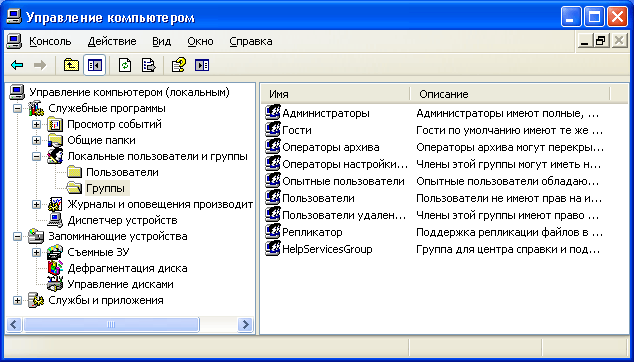 Belonging to a group grants the user certain rights to perform various actions on the computer. Group users Administrators
have unlimited rights. It is recommended that you use administrative access only to perform the following actions:
Belonging to a group grants the user certain rights to perform various actions on the computer. Group users Administrators
have unlimited rights. It is recommended that you use administrative access only to perform the following actions:
- installations operating system and its components (device drivers, system services, service packs);
- update and restore the operating system;
- installation of programs and applications;
- configure the most important parameters of the operating system (password policy, access control, etc.);
- management of security and audit logs;
- archiving and restoration of the system, etc.
How are you system Administrator, must have an account belonging to the group “Administrators”. All other users of the computer must have accounts belonging to either the “Users” group or the “Power users” group.
Add users to a group Userand is the most secure, because the permissions granted to this group do not allow users to change operating system settings or data of other users, install some software, but also do not allow running outdated applications. I myself have repeatedly come across a situation where the old DOS programs did not work under the account of a member of the “Users” group.
Group Power Users supported mainly for compatibility with previous versions Windows to run non-certified and legacy applications. “Advanced Users” have more permissions than members of the “Users” group, and less than “Administrators”. The default permissions granted to this group allow group members to change certain computer settings. If you need support not certified under Windows applications, users must be members of the “Power Users” group.
Account a guest gives access to a computer to any user who does not have an account. To enhance the security of your computer, it is recommended that you disable the “Guest” account and configure existing users to access the shared resources of the PC.
Now let's see how account creation takes place through the “Computer Management” console - “Local Users and Groups”.
Account creation
When installing the original windows version XP (meaning not build from Zver or the like) it is proposed to create computer user accounts. You must create at least one account under which you will be able to log in when you first start. But, as a rule, in real life it is required to create several accounts for each user working at the computer, or for a group of users united by a common task and access permissions.
To add a new account, open the “Local users and groups” snap-in - select the “Users” folder - then in the right window click on an empty space right click mouse click - select “New user”: 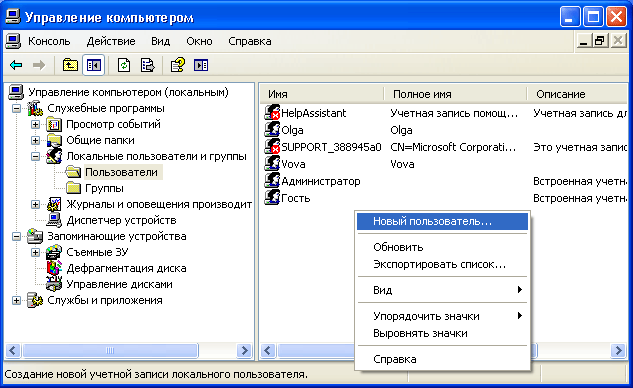 In the window that appears, specify the user name and description. Also set a password for the user (how to create a strong password for the account you can read).
In the window that appears, specify the user name and description. Also set a password for the user (how to create a strong password for the account you can read).
Then configure additional parameters - check or uncheck the boxes next to the required items: 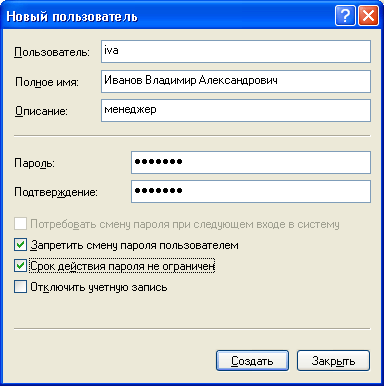 You can uncheck the box next to “Require a password change on the next login to the system” and check the boxes next to “Prevent a user from changing the password” and “Password is not limited in duration”. In this case, the user will not be able to change the password for his account. This can be done only by you, working under an administrative account.
You can uncheck the box next to “Require a password change on the next login to the system” and check the boxes next to “Prevent a user from changing the password” and “Password is not limited in duration”. In this case, the user will not be able to change the password for his account. This can be done only by you, working under an administrative account.
After clicking the “Create” button a new account will appear in the list of users. Double-click on it and go to the “Group Membership” tab in the window that opens. Here click “Add” - “Advanced” - “Search”. Then select the group to which the user should be included (the “Users” or “Power users” group is recommended) and click “OK” in all the displayed windows. After that, here in the “Group Membership” tab, remove from the list all groups except the one you just selected. Click “OK”: 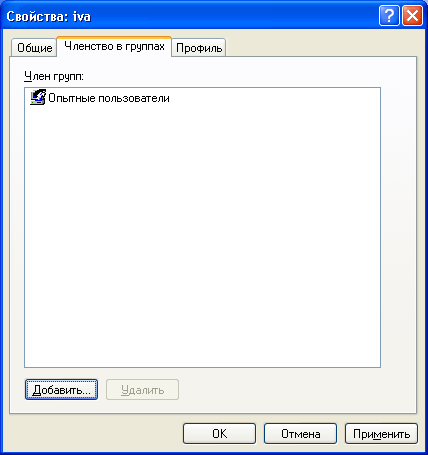 So you created a new account and included it in the group.
So you created a new account and included it in the group.
Now tell the user (in our case, Ivanov) the name of his account ( iva) and password so that he can log in. On all computers on the network, to whose resources Ivanov needs access, you will need to create the same account with the same parameters. If on any computer on the network there is no account for Ivanov and the “Guest” account is disabled, then Ivanov will not be able to view the shared network resources of this computer.
If the user account is no longer needed, you can delete it. But in order to avoid various kinds of problems, it is recommended to disable user accounts before deleting. To do this, right-click on the account name - select “Properties” —in the account properties window, check the box next to “Disable account” and click “OK”. After making sure that this does not cause any problems (watch the network for several days), you can safely delete the account: right-click the account name and in context menu select “Delete”. A deleted user account and all data associated with it cannot be recovered.
Access control
So, let's say, several users work at the same computer, and you have created your own account for each according to the rules described above. But suddenly there was a need to close access to some folders or files on a computer for certain users. This task is solved by assigning certain access rights to computer resources.
Access control is to provide users, groups and computers with certain rights to access objects (files, folders, programs, etc.) on the network and on the local machine.
User Access Control local computerbut done by changing the settings on the “tab Security”In the“ Properties ”window:
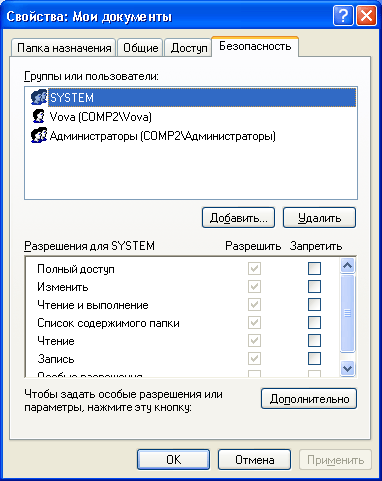
Security Settings for My Documents
“Tab” Access"Same window is used to control network access to shared objects (files, folders, and printers) on networked computers.
In this article we will talk about access control. local users to objects local computer
. This feature is only available in the NTFS file system. If on a computer file system NTFS, but the “Security” tab is not displayed, go to “Start” - “Control Panel” - “Folder Options”. On the “View” tab in the “Advanced Settings” section, uncheck the “ Use simple general access to files (recommended)”And click“ OK ”: 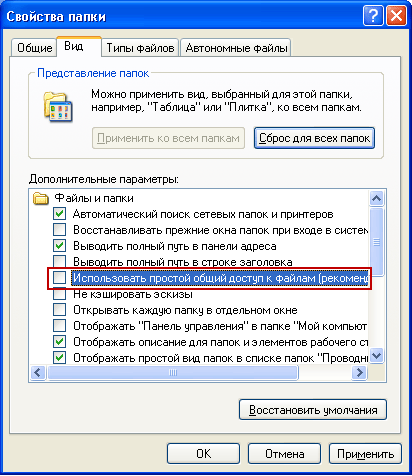 The basic concept associated with access control is Permissions
.
The basic concept associated with access control is Permissions
.
Permissions determine the type of user or group access to an object or its properties. Permissions apply to files, folders, printers, registry objects. To set or change permissions for an object, click on its name with the right mouse button and select the “Properties” command in the context menu. On the “Security” tab, you can change the permissions for a file or folder by checking or unchecking the boxes in the list of permissions.
For each user, you can set your permissions. First you need to select the user in the list, and then specify the permissions for this user. For example, one user can only be allowed to read the contents of a certain file (permission “ Reading"), Another - to make changes to the file (permission" Change"), And all other users in general to deny access to this file (uncheck all the boxes under" Allow"Or check all boxes" To ban”).
To view all valid permissions for files and folders of the local computer, select “Properties” - “Security” - “Advanced” - “Valid permissions” - “Select” - “Advanced” - “Search”, select the name desired user and click “OK”. Items marked with checkboxes have permissions for this user: 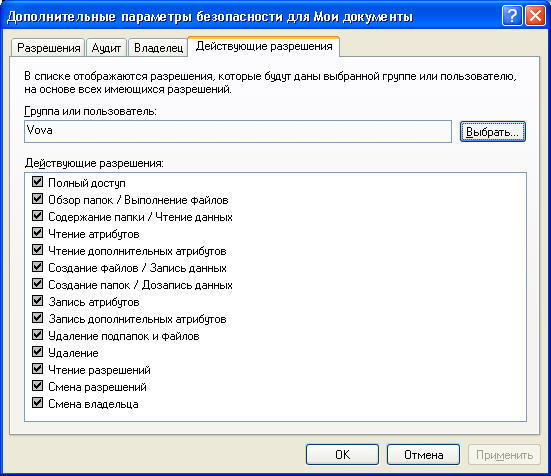 In the same window you can see the tabs “Permissions”, “Audit”, “Owner”. I will not dwell on them in detail in the framework of this article, since it already turns out too voluminous.
In the same window you can see the tabs “Permissions”, “Audit”, “Owner”. I will not dwell on them in detail in the framework of this article, since it already turns out too voluminous.
If there is no user in the list of users on the “Security” tab who needs to be assigned permissions, successively click the following buttons on the “Security” tab: “ To add” – “Additionally” – “Search". From the list, select the name of the user account to which you want to assign permissions and click “OK”. Instead of a separate user, you can select a group — the permissions will apply to all users in this group. Well remember these buttons. You will do this procedure in all cases when you need to add a new user to the list of permissions, auditing, ownership, network access etc.
Access control is applied not only to users local computerbut also to access shared files, folders and printers on the network. About the differentiation of access rights for network users in relation to the folder I have already told in the article.
Today our lesson and discuss user account management.
We have specified the name, now let's choose, for example, the type of the entry “Normal access” and click the “Create account” button. Now we select the newly created account from the list and proceed to its settings.
In principle, the main thing we have already configured is the name of the account and its type. Now we can change something, but add something.
For example, the first item "Changing the name of the account" we will provide the opportunity to change the name accordingly.
We can simply rename the account.
If you want to your account password has been setb, and you could go to the computer just by typing it. Thus, you can restrict access to some of your personal documents that are stored in your profile. Accordingly, you can create a password in this area. Here you enter the password, then enter the same password again for confirmation, and you can also enter a hint that will be displayed to you.
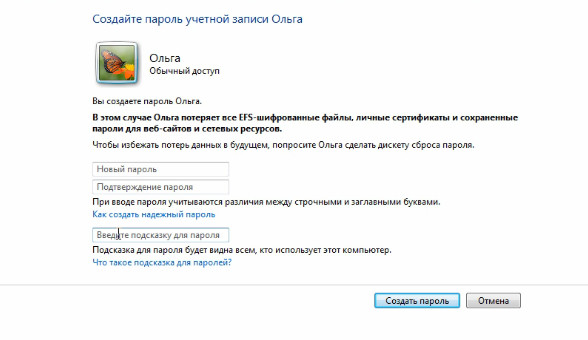
Let's set, for example, some simple password, confirm it, and enter the text hint “text hint to the password”. Click on the button "Create".
If I now, and near the Shut down button, click on the black triangle and select from the drop-down list "Change user", then I will get to the welcome screen.
In order to get into the recording Olga, you need to click on this icon and I have a window where I need to enter a password.
Respectively in order to get into this entry I need to enter a password. If I have forgotten the password or entered it incorrectly, then my hint, the text that I entered, is displayed here.
Let's go back to my user and consider what’s next.
After we have entered the password, we have the opportunity to remove it by simply clicking on this item.
Drawing this here this here is the image that we have associated with our account. As we already know, this image is displayed not only on the welcome screen, but also in the Start menu. Therefore, we can choose this image from some standard ones that are presented to us here.
Let's select, for example, this one here is a sunflower and click on Change Picture. Here, now he has applied.
Or we can use the button. "Search for other pictures" and select an image on your computer, then this image will be displayed as this image of your account.
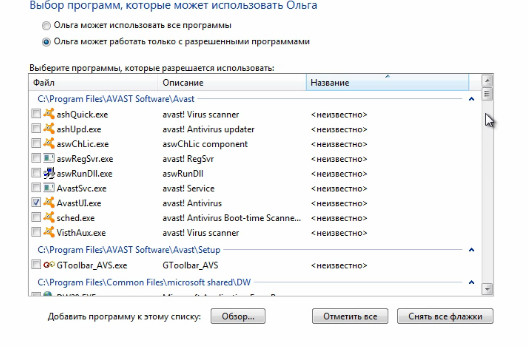
We also have an option “Set parental control”. What it is? If a child is working at your computer, you can create a separate account for it, and then adjust the settings parental control. To do this, we need to choose our account.
Parental control is disabled by default and here we can enable it.

Here we can introduce time limits. That is, here we can specify the time intervals in which access to the computer will be allowed. All we need to do to do this is simply to indicate the hours in which access to the computer will be blocked.
Just blocking those hours that we consider necessary. Or we can block everything at all, and then just indicate the clock when access to the computer will be allowed. After that, respectively, you need to click OK.

And the last thing that can be configured here is permission to work in some programs. Here we can choose the program, here is a list of the programs will be displayed, that is, and we are here to set a checkmark in the programs to which the user will have access.
And accordingly we can uncheck those programs, access to which is undesirable. And accordingly, your child will not be able to run some program that you would not want him to run.
Let's go to general settings. If necessary, we can always change the type of account. That is, we will have this user or Administrator, or will have a regular account. This is done in paragraph "Change Account Type".
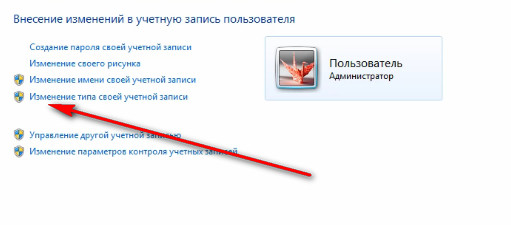
But in order to change the type from normal to Administrator, you must already be an administrator on this computer. That is, you must log on to the computer under an administrative account that already has rights. If you are a type commonly available, then you will not be able to make this change to your account and your account.
This, in principle, is also relevant to “Account deletion"If you want to delete an account, then for this you need to have administrative rights on this computer.
"Delete account" to delete the account, you need to go to the item "Manage Accounts" and accordingly you can choose the account you want, and select. Here at once we will offer to delete or immediately and completely all the files, that is, the whole profile of the user, or "Save File" and remove only windows records. I will not do anything like this yet.
So we learned how to create accounts, I finish this lesson.
Natalia Gerasimenko
This documentation has been moved to the archive and is not supported.
User Account Management
Office 365
Applicable to:Office 365
Last change section:2017-04-26
Microsoft Office 365: Supports the following methods of creating users, authenticating and managing them.
on tools information to help you perform administrative tasks, see. article tools for managing your Office 365 accounts. For information on how to perform day-to-day management tasks, see Frequent management tasks in Office 365.
Office 365: has two systems below that can be used for user credentials.
Work or school account (cloud ID). Users get Azure Active Directory cloud credentials to sign in to Office 365: and other Microsoft cloud services. These credentials are in no way associated with other credentials (corporate or for access to a computer) and represent the default identity. We recommend using them to simplify deployment. For passwords for work or study accounts, use the Azure Active Directory password policy.
Federated Account (Federated Identity). Users in organizations with local Active Directory who use single sign-on can sign in to Office 365 services using their Active Directory credentials. Corporate Active Directory stores password policy and manages it. For information about single sign-on, see Single Sign-On Strategy.
The type of identity affects user interaction and user account management settings, as well as hardware requirements and software and other aspects of deployment.
When creating a new user of his email address and the login is assigned to the default domain, as set up in the Office 365 admin center: For more information, see Add users and domain to Office 365.
Office 365 Subscription Default: Domain Used<company name>.onmicrosoft.comcreated with an account. * You can not save the domain onmicrosoft.com, but add to Office 365 one or more personal domains, and then assign any of the verified domains to users to sign in. Each user domain assigned is an email address that will appear when sending and receiving email messages.
You can place in Office 365: up to 900 registered Internet domains, each of which is represented by a separate namespace.
For organizations using single sign-on, all users in the domain must use the same identification system: either a cloud or a federated identity. For example, there may be one group of users who only need a cloud identity, because they do not have access to local systems, and another group of users who use Office 365: and local systems. In this case, you’ll have to add to Office 365: two domains, for example contractors.contoso.com and staff.contoso.com, and configure single sign-on for only one of them. The entire domain can be converted from a cloud identity to a federated identity or from a federated identity to a cloud one.
For more information about domains in Office 365: see the service description.
* If you are using Office 365 :, provided by 21Vianet in China, the default domain looks like<название_компании>.onmsChina.cn. If you are using Office 365 Germany, the default domain looks like<название_компании>.onmicrosoft.de
With the exception of Internet sites for anonymous access created in SharePoint Online, when accessing Office 365 services: users must be authenticated.
Modern authentication Modern authentication provides logon to Office client applications across platforms based on the Active Directory Authentication Library (ADAL). This triggers logon capabilities such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), use of third-party SAML-based identity providers with Office client applications, and authentication using smart cards and certificate-based authentication. In addition, there is no need to use the standard authentication protocol for Microsoft Outlook. Additional information, including the availability of modern authentication for various applications Office, see the article Principles of modern authentication for Office 2013 and Office 2016 client applications and Using Office 365 modern authentication with clients Offices.
Modern authentication is not enabled by default for Exchange Online. You can read the instructions on how to enable it in the article Enable modern authentication in Exchange Onlinen.
Cloud Identity Authentication. Authentication of users with cloud identities is a traditional request and confirmation authentication. The web browser redirects to the Office 365 login service: where you enter the username and password for your work or school account. The login service authenticates the credentials, creates a service token that the web browser sends to the requested service, and logs in the user.
Authentication of federated identity. Users with federated identities are authenticated using Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) 2.0 or other security token services. The web browser is redirected to the Office 365 login service :, where you enter a corporate identifier in the form of a user principal name (UPN); eg, [email protected] The login service determines that you are part of a federated domain, and offers to redirect you to a local federation server for authentication. If you are logged on to a computer (joined to a domain), you are authenticated (using Kerberos or NTLMv2), and the local security token service creates a token that the web browser sends to the Office 365 login service :. Using this token, the login service creates a token that the web browser sends to the requested service, and then it is logged on. For a list of available security token services, see Single Sign On Strategy.
Office 365: uses forms-based authentication, and authentication traffic passing through the network is always encrypted using TLS / SSL using port 443. Authentication traffic uses a small amount of bandwidth for Office 365 services :.
For full-featured clients, such as classic Microsoft Office applications, authentication can be performed in two ways.
If you have a cloud-based identity, then you are prompted for credentials that the client service sends to the Office 365 login service: for authentication (using WS-Trust).
If you have a federated identity, the client service first accesses the AD FS 2.0 server to authenticate the credentials (using Kerberos or NTLMv2) and receives a login token that is sent to the service. single sign-on Office 365: (using WS-Federation and WS-Trust).
Microsoft Online Services Login Assistant The Login Assistant, which is installed by the Office 365 Desktop Update Installer for Desktop, contains a client service that receives a service token from the Office 365 login service: and returns it to a full-featured client.
Basic / Proxy Authentication over SSL Outlook Client performs basic authentication via SSL in Exchange Online. Exchange Online sends an authentication request to the Office 365 Identity Platform: and then local server Active Directory Federation Server Federation (for single sign-on).
To ensure that Office 365 services are correctly detected and authenticated, administrators must apply components and updates on every workstation that uses full-featured clients (such as Microsoft Office 2010) and connects to Office 365 :. Office 365 Update Installer: Desktop is an automated tool for installing required updates on workstations. For more information, see the article Use installed classic Office applications with Office 365.
The login interface varies depending on the type of Office 365 identity that you are using:
| Cloud ID | Federation certificate | |
|---|---|---|
| Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
|
| Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
|
| Outlook 2010 or Office 2007 on Windows 7 | Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
| Outlook 2010 or Office Outlook 2007 in Windows Vista | Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
| Microsoft Exchange Activesync | Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
| POP, IMAP, Outlook for Mac | Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
| Web interfaces: Office 365 portal: / Outlook Web App / SharePoint Online / Office Online | Login to each browser session4 | Login to each session3 |
| Office 2010 or Office 2007 using SharePoint Online | Login to each SharePoint Online4 session | Sign in to each SharePoint Online3 session |
| Skype for Business Online | Login to each session1 | Without request |
| Outlook for Mac | Login to each session1 | Login to each session2 |
| 1 At the first request, you can save the password for future use. You will not receive the following request until you change the password. 2 You enter your corporate credentials. You can save the password, and then the next request will appear only after changing the password. 3 All applications require you to enter a username or click to login. If the computer is joined to a domain, the password is not requested. If you select the option Remain in the system, the data entry request will not be displayed until you log out. 4 If you select Remain in the system, the data entry request will not be displayed until you log out. |
The way to delete accounts depends on whether directory synchronization is used.
If you do not use directory synchronization, you can delete accounts on the Office 365 administration page: or from using windows PowerShell.
If directory synchronization is used, then you must remove users from your local Active Directory, not from Office 365 :.
The policies and procedures for managing passwords depend on the identification system.
Cloud ID Password Management:
When using cloud identities, passwords are created automatically when you create an account.
For information on the cloud credential password security requirements, see the password policy article.
To increase security, users need to change their passwords when they first access Office 365 services: As a result, before accessing Office 365 services: users must log in to the Office 365 portal: where they will be prompted to change the password.
There are several means of resetting passwords for users with cloud identities:
Password reset by administrator If users lose or forget their passwords, administrators can reset user passwords in the Office 365 portal: or using Windows PowerShell. Users can change their passwords only if they know the current passwords.
Reset passwords using Windows PowerShell Service administrators can reset passwords using Windows PowerShell.
Managing Federated Identity Passwords:
With federated identities, password management is done in Active Directory. The local security token service negotiates authentication with the Office 365: Federation Gateway without transferring local Active Directory user passwords over the Internet to Office 365 :. Local password policies are used or, in the case of web clients, two-factor identification. Outlook Web App does not include a password change hyperlink. Users change passwords using standard local tools or using the login parameters of their desktops.
Office 365 license: Gives the user access to a set of Office 365 services: The administrator assigns a license to each user for the service, access to which he needs. For example, you can assign a user access to Skype for Business Online, but not SharePoint Online.
In Office 365: corporate, the RBAC model is applied: permissions and capabilities are defined by management roles. A user who registers his organization with Office 365: automatically becomes a global or higher level administrator. There are five administrator roles: global administrator, billing administrator, password administrator, service administrator, and user management administrator. For more information about admin roles in Office 365: Enterprise, including how they are used in Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and Skype for Business Online, see Assigning Administrator Roles. If you are using the Office 365:, plan managed by 21Vianet in China, see the article. Want to chat with a customer service representative? Scroll to Select a plan and click the icon. chat on the red banner at the top.

The staff of any organization is constantly updated, some employees go to work, others leave. And, as you know, not always a person is satisfied that he leaves the company. If such a disgruntled ex-employee has the keys to the office, the manager will probably change the lock. If the former user has an account, it must be done so that he cannot use it - especially if there are privileges associated with this account, which in principle give its owner the opportunity to cause harm. This article will discuss how to software tools enable and disable user accounts and set account passwords. In addition, I will talk about the program, with which you can allow users to change passwords even when access to the Windows Security dialog box for security reasons is closed.
Enable and disable accounts
Even if an employee is absent temporarily, it is better for this period to transfer his account to idle mode, so that attackers could not use this account to attack the system. However, you should not delete an inactive account, because in this case you will have to restore all associated security settings when the user returns. Any experienced administrator knows that the account should be disabled for the time it is not in use, and delete it only when there is full confidence that this account will no longer be needed.
To simplify the process of blocking an account when a user is absent and enabling an account when it returns, you can use the program from listing 1 . The script is simple: you first connect to the selected account, then the AccountDisabled parameter changes. You can also disable an account by editing the control flag associated with the account, but the method I suggest is, firstly, simpler and secondly, equally effective for our purposes. If it is necessary for the same program to perform a double duty (i.e., disabling and enabling accounts), the AccountDisabled parameter is required to be made the argument of the program. A small subroutine Help tells the user what value should be entered to get the desired result. Since the program uses the WinNT namespace, it will work with both SAM and Active Directory (AD) domains. By updating the contents of the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in on a domain controller (DC), you will see that an account with a specific name is now disabled or enabled, depending on instructions.
Account password change
Sometimes disabling an account is not appropriate, for example, it is impossible to disable an administrator account used by several employees only because one person leaves. In this case, you need to change the account password.
Active Directory Service Interfaces (ADSI) supports two password change methods: ChangePassword and SetPassword. When using ChangePassword, it is necessary that the password change officer knows the current password. ChangePassword is hardly a tool for administrators, as administrators do not need to know user passwords. However, ChangePassword is really useful when an administrator closes access to the Windows Security dialog box using Group Policy or other means, but wants to allow users to change their passwords. SetPassword just replaces the existing password with a new one.
A program that allows a registered user to change a password should do the following:
- recognize the user name;
- request the current user password;
- prompt the user to enter a new password;
- prompt the user to confirm a new password;
- compare two passwords and do not accept them if they do not match;
- change the password and write the new password to the security database;
How to implement these actions in the form of code was described in previous articles, so here I will focus only on how these parts are assembled together in the program in listing 2 .
First, it is necessary to identify the registered user. Recall that the UserName property of the WshNetwork object returns the user name. Therefore, in order to get the username, you need to create a WshNetwork object (WScript.Network), associate this object with a variable (oNet), and then use the UserName property to retrieve the username, as shown in the A label in Listing 2.
Now that we have the current user name, we can use the InputBox function and query the user for the current and new passwords. The easiest way is to create a small subroutine for this purpose. The CheckPwd subroutine stores the current and new passwords in the global variables sPword1, sPword2 and sPword3. The subroutine prompts the user for the current password (sPword1), a new password (sPword2), and again a new password (sPword3) for confirmation. If the new password and the confirmation password do not match, the subroutine informs the user of this and displays the request again. The comparison of sPword2 and sPword3 is case-sensitive, so frog and frog are not the same thing.
As explained earlier, the VBScript InputBox function always displays the OK and Cancel buttons and depends on three arguments:
InputBox (prompt, title, default)
where prompt is the text of the message box, title is the title text, and default is the default value. Since these arguments are separated by commas, you cannot use commas inside the text of the message box and header. Instead of commas, you can use the concatenation character (&), as in the CheckPwd subroutine.
The InputBox function has one drawback: it does not support masking of input characters. So, if the user enters the word swordfish in the dialog box corresponding to the password, he will see the swordfish on the screen, and not a row of asterisks (*********). If the password change program is executed in Windows 2000 and earlier versions, you will have to accept this restriction, but if the program runs in Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP, there is another possibility. These versions of Windows include the scriptpw.dll component, which masks user-entered characters. The scriptpw component is not perfect - when typing, there is no exact match between the number of characters entered and the asterisks replacing them, but this is more secure than an open set of passwords in the input window.
The HidePwd subroutine contains code using Scriptpw. The HidePwd code is similar to the CheckPwd code, except that HidePwd prompts you to enter characters in command lineand not in the dialog box and HidePwd hides the characters entered by the user. The response line of the command processor after each password request ends with a new line, otherwise all the displayed text would be contained in one line.
In order to not have to have two versions of the program to change the password, Userpword.vbs determines the operating system and only then executes the corresponding password subroutine. An object representing a computer has an OperatingSystemVersion property that can be requested. Exact match is not required. You only need to know if the version number is not less than 5.1, that is, the version number of XP. The program has already used the WshNetwork object to get the computer name, so the code in Listing 2 under the label B checks the version of the operating system on the local computer.
Whatever program of password input is used by the program, it saves the new password in sPword2, and the old password in sPword1, and then transmits them to the code under the label C, which changes the password. If the user does not provide the correct old password, the program will exit with a very eloquent error message: The specified network password is not correct.
Assigning passwords to accounts
If there is no current account password, a slightly different approach is used to assign a password. The program should do the following:
- accept received username and domain name;
- find the user name in the security database;
- prompt for a new password;
- assign a new password;
- request the user to change the password at the next registration (so that the administrator does not know it);
- make a record that the password has been changed.
Most of the Adminpword.vbs program for assigning the password shown in listing 3 , consists of code already written for the first two programs. From Disableuser.vbs, the Adminpword.vbs program takes a code that accepts a username and domain name and connects to the appropriate account. From Userpword.vbs, the Adminpword.vbs program takes subroutines that prompt you to enter a new password. The subroutines in Adminpword.vbs are slightly modified, since the current password is not needed. It would be possible to explicitly specify the default password in Adminpword.vbs, but this should not be done. If you explicitly record a password in Adminpword.vbs, it will be stored as plain text. Quite simply, the remaining part of the task of assigning a new password is implemented in the form of a code, namely, the requirement to change the password at the next registration and the record that the password has been changed.
Because the new password is assigned, the ChangePassword method is replaced with the SetPassword method and only a new password is entered, as shown in the A label in Listing 3. The PasswordExpired property determines whether the user should change the password at the next registration. When the value of this parameter is 0, the password is valid, when 1 - the password has expired. Therefore, in order to achieve a password change, you need to assign the value 1 to this parameter. Since oUser represents a user account, the code in label B in Listing 3 forces you to change the password.
Disabling the account or changing the password should end with the appropriate entry in the event log. Let me remind you that in the previous article on editing the registry it was stated that to write to the Event Log, you need to connect to the WshShell object and use the LogEvent method with the event type and explanatory text as arguments. In our case, the event type is a notification, so this event is type 4. The date and time are automatically recorded with the event, so you can leave them out of the program. To record a password change, you must enter the code shown in the C label in Listing 3 at the end of the main program.
The functions of disabling unused accounts and changing passwords are very important, and their corresponding programs should be as simple and effective as possible. But the procedure for changing the password through the Windows 2000 graphical interface, for example, consists of six steps. Using the program described in this article, administrators can easily enable and disable user accounts, give users the ability to change their passwords without having access to the Windows Security dialog box, and set new passwords for important accounts.